Metallocene Organoactinide Complexes
... instances the regio- and chemo-selectivities displayed by organoactinides are complementary to those observed for other transition-metal complexes. The reactivity of organoactinide complexes lies in their ability to perform bondbreaking and bond-forming reactions of distinct functional groups. Steri ...
... instances the regio- and chemo-selectivities displayed by organoactinides are complementary to those observed for other transition-metal complexes. The reactivity of organoactinide complexes lies in their ability to perform bondbreaking and bond-forming reactions of distinct functional groups. Steri ...
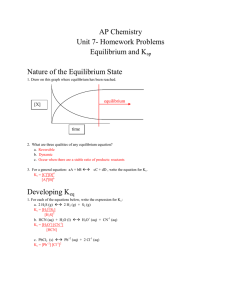
AP Chemistry Unit 7- Homework Problems Equilibrium and Ksp
... 1. Will a ppt of CaCO3 (Ksp= 3.4 x10-9) form if [Ca+2] = 4 x10-6 M and [CO3-2] = 4 x10-3? Q = [4 x10-6][4x10-3] = 1.6x10-8 >> 3.4x10-9 so yes, ppt 2. Will a ppt of Ag2CrO4 (Ksp = 1.1 x10-12 ) form if [Ag+] = 3x10-4 and [CrO4-2] = 2x10-4? Q = [3 x10-4]2 [2x10-4] = 1.8x10-11 >> 1.1x10-12 so yes, ppt 3 ...
... 1. Will a ppt of CaCO3 (Ksp= 3.4 x10-9) form if [Ca+2] = 4 x10-6 M and [CO3-2] = 4 x10-3? Q = [4 x10-6][4x10-3] = 1.6x10-8 >> 3.4x10-9 so yes, ppt 2. Will a ppt of Ag2CrO4 (Ksp = 1.1 x10-12 ) form if [Ag+] = 3x10-4 and [CrO4-2] = 2x10-4? Q = [3 x10-4]2 [2x10-4] = 1.8x10-11 >> 1.1x10-12 so yes, ppt 3 ...
The Application of Hydrolytic Enzymes for Biotransformations of
... antioxidant activity. Other potential pharmaceutical applications of flavonoids can be related to their enzyme inhibition, anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial and anti-cancer properties. Lipases have been used effectively in the production of flavonoid ester derivatives that have shown ...
... antioxidant activity. Other potential pharmaceutical applications of flavonoids can be related to their enzyme inhibition, anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial and anti-cancer properties. Lipases have been used effectively in the production of flavonoid ester derivatives that have shown ...
Chapter 18 pdf
... of hydrogen react. Because the reaction reaches a state of equilibrium, however, fewer than two moles of ammonia will actually be obtained. Chemists need to be able to predict the yield of a reaction. In 1864, the Norwegian chemists Cato Maximilian Guldberg and Peter Waage proposed the law of chemic ...
... of hydrogen react. Because the reaction reaches a state of equilibrium, however, fewer than two moles of ammonia will actually be obtained. Chemists need to be able to predict the yield of a reaction. In 1864, the Norwegian chemists Cato Maximilian Guldberg and Peter Waage proposed the law of chemic ...
Study Guide for Content Mastery - Student Edition
... is worrisome because without ozone all organisms on Earth are subject to harm from too much radiation. In your textbook, read about chlorofluorocarbons. ...
... is worrisome because without ozone all organisms on Earth are subject to harm from too much radiation. In your textbook, read about chlorofluorocarbons. ...
Chapter 18: Chemical Equilibrium
... of hydrogen react. Because the reaction reaches a state of equilibrium, however, fewer than two moles of ammonia will actually be obtained. Chemists need to be able to predict the yield of a reaction. In 1864, the Norwegian chemists Cato Maximilian Guldberg and Peter Waage proposed the law of chemic ...
... of hydrogen react. Because the reaction reaches a state of equilibrium, however, fewer than two moles of ammonia will actually be obtained. Chemists need to be able to predict the yield of a reaction. In 1864, the Norwegian chemists Cato Maximilian Guldberg and Peter Waage proposed the law of chemic ...
