introduction - WordPress.com
... the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is ...
... the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is ...
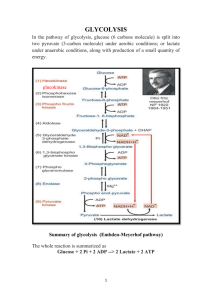
Summary of glycolysis (Embden
... NAD+ by oxidative phosphorylation which needs oxygen. However, during exercise, there is lack of oxygen so this reconversion is not possible, Therefore, the cell has to couple some other reaction in which NAD+ is regenerated in the cytoplasm itself hence, pyruvate is reduced to lactate; the NAD+ thu ...
... NAD+ by oxidative phosphorylation which needs oxygen. However, during exercise, there is lack of oxygen so this reconversion is not possible, Therefore, the cell has to couple some other reaction in which NAD+ is regenerated in the cytoplasm itself hence, pyruvate is reduced to lactate; the NAD+ thu ...
At the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games, David Davies won the silver
... * This system involves the partial breakdown of glucose (oxygen is required for full breakdown). ...
... * This system involves the partial breakdown of glucose (oxygen is required for full breakdown). ...
Bioenergetics of Exercise and Training
... Pyruvate (from slow glycolysis) enters into the Krebs Cycle; the 3-carbon (chain) pyruvate becomes a 2-carbon (chain) acetyl-CoA; the extra carbon that is removed combines with O2 to make carbon dioxide (CO2) which is later ...
... Pyruvate (from slow glycolysis) enters into the Krebs Cycle; the 3-carbon (chain) pyruvate becomes a 2-carbon (chain) acetyl-CoA; the extra carbon that is removed combines with O2 to make carbon dioxide (CO2) which is later ...
Popeye knew what he was doing!
... Popeye knew what he was doing! Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Aerobic Respiration – Overview • There are four main stages in aerobic cellular respiration: 1. Glycolysis – Oxidation of glucose into pyruvate that occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. 2. Kreb’s cycle preparation – Pyruvate is us ...
... Popeye knew what he was doing! Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Aerobic Respiration – Overview • There are four main stages in aerobic cellular respiration: 1. Glycolysis – Oxidation of glucose into pyruvate that occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. 2. Kreb’s cycle preparation – Pyruvate is us ...
File
... Endergonic reactions are those that store energy. During these reactions the reactant has lower free energy than the product. This is expressed by +G (positive Gibbs number). They do not happen spontaneously and need supply of energy to occur. Example would be production of ATP during aerobic respir ...
... Endergonic reactions are those that store energy. During these reactions the reactant has lower free energy than the product. This is expressed by +G (positive Gibbs number). They do not happen spontaneously and need supply of energy to occur. Example would be production of ATP during aerobic respir ...
Energy For Muscular Activity
... 1. What are the differences between the 3 energy systems? 2. List one advantage and one disadvantage of each of the 3 energy systems. 3. Give an example of three activities or sports that use each of (a) the high energy phosphate system, (b) the anaerobic glycolytic system, and (c) the aerobic oxida ...
... 1. What are the differences between the 3 energy systems? 2. List one advantage and one disadvantage of each of the 3 energy systems. 3. Give an example of three activities or sports that use each of (a) the high energy phosphate system, (b) the anaerobic glycolytic system, and (c) the aerobic oxida ...
Cells and Energy
... Photosynthesis is a process that captures energy from sunlight to make sugars that store chemical energy. Therefore, directly or indirectly, the energy for almost all organisms begins as sunlight. Sunlight includes a wide range of radiant energy, such as ultraviolet radiation, microwaves, and the ...
... Photosynthesis is a process that captures energy from sunlight to make sugars that store chemical energy. Therefore, directly or indirectly, the energy for almost all organisms begins as sunlight. Sunlight includes a wide range of radiant energy, such as ultraviolet radiation, microwaves, and the ...
7 NCCR MUST
... experimental investigations on the dynamics of atomic-scale structure in solid state materials. The short wavelength of x-rays combined with short pulse durations allow for diffraction experiments that directly probe changes inatomic scale structure. For lattice motion, the fundamental time scale of ...
... experimental investigations on the dynamics of atomic-scale structure in solid state materials. The short wavelength of x-rays combined with short pulse durations allow for diffraction experiments that directly probe changes inatomic scale structure. For lattice motion, the fundamental time scale of ...
Chapter 6 Slides
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
glycolysis
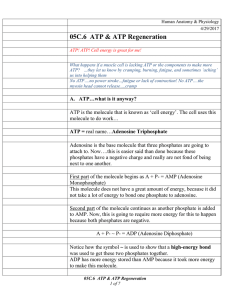
... In this case, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate have to continue to the reaction of payoff phase. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate will converted to 1,3biphosphoglycerate as the first compound that produce in the payoff phase If the enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase that has play role in the conver ...
... In this case, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate have to continue to the reaction of payoff phase. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate will converted to 1,3biphosphoglycerate as the first compound that produce in the payoff phase If the enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase that has play role in the conver ...
