Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
... • Key to the chemical behavior of an atom lies in the number and arrangement of its electrons in their orbitals • Bohr model – electrons in discrete orbits • Modern physics defines orbital as area around a nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found • No orbital can contain more than two el ...
Lecture 5 - Help-A-Bull
... Define the term degenerate as it applies to orbitals Indicate the roles of Coulomb’s Law, shielding and penetration in sublevel splitting Define and apply the aufbau principle and Hund’s rule Determine the expected electron configuration for any atom on the periodic table (complete configuration and ...
... Define the term degenerate as it applies to orbitals Indicate the roles of Coulomb’s Law, shielding and penetration in sublevel splitting Define and apply the aufbau principle and Hund’s rule Determine the expected electron configuration for any atom on the periodic table (complete configuration and ...
video slide
... weak chemical bonds also important reinforce shapes help molecules adhere to each other ...
... weak chemical bonds also important reinforce shapes help molecules adhere to each other ...
1st Term Review
... g) Father of the modern periodic table h) Discovery of the electron i) Atomic model of hydrogen 2. How do isotopes differ from one another? 3. List the periodic trend for the following (across the chart from left to right and down a column) a) Ionization energy b) Electronegativity c) Atomic mass d) ...
... g) Father of the modern periodic table h) Discovery of the electron i) Atomic model of hydrogen 2. How do isotopes differ from one another? 3. List the periodic trend for the following (across the chart from left to right and down a column) a) Ionization energy b) Electronegativity c) Atomic mass d) ...
CHEM 11 Practice Exam 2
... 13) Which of the following is held together by ionic bonds? A) CS2 B) CO2 C) CaCl2 D) SO3 E) SiO2 14) Which noble gas is isoelectronic with an aluminum ion? A) helium B) neon C) argon D) krypton E) xenon ...
... 13) Which of the following is held together by ionic bonds? A) CS2 B) CO2 C) CaCl2 D) SO3 E) SiO2 14) Which noble gas is isoelectronic with an aluminum ion? A) helium B) neon C) argon D) krypton E) xenon ...
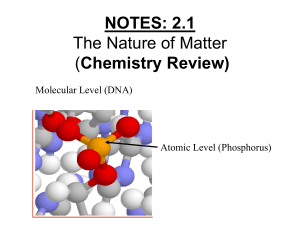
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... a fixed ratio • examples: NaCl, H2O, CO2, C6H12O6 • cmpds. have unique properties beyond those of the combined elements ...
... a fixed ratio • examples: NaCl, H2O, CO2, C6H12O6 • cmpds. have unique properties beyond those of the combined elements ...
Semester Exam Practice Questions
... c. the same number of energy levels b. similar atomic masses d. similar atomic diameters Examine the following electron configuration and choose the correct location of the element it represents in the periodic table: 1s22s22p63s24s23d104p65s24d7 a. row 7, column 4 (Rf) c. row 5, column 7 (Tc) b. ro ...
... c. the same number of energy levels b. similar atomic masses d. similar atomic diameters Examine the following electron configuration and choose the correct location of the element it represents in the periodic table: 1s22s22p63s24s23d104p65s24d7 a. row 7, column 4 (Rf) c. row 5, column 7 (Tc) b. ro ...
The Chemical Context of Life PPT
... of its location or structure, there are many kinds…not just gravitational PE! • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, or electron shell* * “Shell” is fraught with misconception—but biologists often u ...
... of its location or structure, there are many kinds…not just gravitational PE! • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, or electron shell* * “Shell” is fraught with misconception—but biologists often u ...
The Chemical Context of Life
... of its location or structure, there are many kinds…not just gravitational PE! • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, or electron shell* * “Shell” is fraught with misconception—but biologists often u ...
... of its location or structure, there are many kinds…not just gravitational PE! • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • An electron’s state of potential energy is called its energy level, or electron shell* * “Shell” is fraught with misconception—but biologists often u ...
Structural, electric, and magnetic properties of Mn perovskites
... anisotropy. The term H Hund parameterizes the Hund’s coupling between e g and t 2 g spins, H onsite also parameterizes the on-site Coulomb interactions between e g electrons, and H S denotes the magnitude of the AF coupling between nearest neighboring t 2 g spins; for the reasonable value of this c ...
... anisotropy. The term H Hund parameterizes the Hund’s coupling between e g and t 2 g spins, H onsite also parameterizes the on-site Coulomb interactions between e g electrons, and H S denotes the magnitude of the AF coupling between nearest neighboring t 2 g spins; for the reasonable value of this c ...
Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Inter-atomic Bonding
... are made of elements or combinations of these elements. atom – The smallest building block of an element, consisting of a central nucleus of protons and neutrons with electrons orbiting the nucleus. nucleus – The central portion of the atom containing the protons and neutrons. protons – Positively c ...
... are made of elements or combinations of these elements. atom – The smallest building block of an element, consisting of a central nucleus of protons and neutrons with electrons orbiting the nucleus. nucleus – The central portion of the atom containing the protons and neutrons. protons – Positively c ...
Chemistry (CP) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 50. What is the maximum number of d orbitals in a principal energy level? a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 5 ____ 51. What types of atomic orbitals are in the third principal energy level? a. s and p only c. s, p, and d only b. p and d only d. s, p, d, and f ____ 52. What is the next atomic orbital in the ser ...
... ____ 50. What is the maximum number of d orbitals in a principal energy level? a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 5 ____ 51. What types of atomic orbitals are in the third principal energy level? a. s and p only c. s, p, and d only b. p and d only d. s, p, d, and f ____ 52. What is the next atomic orbital in the ser ...
Ch. 3
... The oxidations number indicates if an atom is going to give up electrons or take in electrons in order to become stable. Positive oxidation numbers mean the atom is going to give up electrons. ...
... The oxidations number indicates if an atom is going to give up electrons or take in electrons in order to become stable. Positive oxidation numbers mean the atom is going to give up electrons. ...
Midterm Review.ppt - Chemistry R: 4(AE)
... 1. Ar, Kr, Ne, Xe 2. Kr, Xe, Ar, Ne 3. Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe 4. Xe, Kr, Ar, Ne ...
... 1. Ar, Kr, Ne, Xe 2. Kr, Xe, Ar, Ne 3. Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe 4. Xe, Kr, Ar, Ne ...
Midterm Review
... • A student investigated the physical and chemical properties of a sample of unknown gas and then investigated the gas. Which statement represents a conclusion rather than an experimental observation? 1. The gas is colorless. 2 The gas is carbon dioxide. ...
... • A student investigated the physical and chemical properties of a sample of unknown gas and then investigated the gas. Which statement represents a conclusion rather than an experimental observation? 1. The gas is colorless. 2 The gas is carbon dioxide. ...
Chapter 2 Chemical context of Life
... An orbital is a three-dimensional space where the electron is found 90% of the time. An orbital contains a maximum of two electrons. Electrons in orbitals with similar energies occupy the same principal energy level. The orbitals of an energy level are designated by the letters s, p, d and f. See fi ...
... An orbital is a three-dimensional space where the electron is found 90% of the time. An orbital contains a maximum of two electrons. Electrons in orbitals with similar energies occupy the same principal energy level. The orbitals of an energy level are designated by the letters s, p, d and f. See fi ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.