Chemistry (Revised)
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) (i) Hydrogen sulfide gas is very soluble in water. Draw a diagram to show an assembled apparatus that could be used to measure the volume of H2S gas produced when a sample of ...
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) (i) Hydrogen sulfide gas is very soluble in water. Draw a diagram to show an assembled apparatus that could be used to measure the volume of H2S gas produced when a sample of ...
AQA A-level Chemistry
... lines is labelled ΔH (change in enthalpy). In an endothermic reaction this has a positive value. In an exothermic reaction this has a negative value. All values are measured in kJ mol−1. If the actual reactants and products are known, the lines should be labelled with their names or formulae. Otherw ...
... lines is labelled ΔH (change in enthalpy). In an endothermic reaction this has a positive value. In an exothermic reaction this has a negative value. All values are measured in kJ mol−1. If the actual reactants and products are known, the lines should be labelled with their names or formulae. Otherw ...
Chemistry 101L
... will be making. Remember to include room for multiple trials and average values, if appropriate. If appropriate, have room for classmates’ data. Now organize your list into things that are similar or data that should be compared. Tables columns/rows do not have to be listed in the same order that th ...
... will be making. Remember to include room for multiple trials and average values, if appropriate. If appropriate, have room for classmates’ data. Now organize your list into things that are similar or data that should be compared. Tables columns/rows do not have to be listed in the same order that th ...
Concept Development Studies in Chemistry
... answer to the question of what it means to combine two elements to make a compound, and it should even permit prediction of what quantity of lead sul de will be produced by a given amount of lead. For example, 6.5g of lead will produce exactly 7.5g of lead sul de, 50g of lead will produce 57.7g of l ...
... answer to the question of what it means to combine two elements to make a compound, and it should even permit prediction of what quantity of lead sul de will be produced by a given amount of lead. For example, 6.5g of lead will produce exactly 7.5g of lead sul de, 50g of lead will produce 57.7g of l ...
General and Inorganic Chemistry
... 4. I.4 Naming compounds ......................................................................................................... 4 4.1. I.4.1 Naming ions ..................................................................................................... 5 4.1.1. I.4.1.1 Naming cations ........... ...
... 4. I.4 Naming compounds ......................................................................................................... 4 4.1. I.4.1 Naming ions ..................................................................................................... 5 4.1.1. I.4.1.1 Naming cations ........... ...
2013 - SQA
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) (i) Hydrogen sulfide gas is very soluble in water. Draw a diagram to show an assembled apparatus that could be used to measure the volume of H2S gas produced when a sample of ...
... FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) (i) Hydrogen sulfide gas is very soluble in water. Draw a diagram to show an assembled apparatus that could be used to measure the volume of H2S gas produced when a sample of ...
D--All Websites-eChemistryHelp-.mdi
... Redox reactions are the chemical reactions which involve both oxidation as well as reduction simultaneously. In fact, oxidation and reduction go hand in hand. The redox reactions are of two types : (i) Direct redox and (ii) Indirect redox reactions. When chemical reactions are carried out then some ...
... Redox reactions are the chemical reactions which involve both oxidation as well as reduction simultaneously. In fact, oxidation and reduction go hand in hand. The redox reactions are of two types : (i) Direct redox and (ii) Indirect redox reactions. When chemical reactions are carried out then some ...
kinetics, catalysis, and reaction engineering
... was used to determine the main effects and two-factor interactions for the factors of C3H6 concentration, NO concentration, temperature, and GHSV on HCN conversion. A table of contrast was used to estimate the significance of these factors. The specific levels (lowest and highest values), HCN conver ...
... was used to determine the main effects and two-factor interactions for the factors of C3H6 concentration, NO concentration, temperature, and GHSV on HCN conversion. A table of contrast was used to estimate the significance of these factors. The specific levels (lowest and highest values), HCN conver ...
odd - WWW2
... formed by the most electropositive metals. These may contain the dicarbide(2 ) ion, C22 , or the true carbide ion C4 . Both types of ionic carbides react with water to produce the appropriate hydrocarbon. Covalent carbides are formed by nonmetals, specifically boron and silicon, more electronegative ...
... formed by the most electropositive metals. These may contain the dicarbide(2 ) ion, C22 , or the true carbide ion C4 . Both types of ionic carbides react with water to produce the appropriate hydrocarbon. Covalent carbides are formed by nonmetals, specifically boron and silicon, more electronegative ...
Improved Synthesis of Seven-Coordinate Molybdenum( I I) and
... SnC13-,halide) can be displaced,5bJ2and this reaction has been employed here to prepare the [M(CNR),(cN)]+ (from X = halide) and [Mo(CNR),I2+ (from X = SnC13-) complexes. X-ray crystallographic studies of these complexes have been described e l s e ~ h e r e . ' ~ JFinally, ...
... SnC13-,halide) can be displaced,5bJ2and this reaction has been employed here to prepare the [M(CNR),(cN)]+ (from X = halide) and [Mo(CNR),I2+ (from X = SnC13-) complexes. X-ray crystallographic studies of these complexes have been described e l s e ~ h e r e . ' ~ JFinally, ...
Experimental Chemistry I
... The reaction between a strong acid and a strong base can be basically considered as a neutralization reaction. In a neutralization reaction, an acid reacts with a base to produce salt and water: NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → 2H2O(l) + Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) An indicator enables detection of the stoichiometric poi ...
