Unit A Review Questions
... Unit A Review Questions 1. a. solute b. solvent c. solution 2. a. The two electrolyte solutions are II and III. b. The two non-electrolyte solutions are I and IV. 3. Although answers may vary, each response should make reference to the associations that form between the ions in the solute and water. ...
... Unit A Review Questions 1. a. solute b. solvent c. solution 2. a. The two electrolyte solutions are II and III. b. The two non-electrolyte solutions are I and IV. 3. Although answers may vary, each response should make reference to the associations that form between the ions in the solute and water. ...
photosynthesis in bacteria
... The thylakoid membranes are functionally distinct from the cell membrane: the hitter never has phycobilisome attached to it. Components of the Photosynthetic electron transport system (e.g. ferredoxin, plastocyanin and cytochrome f) have been located in the thylakoid membrane. The only chlorophyll f ...
... The thylakoid membranes are functionally distinct from the cell membrane: the hitter never has phycobilisome attached to it. Components of the Photosynthetic electron transport system (e.g. ferredoxin, plastocyanin and cytochrome f) have been located in the thylakoid membrane. The only chlorophyll f ...
Nerve activates contraction
... 1. The formation of ATP is endergonic and is coupled to the creation of a proton gradient. 2. The energy of an exergonic reaction can be used to drive an endergonic reaction EX: Step 3 of glycolysis yields +3.0 kcal/mol of free energy; Step 4 has a free energy of -9.0. Together = -6.0, so together t ...
... 1. The formation of ATP is endergonic and is coupled to the creation of a proton gradient. 2. The energy of an exergonic reaction can be used to drive an endergonic reaction EX: Step 3 of glycolysis yields +3.0 kcal/mol of free energy; Step 4 has a free energy of -9.0. Together = -6.0, so together t ...
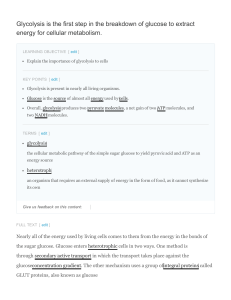
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to
... pyruvate and produces ATP and NADH for the cell to use for energy. Overall, the process of glycolysis produces a net gain of two pyruvate molecules, two ATP molecules, and two NADH molecules for the cell to use for energy. Following the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, the glycolytic pathway is li ...
... pyruvate and produces ATP and NADH for the cell to use for energy. Overall, the process of glycolysis produces a net gain of two pyruvate molecules, two ATP molecules, and two NADH molecules for the cell to use for energy. Following the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, the glycolytic pathway is li ...
ch10.2012 - Issaquah Connect
... • Van Niel disagreed & used sulfurous bacteria to support his idea: CO2 + 2H2S [CH2O] + 2S • The O in the sugar must be coming from CO2 or an analagous source. • 2 expts. radioctively label O in CO2 and then in a 2nd expt. Label the O in H2O. Confirmed! Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. pub ...
... • Van Niel disagreed & used sulfurous bacteria to support his idea: CO2 + 2H2S [CH2O] + 2S • The O in the sugar must be coming from CO2 or an analagous source. • 2 expts. radioctively label O in CO2 and then in a 2nd expt. Label the O in H2O. Confirmed! Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. pub ...
cell respiration
... energy found in NADH and FADH2 to make more ATP. This involves the cristae. There are electron transport chains that are used. The electrons from the NADH and FADH2 are used to move on the electron transport chain. As the electrons move down the electron transport chain, H+ ions are pumped across th ...
... energy found in NADH and FADH2 to make more ATP. This involves the cristae. There are electron transport chains that are used. The electrons from the NADH and FADH2 are used to move on the electron transport chain. As the electrons move down the electron transport chain, H+ ions are pumped across th ...
BI0 120 cell and tissues
... 13. What acronym identifies a dinucleotide, intermediate electron carrier that is only active in the Krebs cycle? A. ATP. B. FAD. C. G3P. D. NAD+. E. CoA. 14. Which statement is TRUE for an electron transport system? A. Reduced oxygen feeds electrons to the system. B. The final electron acceptor is ...
... 13. What acronym identifies a dinucleotide, intermediate electron carrier that is only active in the Krebs cycle? A. ATP. B. FAD. C. G3P. D. NAD+. E. CoA. 14. Which statement is TRUE for an electron transport system? A. Reduced oxygen feeds electrons to the system. B. The final electron acceptor is ...