AS Chemistry - Edexcel
... (b) A coin, of mass 5.00 g, contains silver. The coin is dissolved in 500 cm3 of concentrated nitric acid to form silver nitrate solution, AgNO3(aq). 50.0 cm3 of this solution is reacted with excess sodium chloride solution to form a precipitate of silver chloride, AgCl. Ag+(aq) + Cl−(aq) → AgCl(s) ...
... (b) A coin, of mass 5.00 g, contains silver. The coin is dissolved in 500 cm3 of concentrated nitric acid to form silver nitrate solution, AgNO3(aq). 50.0 cm3 of this solution is reacted with excess sodium chloride solution to form a precipitate of silver chloride, AgCl. Ag+(aq) + Cl−(aq) → AgCl(s) ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) atoms must be balanced on both sides of the reaction arrow. B) mass must be conserved. C) molecules must be balanced on both sides of the reaction arrow. D) net charge must be balanced on both sides of the reaction arrow. Answer: C Diff: 1 Topic: Section 6.2 Balancing Chemical Equations 2) Which ...
... A) atoms must be balanced on both sides of the reaction arrow. B) mass must be conserved. C) molecules must be balanced on both sides of the reaction arrow. D) net charge must be balanced on both sides of the reaction arrow. Answer: C Diff: 1 Topic: Section 6.2 Balancing Chemical Equations 2) Which ...
Water Chemistry - U
... questions: (1) is there a need for another text in the field, and (2) how will their text be different from what is already available? It is obvious from the fact that this book exists that we answered yes to the first question. Our reasons for doing so are based on our answers to the second question, ...
... questions: (1) is there a need for another text in the field, and (2) how will their text be different from what is already available? It is obvious from the fact that this book exists that we answered yes to the first question. Our reasons for doing so are based on our answers to the second question, ...
Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... to produce glucose, C6H12O6, and oxygen from the reaction of carbon dioxide and water. What mass, in grams, of glucose is produced when 3.00 mol of water react with carbon dioxide? 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 3.00 mol H2O X 1 mol C6H12O6 X 180.18g = 6 mol H2O 1 mol C6 X 12.01 = 72.06 H12 X 1.01 = 12 ...
... to produce glucose, C6H12O6, and oxygen from the reaction of carbon dioxide and water. What mass, in grams, of glucose is produced when 3.00 mol of water react with carbon dioxide? 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 3.00 mol H2O X 1 mol C6H12O6 X 180.18g = 6 mol H2O 1 mol C6 X 12.01 = 72.06 H12 X 1.01 = 12 ...
BRIEF ANSWERS TO SELECTED PROBLEMS APPENDIX G
... • 2.1 Compounds contain different types of atoms; there is only one type of atom in an element. 2.4(a) The presence of more than one element makes pure calcium chloride a compound. (b) There is only one kind of atom, so sulfur is an element. (c) The presence of more than one compound makes baking po ...
... • 2.1 Compounds contain different types of atoms; there is only one type of atom in an element. 2.4(a) The presence of more than one element makes pure calcium chloride a compound. (b) There is only one kind of atom, so sulfur is an element. (c) The presence of more than one compound makes baking po ...
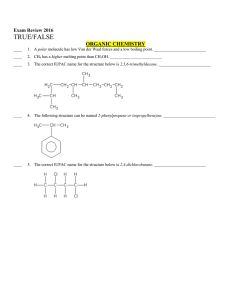
Multiple Choice Exam Review June 2016
... ____ 12. The shape of SO2 is trigonal planar. ____________________ ____ 13. The valence p orbitals in phosphorus, P, are half-filled. ____________________ ____ 14. All of the valence electrons in Fe2+ must have the same spin. _________________________ ____ 15. The shape of boron trifluoride, BF3, is ...
... ____ 12. The shape of SO2 is trigonal planar. ____________________ ____ 13. The valence p orbitals in phosphorus, P, are half-filled. ____________________ ____ 14. All of the valence electrons in Fe2+ must have the same spin. _________________________ ____ 15. The shape of boron trifluoride, BF3, is ...