... The reaction between a strong acid and a strong base can be basically considered as a neutralization reaction. In a neutralization reaction, an acid reacts with a base to produce salt and water: NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → 2H2O(l) + Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) An indicator enables detection of the stoichiometric poi ...
sol-gel chemistry of transition metal oxides
... author proposed a mechanism of hydrolysis in which hydroxyl groups are added to the which leads to the formation of condensed species. ...
... author proposed a mechanism of hydrolysis in which hydroxyl groups are added to the which leads to the formation of condensed species. ...
Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... A) H2O B) CH3OH C) CH3CH2OH D) HF E) NaF Ans: E Category: Easy Section: 4.1 2. Which of the following compounds is a weak electrolyte? A) HNO3 B) NaNO3 C) HNO2 D) NaNO2 E) NaOH Ans: C Category: Easy Section: 4.1 3. Which of the following compounds is a strong electrolyte? A) H2O D) CH3CH2OH (ethanol ...
... A) H2O B) CH3OH C) CH3CH2OH D) HF E) NaF Ans: E Category: Easy Section: 4.1 2. Which of the following compounds is a weak electrolyte? A) HNO3 B) NaNO3 C) HNO2 D) NaNO2 E) NaOH Ans: C Category: Easy Section: 4.1 3. Which of the following compounds is a strong electrolyte? A) H2O D) CH3CH2OH (ethanol ...
Chapter 6 Table of Contents
... At Contrived State University in Anytown, Ohio, a new building was dedicated in March 2010 to house the College of Education. The 100,000-square-foot building has enough office space to accommodate 86 full-time faculty members and 167 full-time staff. In a fit of monetary excess, the university admi ...
... At Contrived State University in Anytown, Ohio, a new building was dedicated in March 2010 to house the College of Education. The 100,000-square-foot building has enough office space to accommodate 86 full-time faculty members and 167 full-time staff. In a fit of monetary excess, the university admi ...
indian association of chemistry teachers
... The isotope of carbon which is used in carbon dating (a method to estimate the age of an ancient sample containing carbon) is (A) carbon-12 (B) carbon-13 (C) carbon-14 (D) carbon-15 [C] Electronic configurations for the atoms of four elements are given below. The configuration that indicates colourl ...
... The isotope of carbon which is used in carbon dating (a method to estimate the age of an ancient sample containing carbon) is (A) carbon-12 (B) carbon-13 (C) carbon-14 (D) carbon-15 [C] Electronic configurations for the atoms of four elements are given below. The configuration that indicates colourl ...
Chemical Equilibrium - 2012 Book Archive
... you need to bail out water. You grab a bucket and begin to bail. After a few minutes, your efforts against the leak keep the water to only about half an inch, but any further bailing doesn’t change the water level; the leak brings in as much water as you bail out. You are at equilibrium. Two opposin ...
... you need to bail out water. You grab a bucket and begin to bail. After a few minutes, your efforts against the leak keep the water to only about half an inch, but any further bailing doesn’t change the water level; the leak brings in as much water as you bail out. You are at equilibrium. Two opposin ...
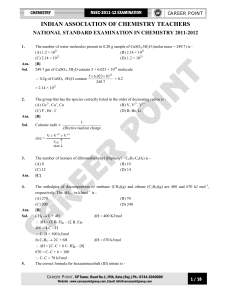
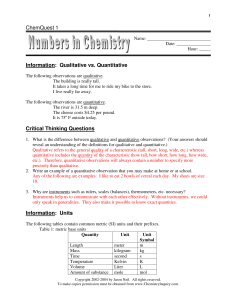
ChemQuest 1 Information: Qualitative vs. Quantitative Critical
... 5. How are compounds different from mixtures? Compounds are formed by a chemical change (i.e. two hydrogen and one oxygen atom bonding to form a water molecule), but mixtures are formed by a physical change (i.e. stirring salt and water together. 6. How are pure substances different from mixtures? P ...
... 5. How are compounds different from mixtures? Compounds are formed by a chemical change (i.e. two hydrogen and one oxygen atom bonding to form a water molecule), but mixtures are formed by a physical change (i.e. stirring salt and water together. 6. How are pure substances different from mixtures? P ...
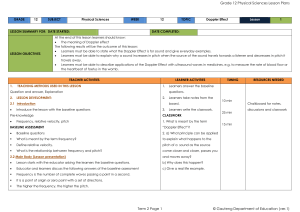
Physical Sciences Grade 12 Term 2
... The siren of a burglar alarm system has a frequency of 960 Hz. During a patrol, a security officer, travelling in his car, hears the siren of the alarm of a house and approaches the house at 2.1 Name the phenomenon that explains the change in the observed frequency. 2.2 Calculate the speed at which ...
... The siren of a burglar alarm system has a frequency of 960 Hz. During a patrol, a security officer, travelling in his car, hears the siren of the alarm of a house and approaches the house at 2.1 Name the phenomenon that explains the change in the observed frequency. 2.2 Calculate the speed at which ...
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
... Breaking Elements Apart with Nuclear Fission .................... 52 Mass defect: Where does all that energy come from? .................................................... 52 Chain reactions and critical mass ............................... 53 Coming Together with Nuclear Fusion.................... ...
... Breaking Elements Apart with Nuclear Fission .................... 52 Mass defect: Where does all that energy come from? .................................................... 52 Chain reactions and critical mass ............................... 53 Coming Together with Nuclear Fusion.................... ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.