Other High Energy Compounds
... go back to the stable low energy ket form and the surplus energy is released. ...
... go back to the stable low energy ket form and the surplus energy is released. ...
Chapter 9 Pictures
... March 19. Do it before you leave for spring break. No excuses !!!!! Final Day to drop a class is Friday, March ...
... March 19. Do it before you leave for spring break. No excuses !!!!! Final Day to drop a class is Friday, March ...
Cellular Respiration
... Acety CoA (2C) + 3NAD + FAD + ADP 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + FADH2 + ATP Electron Transport Chain ATP Synthesis Electron Transport Chain: is a series of H-acceptors and electron-acceptors associated with the inner membrane of Mitochondria. NADH passes its 2 electrons to first H-acceptor and 2 H+ are pumped ...
... Acety CoA (2C) + 3NAD + FAD + ADP 2 CO2 + 3 NADH + FADH2 + ATP Electron Transport Chain ATP Synthesis Electron Transport Chain: is a series of H-acceptors and electron-acceptors associated with the inner membrane of Mitochondria. NADH passes its 2 electrons to first H-acceptor and 2 H+ are pumped ...
CHEMISTRY 102B Name Hour Exam II March 19, 2015 Signature
... orbital and nitrogen has all unpaired electrons. c) It is consistent with the general trend relating changes in ionization energy across a period from left to right because it is harder to take an electron from an oxygen atom than from a nitrogen atom. d) It is inconsistent with the general trend re ...
... orbital and nitrogen has all unpaired electrons. c) It is consistent with the general trend relating changes in ionization energy across a period from left to right because it is harder to take an electron from an oxygen atom than from a nitrogen atom. d) It is inconsistent with the general trend re ...
Unit 3
... breakdown of glucose to pyruvate without the use of oxygen. Pyruvate is then converted into lactic acid, which limits the amount of ATP produced (2 ATP molecules). ...
... breakdown of glucose to pyruvate without the use of oxygen. Pyruvate is then converted into lactic acid, which limits the amount of ATP produced (2 ATP molecules). ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... ATP without the production of oxygen; water is not used as an electron donor. These organisms are relics of the time when the ancient atmosphere of the earth lacked oxygen; light is the source of energy but the electron donors are reduced inorganic compounds such as hydrogen sulfide or thiosulfate ( ...
... ATP without the production of oxygen; water is not used as an electron donor. These organisms are relics of the time when the ancient atmosphere of the earth lacked oxygen; light is the source of energy but the electron donors are reduced inorganic compounds such as hydrogen sulfide or thiosulfate ( ...
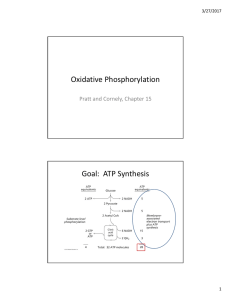
Oxidative Phosphorylation Goal: ATP Synthesis
... energy has been used to cause an energy conformation that favors ATP formation ...
... energy has been used to cause an energy conformation that favors ATP formation ...
Cellular Respiration
... molecule represents stored energy that can “fall” down the energy gradient with oxygen as the final acceptor) • Controlled release of energy • The ETC creates the H+ gradient ...
... molecule represents stored energy that can “fall” down the energy gradient with oxygen as the final acceptor) • Controlled release of energy • The ETC creates the H+ gradient ...
An Introduction to Metabolism
... First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed Second Law of Thermodynamics: energy transformation must make the universe more ...
... First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed Second Law of Thermodynamics: energy transformation must make the universe more ...
Chapter 8 Exam Review
... 7. The Electron Transport Chain is a series of carriers on the cristae of the mitochondria. True or false? 8. ________________ (which process?) starts with a molecule of glucose. 9. _________________(which process?) ends with 2, 2-carbon acetyl CoA molecules. 10. _________________(which process?) pr ...
... 7. The Electron Transport Chain is a series of carriers on the cristae of the mitochondria. True or false? 8. ________________ (which process?) starts with a molecule of glucose. 9. _________________(which process?) ends with 2, 2-carbon acetyl CoA molecules. 10. _________________(which process?) pr ...
AP Biology Cellular Respiration Notes 9.1
... on their next turn after another acetyl group is added. How many times does the Citric Acid cycle turn to completely oxidize one glucose molecule? 9.13 Describe the point at which glucose is completely oxidized during cellular respiration. ...
... on their next turn after another acetyl group is added. How many times does the Citric Acid cycle turn to completely oxidize one glucose molecule? 9.13 Describe the point at which glucose is completely oxidized during cellular respiration. ...
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration
... • Food chains were not very complex; few trophic levels. • Could support very few animals with such poor efficiency. ...
... • Food chains were not very complex; few trophic levels. • Could support very few animals with such poor efficiency. ...
Atomic Structure. Chemical Bonds.
... n the principal quantum number l the orbital quantum number ml the magnetic quantum number The fourth quantum number is ms spin magnetic quantum number. ...
