Slide 1
... Lecture 15 The Redox Sequence Oxidation State Half-Reactions Balanced Oxidation-Reduction reactions Predicted Sequence of Redox Reactions Tracers for these reactions ...
... Lecture 15 The Redox Sequence Oxidation State Half-Reactions Balanced Oxidation-Reduction reactions Predicted Sequence of Redox Reactions Tracers for these reactions ...
Chemical Reaction
... Chemical Reaction Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
... Chemical Reaction Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
CHEMISTRY 1710 - Practice Exam #2 (KATZ)
... liquid retained in the flask is 1.362 g, what is its molar mass? a. ...
... liquid retained in the flask is 1.362 g, what is its molar mass? a. ...
File
... only the element is there, you must put a 2 subscript. • It is still possible for there to be only one of these elements, if it is bonded to something else. ▫ Example: MgO ...
... only the element is there, you must put a 2 subscript. • It is still possible for there to be only one of these elements, if it is bonded to something else. ▫ Example: MgO ...
HOCl wt/wt 0.06 x mL 90 one cy
... Refer to your tables (makes a good starting point). What was observed during the reaction? Any colour change, any precipitate (why?), is it a homogeneous mixture, bubbling of gas? Was there any odour? What was the appearance of the product after recrystallization. Can you explain why these changes a ...
... Refer to your tables (makes a good starting point). What was observed during the reaction? Any colour change, any precipitate (why?), is it a homogeneous mixture, bubbling of gas? Was there any odour? What was the appearance of the product after recrystallization. Can you explain why these changes a ...
Chemistry Spring Final Review
... during chemical or physical processes. C. Energy that always flows from a warmer object to a cooler object (high concentration to lower concentration). D. In any chemical or physical process, energy is neither created nor destroyed. E. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram o ...
... during chemical or physical processes. C. Energy that always flows from a warmer object to a cooler object (high concentration to lower concentration). D. In any chemical or physical process, energy is neither created nor destroyed. E. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram o ...
Chapter 4 Stoichiometry Power Point
... In the above equation, one mole of OH- ions will neutralize one mole of the H+ ions. HSO4-(aq) D H+(aq) + SO42-(aq) In the above equation, one mole of OH- ions will neutralize one mole of the H+ ions. Therefore, we need a total of 2 moles of NaOH in order to neutralize one mole of H2SO4 Let’s Finish ...
... In the above equation, one mole of OH- ions will neutralize one mole of the H+ ions. HSO4-(aq) D H+(aq) + SO42-(aq) In the above equation, one mole of OH- ions will neutralize one mole of the H+ ions. Therefore, we need a total of 2 moles of NaOH in order to neutralize one mole of H2SO4 Let’s Finish ...
Ch 13 kinetics
... c) A first order reaction takes 400.0 s to decrease from 0.200 M to 0.00820 M. What is the half-life of this reaction? How long will it take for the same reaction to decrease from 1.00 M to 0.125 M? ...
... c) A first order reaction takes 400.0 s to decrease from 0.200 M to 0.00820 M. What is the half-life of this reaction? How long will it take for the same reaction to decrease from 1.00 M to 0.125 M? ...
Practice Test Packet
... [A] 2S3 = Ksp [B] 108S5 = Ksp [C] 2S2 = Ksp [D] 4S3 = Ksp [E] 8S3 = Ksp 19. A weak acid, HF, is in solution with dissolved sodium fluoride, NaF. If HCl is added, which ion will react with the extra hydrogen ions from the HCl to keep the pH from changing? [A] F [B] Na+[C] Na [D] OH 20. Which of the f ...
... [A] 2S3 = Ksp [B] 108S5 = Ksp [C] 2S2 = Ksp [D] 4S3 = Ksp [E] 8S3 = Ksp 19. A weak acid, HF, is in solution with dissolved sodium fluoride, NaF. If HCl is added, which ion will react with the extra hydrogen ions from the HCl to keep the pH from changing? [A] F [B] Na+[C] Na [D] OH 20. Which of the f ...
Chapters 6 and 17: Chemical Thermodynamics
... (d) If the volume of the combustion container is 10.0 liters, calculate the final pressure in the container when the temperature is changed to 110°C. (Assume no oxygen remains unreacted and that all products are gaseous.) ...
... (d) If the volume of the combustion container is 10.0 liters, calculate the final pressure in the container when the temperature is changed to 110°C. (Assume no oxygen remains unreacted and that all products are gaseous.) ...
chemistry 110 lecture
... When most reactions are performed, some of the reactants is usually present in excess of the amount needed. If the reaction goes to completion, then some of this excess reactant will be left-over. The limiting reactant is the reactant used-up completely and it "limits" the reaction. For example: ...
... When most reactions are performed, some of the reactants is usually present in excess of the amount needed. If the reaction goes to completion, then some of this excess reactant will be left-over. The limiting reactant is the reactant used-up completely and it "limits" the reaction. For example: ...