MEDICAL CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE
... ions or molecules. This term is usually used to describe homogeneous mixtures of two or more liquids or of a liquid and one or more solids. Solutions may exist as gases, liquids, or solids. Nonreactive gases can mix in all proportions to give a gaseous solution. Liquid solutions are the most common ...
... ions or molecules. This term is usually used to describe homogeneous mixtures of two or more liquids or of a liquid and one or more solids. Solutions may exist as gases, liquids, or solids. Nonreactive gases can mix in all proportions to give a gaseous solution. Liquid solutions are the most common ...
study guide spring 2012
... What is the name of a list of elements arranged according to the ease with which they undergo certain chemical reactions? a. reactivity list c. activity series b. reaction sequence d. periodic list An element in the activity series can replace any element a. in the periodic table. c. above it on the ...
... What is the name of a list of elements arranged according to the ease with which they undergo certain chemical reactions? a. reactivity list c. activity series b. reaction sequence d. periodic list An element in the activity series can replace any element a. in the periodic table. c. above it on the ...
Chapter 3: Mass Relationships in Chemical
... 58. A mass spectrometer works by ionizing atoms or molecules, and then accelerating them past oppositely charged plates. The mass is obtained by A) measuring the force of impact on a detecting screen, and then calculating the mass using force = mass acceleration. B) suspending the ions in an appli ...
... 58. A mass spectrometer works by ionizing atoms or molecules, and then accelerating them past oppositely charged plates. The mass is obtained by A) measuring the force of impact on a detecting screen, and then calculating the mass using force = mass acceleration. B) suspending the ions in an appli ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... a. available amount of one of the reactants. c. available amount of each reactant. b. amount of product formed. d. speed of the reaction. ____ 130. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of matter are in motion in a. gases only. c. solids, liquids, and gases. b. gases and liquids. d. s ...
... a. available amount of one of the reactants. c. available amount of each reactant. b. amount of product formed. d. speed of the reaction. ____ 130. According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of matter are in motion in a. gases only. c. solids, liquids, and gases. b. gases and liquids. d. s ...
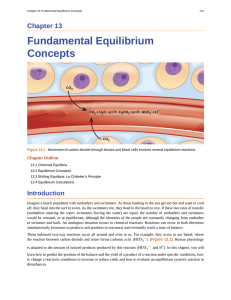
Fundamental Equilibrium Concepts
... beverage container, however, a cascade of equilibrium shifts occurs. First, the CO2 gas in the air space on top of the bottle escapes, causing the equilibrium between gas-phase CO2 and dissolved or aqueous CO2 to shift, lowering the concentration of CO2 in the soft drink. Less CO2 dissolved in the l ...
... beverage container, however, a cascade of equilibrium shifts occurs. First, the CO2 gas in the air space on top of the bottle escapes, causing the equilibrium between gas-phase CO2 and dissolved or aqueous CO2 to shift, lowering the concentration of CO2 in the soft drink. Less CO2 dissolved in the l ...
Introductory Chemistry, 2nd Edition Nivaldo Tro
... Mass-to-Mass Conversions • We learned previously to convert between moles and grams using the molar mass. • Combining this with moles to moles conversions allows us to related grams of one substrance in an equation to grams of another substance. g of A ...
... Mass-to-Mass Conversions • We learned previously to convert between moles and grams using the molar mass. • Combining this with moles to moles conversions allows us to related grams of one substrance in an equation to grams of another substance. g of A ...
Major 01 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Solution of the 1st Major Exam, Term 061, Version 000, all correct choices are A 1. All of the following are properties of sodium. Which one is a physical change? A. It is a solid at 25oC and melts at 98oC. Since melting has no change of the chemical composition involved, this is a physical change. ...
... Solution of the 1st Major Exam, Term 061, Version 000, all correct choices are A 1. All of the following are properties of sodium. Which one is a physical change? A. It is a solid at 25oC and melts at 98oC. Since melting has no change of the chemical composition involved, this is a physical change. ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.