contents 2002 MAY
... R Amrutha , L Sangeetha & P Chandran* Cumulenes are compounds containing a unit of ‘n’ carbon atoms with (n-1) double bonds between them (n>3).The members are propadiene(allene), butatriene, pentatetraene etc. A systematic study of chlorination on cumulenes is done in the present study. Geometrical ...
... R Amrutha , L Sangeetha & P Chandran* Cumulenes are compounds containing a unit of ‘n’ carbon atoms with (n-1) double bonds between them (n>3).The members are propadiene(allene), butatriene, pentatetraene etc. A systematic study of chlorination on cumulenes is done in the present study. Geometrical ...
Unit 3 Physical Science: Chemical Reactions
... industrialized regions of the United States and Canada. The problem is further complicated by our own industrial plants and power generation plants. In addition, much of our region has thin soils and granite bedrock, which results in a high sensitivity to acid damage. In this context students will c ...
... industrialized regions of the United States and Canada. The problem is further complicated by our own industrial plants and power generation plants. In addition, much of our region has thin soils and granite bedrock, which results in a high sensitivity to acid damage. In this context students will c ...
Acid-Base Reactions Worksheet #2 - Mro
... large quantities that it flows down the body and drips onto the ground. Since the purpose of perspiration is to produce a cooling effect by evaporation, why does the human body not produce just enough perspiration to keep the skin surface moist? The production of perspiration requires relatively lar ...
... large quantities that it flows down the body and drips onto the ground. Since the purpose of perspiration is to produce a cooling effect by evaporation, why does the human body not produce just enough perspiration to keep the skin surface moist? The production of perspiration requires relatively lar ...
Document
... is oxidized to Cu2+(aq) (blue color). From the HCl analysis, we know that H+(aq) is not strong enough as an oxidizing agent to oxidize Cu(s) to Cu 2+(aq), and we know that NO3–(aq) is an oxidizing agent here because the N atom has its highest possible oxidation number, +5. Therefore, copper is being ...
... is oxidized to Cu2+(aq) (blue color). From the HCl analysis, we know that H+(aq) is not strong enough as an oxidizing agent to oxidize Cu(s) to Cu 2+(aq), and we know that NO3–(aq) is an oxidizing agent here because the N atom has its highest possible oxidation number, +5. Therefore, copper is being ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... nature as a diatomic molecule? b. 3 a. Nitrogen c. 4 b. Helium d. 2 c. Hydrogen 11. In the correct Lewis structure for the methane d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules ...
... nature as a diatomic molecule? b. 3 a. Nitrogen c. 4 b. Helium d. 2 c. Hydrogen 11. In the correct Lewis structure for the methane d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules ...
Support material for lesson planning – AS content
... Suggestions for suitable practical work are included throughout the table. This is by no means and exhaustive list of potential practical activities. In the table, the abbreviation ‘PAG’ stands for ‘Practical Activity Group’, and refers to the groups defined in Appendix 5g of the A Level specificati ...
... Suggestions for suitable practical work are included throughout the table. This is by no means and exhaustive list of potential practical activities. In the table, the abbreviation ‘PAG’ stands for ‘Practical Activity Group’, and refers to the groups defined in Appendix 5g of the A Level specificati ...
Slide 1
... DHorxn = S DHof,products - S DHof,reactants It is important to notice that in this relationship, we only need the DHof of the chemical COMPOUNDS involved, not of any ...
... DHorxn = S DHof,products - S DHof,reactants It is important to notice that in this relationship, we only need the DHof of the chemical COMPOUNDS involved, not of any ...
Exam #2
... 44. The metal calcium reacts with molecular hydrogen to form a compound. All of the following statements concerning this compound are true EXCEPT: (A) Its formula is CaH2. (B) It is ionic. (C) It is solid at room temperatur(E) (D) When added to water, it reacts to produce H2 gas. (E) When added to w ...
... 44. The metal calcium reacts with molecular hydrogen to form a compound. All of the following statements concerning this compound are true EXCEPT: (A) Its formula is CaH2. (B) It is ionic. (C) It is solid at room temperatur(E) (D) When added to water, it reacts to produce H2 gas. (E) When added to w ...
17.2.3 Interhalogen compounds(65-67)
... is determined principally by weak intermolecular van der Waals' and dipolar forces, and dissolution is commonly favoured by less-polar solvents such as benzene, CCl4 or CS2. Trends in chemical reactivity are also apparent, e.g. ease of hydrolysis tends to increase from the non-hydrolysing predominan ...
... is determined principally by weak intermolecular van der Waals' and dipolar forces, and dissolution is commonly favoured by less-polar solvents such as benzene, CCl4 or CS2. Trends in chemical reactivity are also apparent, e.g. ease of hydrolysis tends to increase from the non-hydrolysing predominan ...
chem - CBSE Guess
... Ans. The copper vessel will be corroded and a green layer of basic copper carbonate CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 will be deposited on the copper vessel. Q. Explain what corrosion of iron means.? 1 Ans see page 1 Q. Why is sodium or potassium metals are kept immersed in kerosene oil?. 1 Ans.Sodium and potassium met ...