Theoretical problems (official version)
... Much of the photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts – organelles found in plant cells and containing chlorophyll – the light-absorbing substance. Hill isolated chloroplasts from the cells by grinding the leaves in the sucrose solutions. The cell-free chloroplasts did not produce oxygen under illu ...
... Much of the photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts – organelles found in plant cells and containing chlorophyll – the light-absorbing substance. Hill isolated chloroplasts from the cells by grinding the leaves in the sucrose solutions. The cell-free chloroplasts did not produce oxygen under illu ...
Questions 1-2
... 36. A sample of a solution of an unknown was treated with dilute hydrochloric acid. The white precipitate formed was filtered and washed with hot water. A few drops of potassium iodide solution were added to the hot water filtrate and a bright yellow precipitate was produced. The white precipitate ...
... 36. A sample of a solution of an unknown was treated with dilute hydrochloric acid. The white precipitate formed was filtered and washed with hot water. A few drops of potassium iodide solution were added to the hot water filtrate and a bright yellow precipitate was produced. The white precipitate ...
Spectrum05
... I first put reactants together the forward reaction starts. Since there are no products there is no reverse reaction. As the forward reaction proceeds the reactants are used up so the forward reaction slows. The products build up, and the reverse reaction speeds up. ...
... I first put reactants together the forward reaction starts. Since there are no products there is no reverse reaction. As the forward reaction proceeds the reactants are used up so the forward reaction slows. The products build up, and the reverse reaction speeds up. ...
國立屏東教育大學95學年度研究所碩士班入學考試
... (A) must be rigid and have rough surfaces (B) must be rigid and chemically inert (C) must be rigid and must not degrade over time (D) must be flexible and have an open porous structure (E) should be designed such that it encourages coagulation of blood 第 1 頁,共 5 頁 ...
... (A) must be rigid and have rough surfaces (B) must be rigid and chemically inert (C) must be rigid and must not degrade over time (D) must be flexible and have an open porous structure (E) should be designed such that it encourages coagulation of blood 第 1 頁,共 5 頁 ...
Name - Deans Community High School
... b) Is the forward reaction is exothermic or endothermic. ............................................ 1 c) Gold and platinum both catalyse the reaction. For the forward reaction EA using gold is 30 kJ, while EA using platinum is 40 kJ. i) using different dotted lines add this information to the grap ...
... b) Is the forward reaction is exothermic or endothermic. ............................................ 1 c) Gold and platinum both catalyse the reaction. For the forward reaction EA using gold is 30 kJ, while EA using platinum is 40 kJ. i) using different dotted lines add this information to the grap ...
CH1710 PrEX#2 Sp2013 answers
... B) 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → K2SO4(s) C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H2O(l) + K2SO4(s) D) H22+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2(OH)2(l) _____ 18. The titration of 25.0 mL of an unknown concentration H2SO4 solution requires 83.6 mL of 0.12 M LiOH solution. What is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution ...
... B) 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → K2SO4(s) C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H2O(l) + K2SO4(s) D) H22+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2(OH)2(l) _____ 18. The titration of 25.0 mL of an unknown concentration H2SO4 solution requires 83.6 mL of 0.12 M LiOH solution. What is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution ...
Spring Exam 4 - Chemistry
... At 20C, a liquid solution contains 138 g sodium acetate trihydrate in 100 g water. The composition of a saturated solution of sodium acetate trihydrate at 20C is 46.5 g sodium acetate trihydrate in 100 g water. The liquid solution is said to be: A. Supersaturated ...
... At 20C, a liquid solution contains 138 g sodium acetate trihydrate in 100 g water. The composition of a saturated solution of sodium acetate trihydrate at 20C is 46.5 g sodium acetate trihydrate in 100 g water. The liquid solution is said to be: A. Supersaturated ...
Introduction to Organic Synthesis
... simpler molecules by means of DISCONNECTIONS and/or FUNCTIONAL GROUP INTERCONVERSIONS that correspond to known reactions. When you've got to a simple enough starting material (like something you can buy [and usually is cheap]) then the synthetic plan is simply the reverse of the analysis. The design ...
... simpler molecules by means of DISCONNECTIONS and/or FUNCTIONAL GROUP INTERCONVERSIONS that correspond to known reactions. When you've got to a simple enough starting material (like something you can buy [and usually is cheap]) then the synthetic plan is simply the reverse of the analysis. The design ...
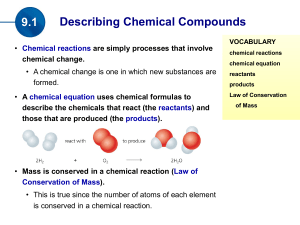
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... • Coefficients in a chemical equation describe the number of molecules of each compound or element, whereas subscripts describe the number of atoms of each element. • Balancing an equation involves changing the coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts ...
... • Coefficients in a chemical equation describe the number of molecules of each compound or element, whereas subscripts describe the number of atoms of each element. • Balancing an equation involves changing the coefficients as required throughout the equation so that atoms are conserved. Subscripts ...
2009
... 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this informa ...
... 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of this informa ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.