01 - ALCA
... The build up of lactic acid gives the muscle a ‘burning’ feeling. Some athletes use the term ‘feel the burn’ to know that they are pushing the endurance of the muscle metabolism to its limit. Lactic acid has a bad rap, because it has a positive purpose to protect the muscles from working to a point ...
... The build up of lactic acid gives the muscle a ‘burning’ feeling. Some athletes use the term ‘feel the burn’ to know that they are pushing the endurance of the muscle metabolism to its limit. Lactic acid has a bad rap, because it has a positive purpose to protect the muscles from working to a point ...
video slide - Biology at Mott
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
BI0 120 cell and tissues
... B. matrix of the mitochondria. C. membranes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. D. intermembrane space of mitochondria. E. inner membrane of the chloroplasts. 38. What is the fate of the carbon fragment that proceeds through the citric acid cycle? A. conversion to heat. B. synthesis of glucose. C. i ...
... B. matrix of the mitochondria. C. membranes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. D. intermembrane space of mitochondria. E. inner membrane of the chloroplasts. 38. What is the fate of the carbon fragment that proceeds through the citric acid cycle? A. conversion to heat. B. synthesis of glucose. C. i ...
Photosynthetic Research in Plant Science
... 1964, Hatch and Slack 1965) and named C4 photosynthesis. Although photosynthesis plays the central role in the energy metabolism of plants, historically there have not been strong interactions between photosynthesis research and other fields of plant science. Many techniques and tools developed for p ...
... 1964, Hatch and Slack 1965) and named C4 photosynthesis. Although photosynthesis plays the central role in the energy metabolism of plants, historically there have not been strong interactions between photosynthesis research and other fields of plant science. Many techniques and tools developed for p ...
Chapter 8 Powerpoint (To the Point)
... In mitochondria...the electron transport chain comprises an enzymatic series of electron donors and acceptors. Each electron donor passes electrons to a more electronegative acceptor, which in turn donates these electrons to another acceptor, a process that continues down the series until electrons ...
... In mitochondria...the electron transport chain comprises an enzymatic series of electron donors and acceptors. Each electron donor passes electrons to a more electronegative acceptor, which in turn donates these electrons to another acceptor, a process that continues down the series until electrons ...
Chapter 6
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
Slides - WordPress.com
... since been identified in a variety of chemoautotrophs rTCA cycle specific enzymes are 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (Oor), fumarate reductase (Frd), and ATP citrate lyase (Acl) rTCA cycle pathway tends to be in organisms that live in low O2 ...
... since been identified in a variety of chemoautotrophs rTCA cycle specific enzymes are 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (Oor), fumarate reductase (Frd), and ATP citrate lyase (Acl) rTCA cycle pathway tends to be in organisms that live in low O2 ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION: AEROBIC HARVESTING OF ENERGY
... – the cells are packed full of mitochondria, – the inner mitochondrial membrane contains an uncoupling protein, which allows H+ to flow back down its concentration gradient without generating ATP, and – ongoing oxidation of stored fats generates additional ...
... – the cells are packed full of mitochondria, – the inner mitochondrial membrane contains an uncoupling protein, which allows H+ to flow back down its concentration gradient without generating ATP, and – ongoing oxidation of stored fats generates additional ...
04. Introduction to metabolism
... are oxidized to common metabolite (acetyl CoA) Stage III. Acetyl CoA is oxidized in citric acid cycle to CO2 and water. As result reduced cofactor, NADH2 and FADH2, are formed which give up their electrons. Electrons are transported via the tissue respiration chain and released energy is coupled dir ...
... are oxidized to common metabolite (acetyl CoA) Stage III. Acetyl CoA is oxidized in citric acid cycle to CO2 and water. As result reduced cofactor, NADH2 and FADH2, are formed which give up their electrons. Electrons are transported via the tissue respiration chain and released energy is coupled dir ...
Ch 9 Homework Plan - Dublin City Schools
... o Explain how the exergonic “slide” of electrons down the electron transport chain is coupled to the endergonic production of ATP by chemiosmosis o Describe the process of chemiosmosis o Explain how membrane structure is related to membrane function. Complete the Cellular Respiration Review Activi ...
... o Explain how the exergonic “slide” of electrons down the electron transport chain is coupled to the endergonic production of ATP by chemiosmosis o Describe the process of chemiosmosis o Explain how membrane structure is related to membrane function. Complete the Cellular Respiration Review Activi ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... To calculate the energy released by lipid breakdown, there are two steps. Step One: beta-oxidation step that converts a long chain of carbons into a series of acetyl-CoA The oxidation of fatty acids into acetyl-CoA molecules requires the breaking of bonds, always one less bond that the number of ac ...
... To calculate the energy released by lipid breakdown, there are two steps. Step One: beta-oxidation step that converts a long chain of carbons into a series of acetyl-CoA The oxidation of fatty acids into acetyl-CoA molecules requires the breaking of bonds, always one less bond that the number of ac ...