Higher Chemistry Resources Guide - Glow Blogs
... http://bit.ly/1eKi0mI The RSC has an interactive Periodic Table available: http://rsc.li/1eSlfuQ There are a number of videos on the Periodic Table on Twig ion the Glow web site: http://bit.ly/1kBBKxK http://bit.ly/1qLkZnA http://bit.ly/1dfekcr The University of Nottingham website on the Periodic Ta ...
... http://bit.ly/1eKi0mI The RSC has an interactive Periodic Table available: http://rsc.li/1eSlfuQ There are a number of videos on the Periodic Table on Twig ion the Glow web site: http://bit.ly/1kBBKxK http://bit.ly/1qLkZnA http://bit.ly/1dfekcr The University of Nottingham website on the Periodic Ta ...
IJEMS 3(6) 243-247
... It is interesting to note that, with increase in reducing agents from 0 to 2%, the dissolution increases sharply except in the case of sodium sulphite where a marginal increase is found even at 5%. However, further increase in reductant con.centrations (upto 5%) do not show an appreciable increase i ...
... It is interesting to note that, with increase in reducing agents from 0 to 2%, the dissolution increases sharply except in the case of sodium sulphite where a marginal increase is found even at 5%. However, further increase in reductant con.centrations (upto 5%) do not show an appreciable increase i ...
text
... base. For example, the acetate ion, CH3COO–, in reaction 6.7 is a base that can accept a proton from the acidic ammonium ion, NH +4 , forming acetic acid and ammonia. We call the acetate ion the conjugate base of acetic acid, and we call the ammonium ion the conjugate acid of ammonia. Strong and Wea ...
... base. For example, the acetate ion, CH3COO–, in reaction 6.7 is a base that can accept a proton from the acidic ammonium ion, NH +4 , forming acetic acid and ammonia. We call the acetate ion the conjugate base of acetic acid, and we call the ammonium ion the conjugate acid of ammonia. Strong and Wea ...
Higher Chemistry Resources Guide - Glow Blogs
... http://bit.ly/1qLkZnA http://bit.ly/1dfekcr University of Nottingham website - Periodic Table video portraits of the elements: http://bit.ly/1dUQdmz This is Experiment 51 from Classic Chemistry Experiments from the RSC. http://rsc.li/1p39xA6 SSERC has details of the silicon from sand demonstration. ...
... http://bit.ly/1qLkZnA http://bit.ly/1dfekcr University of Nottingham website - Periodic Table video portraits of the elements: http://bit.ly/1dUQdmz This is Experiment 51 from Classic Chemistry Experiments from the RSC. http://rsc.li/1p39xA6 SSERC has details of the silicon from sand demonstration. ...
CHEMISTRY OF p-ELEMENTS - Львівський національний
... The boron halides are typical covalent nonmetal halides. Boron trifluoride, BF3, and boron trichloride, BCl3, are gases at room temperature; BBr3 is a liquid, and BI3 is a solid. They all consist of molecules with the expected AX3 planar triangular structure. Although the electronegativity differenc ...
... The boron halides are typical covalent nonmetal halides. Boron trifluoride, BF3, and boron trichloride, BCl3, are gases at room temperature; BBr3 is a liquid, and BI3 is a solid. They all consist of molecules with the expected AX3 planar triangular structure. Although the electronegativity differenc ...
sample problem - KFUPM Resources
... How does the value of ΔG change when the pressures of the H2, Cl2 and HCl gases are changed to 0.25 atm, 0.45 atm and 0.30 atm, respectively, at 25C? (ΔGf for HCl(g) is ‒ 95.27 kJ/mol) ...
... How does the value of ΔG change when the pressures of the H2, Cl2 and HCl gases are changed to 0.25 atm, 0.45 atm and 0.30 atm, respectively, at 25C? (ΔGf for HCl(g) is ‒ 95.27 kJ/mol) ...
CHEM 121 Chp 5 Spaulding
... The formula weight is the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms in a compound, reported in atomic mass units The molar mass is the mass of one mole of any substance, reported in grams ◦ The value of the molar mass of a compound in grams equals the value of its formula weight in ...