... n the principal quantum number l the orbital quantum number ml the magnetic quantum number The fourth quantum number is ms spin magnetic quantum number. ...
The molecular machinery of Keilin`s respiratory chain
... of the exergonic electron-transfer reactions is not lost as heat, but is instead coupled to the generation of an electrochemical gradient of protons across the membrane in which they are located, which is used subsequently to drive the synthesis of ATP via the ATP synthases that are embedded in the ...
... of the exergonic electron-transfer reactions is not lost as heat, but is instead coupled to the generation of an electrochemical gradient of protons across the membrane in which they are located, which is used subsequently to drive the synthesis of ATP via the ATP synthases that are embedded in the ...
Solon City Schools
... • Same as any other titration. • the permanganate ion is used often because it is its +2 is colorless. own indicator. MnO4 is purple, Mn When reaction solution remains clear, MnO4 is gone. • Chromate ion is also useful, but color change, orangish yellow to green, is harder to detect. ...
... • Same as any other titration. • the permanganate ion is used often because it is its +2 is colorless. own indicator. MnO4 is purple, Mn When reaction solution remains clear, MnO4 is gone. • Chromate ion is also useful, but color change, orangish yellow to green, is harder to detect. ...
Enzyme Notes Activation Energy
... • Energy is the ability to cause matter to move or change. • All life processes are driven by energy • Where does all energy come from? ...
... • Energy is the ability to cause matter to move or change. • All life processes are driven by energy • Where does all energy come from? ...
Chapter 2
... • Same as any other titration. • the permanganate ion is used often because it is its +2 is colorless. own indicator. MnO4 is purple, Mn When reaction solution remains clear, MnO4 is gone. • Chromate ion is also useful, but color change, orangish yellow to green, is harder to detect. ...
... • Same as any other titration. • the permanganate ion is used often because it is its +2 is colorless. own indicator. MnO4 is purple, Mn When reaction solution remains clear, MnO4 is gone. • Chromate ion is also useful, but color change, orangish yellow to green, is harder to detect. ...
WORD
... • Activation Energy - The energy needed to ______________ __________ a reaction. • Catalyst – any compound that speeds up a reaction by _____________ the __________________ energy. • Enzymes are reaction specific! • Substrate – • Active site – • Enzymes always pick up another substrate when the acti ...
... • Activation Energy - The energy needed to ______________ __________ a reaction. • Catalyst – any compound that speeds up a reaction by _____________ the __________________ energy. • Enzymes are reaction specific! • Substrate – • Active site – • Enzymes always pick up another substrate when the acti ...
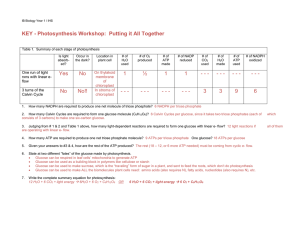
KEY - Photosynthesis Workshop: Putting it All Together
... consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
... consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
Capturing Solar Energy: Photosynthesis
... photosynthesis • Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis – Have a membrane system within internal space (stroma) – Arranged in disk-shaped sacks (thylakoids) • The thylakoids contain light-harvesting photosynthetic pigments & enzymes • Internal membranes define space (lumen) that is separate fr ...
... photosynthesis • Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis – Have a membrane system within internal space (stroma) – Arranged in disk-shaped sacks (thylakoids) • The thylakoids contain light-harvesting photosynthetic pigments & enzymes • Internal membranes define space (lumen) that is separate fr ...
Biochemistry I, Spring Term 2000 - Third Exam
... Both are involved with the control of metabolic pathways. The first describes inhibition directly by the product, the other describes inhibition by a metabolite, intermediate, or final product further down the pathway. ii) What are the similarities and differences between substrate level phosphoryla ...
... Both are involved with the control of metabolic pathways. The first describes inhibition directly by the product, the other describes inhibition by a metabolite, intermediate, or final product further down the pathway. ii) What are the similarities and differences between substrate level phosphoryla ...
Cellular respiration
... through their roots. 3. The stomata allows water into the leaves. 4. The guard cells open and close the stomata at the most opportune times of day for the plant. 5. Plants produce glucose during photosynthesis. ...
... through their roots. 3. The stomata allows water into the leaves. 4. The guard cells open and close the stomata at the most opportune times of day for the plant. 5. Plants produce glucose during photosynthesis. ...
Enzymes & Photosynthesis
... NADP+ Reductase this enzyme reduces NADP+ into NADPH. • Redox Reactions- 2 molecules exchanging e- ...
... NADP+ Reductase this enzyme reduces NADP+ into NADPH. • Redox Reactions- 2 molecules exchanging e- ...
Cell Respiration
... All of the reactions of glucose oxidation that follow glycolysis involving the transfer of electrons to their final acceptor, oxygen, take place in eukaryotic cells in the ___________. ...
... All of the reactions of glucose oxidation that follow glycolysis involving the transfer of electrons to their final acceptor, oxygen, take place in eukaryotic cells in the ___________. ...