... Ans. The copper vessel will be corroded and a green layer of basic copper carbonate CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 will be deposited on the copper vessel. Q. Explain what corrosion of iron means.? 1 Ans see page 1 Q. Why is sodium or potassium metals are kept immersed in kerosene oil?. 1 Ans.Sodium and potassium met ...
Stoichiometry – Chapter 9
... 4. The fizz produced when some antacid tablets are dropped into water is created by the production of carbon dioxide during the reaction between sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. 3NaHCO3 + H 3C6 H 5O7 → 3CO 2 + 3H 2O + Na 3C6 H 5O7 Suppose 2.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate and 0.50 g of citric acid ...
... 4. The fizz produced when some antacid tablets are dropped into water is created by the production of carbon dioxide during the reaction between sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. 3NaHCO3 + H 3C6 H 5O7 → 3CO 2 + 3H 2O + Na 3C6 H 5O7 Suppose 2.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate and 0.50 g of citric acid ...
Activity C14: Rate of a Chemical Reaction 1
... In this activity you will determine the effect of changes in concentration of the reactants on the rate of the chemical reaction. The reaction for this activity is the acidic reduction of the thiosulfate ion to sulfur and sulfur dioxide. The equation for the reaction is: S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) ====== ...
... In this activity you will determine the effect of changes in concentration of the reactants on the rate of the chemical reaction. The reaction for this activity is the acidic reduction of the thiosulfate ion to sulfur and sulfur dioxide. The equation for the reaction is: S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) ====== ...
CHE 106 Chapter 5
... Heat of Formation (DH compound from elements) labeled DHf Heat of formation (DHf) is usually given for reactants and products in standard states (since DH depends on the state of these items). When in standard state, the denotation is DH°f ...
... Heat of Formation (DH compound from elements) labeled DHf Heat of formation (DHf) is usually given for reactants and products in standard states (since DH depends on the state of these items). When in standard state, the denotation is DH°f ...
MC94 - Southchemistry.com
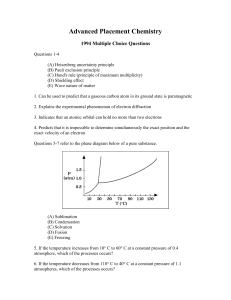
... Advanced Placement Chemistry: 1994 Multiple Choice Questions (answer key) ...
... Advanced Placement Chemistry: 1994 Multiple Choice Questions (answer key) ...
Unit 3 Homework Booklet
... Two chemicals A and B react in solution to form C. The reaction has an activation energy of 150 kJ mol-1. If hydrogen ions are used as a catalyst the activation energy is 50 kJ mol-1. The enthalpy change for the reaction is -125 kJ mol-1. Present this information as a potential energy diagram using ...
... Two chemicals A and B react in solution to form C. The reaction has an activation energy of 150 kJ mol-1. If hydrogen ions are used as a catalyst the activation energy is 50 kJ mol-1. The enthalpy change for the reaction is -125 kJ mol-1. Present this information as a potential energy diagram using ...
Organic Chemistry
... • Carbon forms a variety of strong covalent bonds (共价键) to itself and other atoms. • This allows organic compounds to be structurally diverse. ...
... • Carbon forms a variety of strong covalent bonds (共价键) to itself and other atoms. • This allows organic compounds to be structurally diverse. ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... blood gases in scuba diving CO2 in carbonated beverages buffers in our blood ...
... blood gases in scuba diving CO2 in carbonated beverages buffers in our blood ...
Part I - American Chemical Society
... of this ID number because you will use the same number on both Parts II and III. Each item in Part I consists of a question or an incomplete statement that is followed by four possible choices. Select the single choice that best answers the question or completes the statement. Then use a pencil to b ...
... of this ID number because you will use the same number on both Parts II and III. Each item in Part I consists of a question or an incomplete statement that is followed by four possible choices. Select the single choice that best answers the question or completes the statement. Then use a pencil to b ...
Presentation
... variescharges +1 totend +7 (oxidation or negative Nonmetals to have numbers) can be predicted for negative oxidations single (monatomic) numbers. (gain atoms. e-) varies ...
... variescharges +1 totend +7 (oxidation or negative Nonmetals to have numbers) can be predicted for negative oxidations single (monatomic) numbers. (gain atoms. e-) varies ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry
... 11. Utilized as a coating to protect Fe from corrosion 12. Is added to silicon to enhance its properties as a semiconductor 13. Utilized as a shield from sources of radiation Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select ...
... 11. Utilized as a coating to protect Fe from corrosion 12. Is added to silicon to enhance its properties as a semiconductor 13. Utilized as a shield from sources of radiation Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select ...
1 - Academics
... a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a particle cannot be simultaneously ...
... a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a particle cannot be simultaneously ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.