... The formula weight is the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms in a compound, reported in atomic mass units The molar mass is the mass of one mole of any substance, reported in grams ◦ The value of the molar mass of a compound in grams equals the value of its formula weight in ...
Chapter 1: Chemistry: The Study of Change
... NH2 (the compound must be N2H4, Hydrazine) 13. Calculate the molecular mass of ethylene glycol, C2H6O2, a compound frequently used as automobile antifreeze. (Section: 3.3) Ans: 62 amu 14. Calculate the percent composition by mass of sodium in Na2CO3. (Section: 3.5) Ans: 43.396 % 15. Calculate the pe ...
... NH2 (the compound must be N2H4, Hydrazine) 13. Calculate the molecular mass of ethylene glycol, C2H6O2, a compound frequently used as automobile antifreeze. (Section: 3.3) Ans: 62 amu 14. Calculate the percent composition by mass of sodium in Na2CO3. (Section: 3.5) Ans: 43.396 % 15. Calculate the pe ...
Chemical Equations
... Identify the substances involved in a chemical process Distinguish between the reactants and products in a chemical process Allow easy determination of quantities of substances involved in chemical processes ...
... Identify the substances involved in a chemical process Distinguish between the reactants and products in a chemical process Allow easy determination of quantities of substances involved in chemical processes ...
PDF File
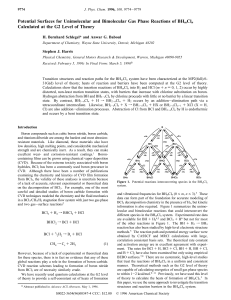
... the observed K1/2 values equal the dissociation constants Kd (see also ref 37): The same K1/2 values were observed in concentration dependences in which the maximal rate constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the ...
... the observed K1/2 values equal the dissociation constants Kd (see also ref 37): The same K1/2 values were observed in concentration dependences in which the maximal rate constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the ...
Degradation of bidentate coordinated platinum(II)
... used, indicating that drug degradation is not due to a decrease in the pH of the solution as protons are ...
... used, indicating that drug degradation is not due to a decrease in the pH of the solution as protons are ...
At equilibrium
... – if Q < K it follows that the reaction can only go forward. (eg. when we start with only “reactants”) – if Q > K it follows that the reaction can only go backward. (eg. When we start with only “products”) – if Q = K it follows that the reaction is at equilibrium • Therefore by finding Q at any poin ...
... – if Q < K it follows that the reaction can only go forward. (eg. when we start with only “reactants”) – if Q > K it follows that the reaction can only go backward. (eg. When we start with only “products”) – if Q = K it follows that the reaction is at equilibrium • Therefore by finding Q at any poin ...
Appendices - Mattson Creighton
... 5. The syringe should be upright when removing the cap to that the liquid will not spray out onto your hand, clothing, laboratory book, etc. 6. Vigorously shaking the syringe mixes the chemicals. This becomes even more important if one of the reagents is a gas. 7. If some of the solid reagent spills ...
... 5. The syringe should be upright when removing the cap to that the liquid will not spray out onto your hand, clothing, laboratory book, etc. 6. Vigorously shaking the syringe mixes the chemicals. This becomes even more important if one of the reagents is a gas. 7. If some of the solid reagent spills ...
EQUILIBRIUM
... For chemical reactions – Keq, Kc, and Kp are the important quantities For physical changes – Ka, Kb, Ksp, Kionize, and Kdissocation are the important quantities Important points ...
... For chemical reactions – Keq, Kc, and Kp are the important quantities For physical changes – Ka, Kb, Ksp, Kionize, and Kdissocation are the important quantities Important points ...
Exam Review Packet Table of Contents
... absent and the highest energy electrons are 3p, which has a much smaller size because the (-‐) / (+) charge ratio is less than 1 causing a contraction of the electron shell. b) Lattice energy ...
... absent and the highest energy electrons are 3p, which has a much smaller size because the (-‐) / (+) charge ratio is less than 1 causing a contraction of the electron shell. b) Lattice energy ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.