Chapter 19
... • a-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: inhibited by ATP, NADH, and succinyl CoA; activated by ADP and NAD+. ...
... • a-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: inhibited by ATP, NADH, and succinyl CoA; activated by ADP and NAD+. ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... In order to fix carbon, the enzyme Rubisco attaches carbon dioxide to RuDP which forms an unstable six carbon sugar. This unstable sugar immediately breaks down into two PGA molecules. In this cycle, only one PGA is shown proceeding through. The reason is simplicity which will be explained later. P ...
... In order to fix carbon, the enzyme Rubisco attaches carbon dioxide to RuDP which forms an unstable six carbon sugar. This unstable sugar immediately breaks down into two PGA molecules. In this cycle, only one PGA is shown proceeding through. The reason is simplicity which will be explained later. P ...
Ecology
... a process that uses energy from inorganic compounds to produce carbohydrates. Chemosynthesis is important in bacteria involved in nutrient cycling, and in some ecosystems such as ocean vent communities. ...
... a process that uses energy from inorganic compounds to produce carbohydrates. Chemosynthesis is important in bacteria involved in nutrient cycling, and in some ecosystems such as ocean vent communities. ...
Name_____________________________________ Chemistry
... b. energy must be absorbed. c. radiation must be emitted. d. the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy level. ____ 31. If electrons in an atom have the lowest possible energies, the atom is in the a. ground state. c. excited state. b. inert state. d. radiation-emitting stat ...
... b. energy must be absorbed. c. radiation must be emitted. d. the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy level. ____ 31. If electrons in an atom have the lowest possible energies, the atom is in the a. ground state. c. excited state. b. inert state. d. radiation-emitting stat ...
20121016083538
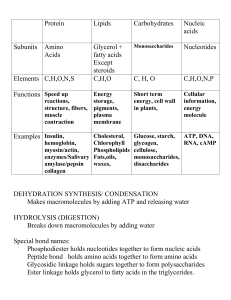
... fuels for energy (ATP) raw materials for building more molecules carbohydrates, fats, proteins, nucleic acids ...
... fuels for energy (ATP) raw materials for building more molecules carbohydrates, fats, proteins, nucleic acids ...
Ch 2 Review Sheet - Phillips Scientific Methods
... sterilize products and kill cancer cells. F. ...
... sterilize products and kill cancer cells. F. ...
Document
... a. number of electrons b. number of valence electrons c. number of protons d. number of neutrons _____ 16. Which group on the periodic table contains elements that do not normally form chemical bonds? a. Group 2 c. Group 10 b. Group 6 d. Group 18 17. The outermost energy level of an atom is consider ...
... a. number of electrons b. number of valence electrons c. number of protons d. number of neutrons _____ 16. Which group on the periodic table contains elements that do not normally form chemical bonds? a. Group 2 c. Group 10 b. Group 6 d. Group 18 17. The outermost energy level of an atom is consider ...
chapter 6 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... 4.The production of NADH by glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, instead of just the direct production of ATP, can get confusing for students. Help students understand that NADH molecules have energy “value,” to be “cashed in” by the electron transport chain. The NADH can therefore be thought of as ...
... 4.The production of NADH by glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, instead of just the direct production of ATP, can get confusing for students. Help students understand that NADH molecules have energy “value,” to be “cashed in” by the electron transport chain. The NADH can therefore be thought of as ...
Metabolism Review - Local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Enzyme A has an optimum near human body temp and would be nonfunctional at higher temps where these bacteria are found. Enzyme B has an optimum that would allow it to function at higher temperatures Essential knowledge 4.B.1: Interactions between molecules affect their structure and function. d. The ...
... Enzyme A has an optimum near human body temp and would be nonfunctional at higher temps where these bacteria are found. Enzyme B has an optimum that would allow it to function at higher temperatures Essential knowledge 4.B.1: Interactions between molecules affect their structure and function. d. The ...
Evolution V: Macroevolution & the Origin of Life
... few fossils of intermediate stages are found, since they only occur in short bursts of evolutionary time ...
... few fossils of intermediate stages are found, since they only occur in short bursts of evolutionary time ...
BIOLOGY COMPETITION REVIEW QUESTIONS PRACTICE EXAM
... 30. Which statement about ATP synthesis is FALSE? a. ATP is synthesized only in chloroplasts and mitochondria. b. ATP synthesis in the chloroplast occurs in the thylakoid region of this organelle. c. Proton motive force (proton gradient) drives the formation of ATP in mitochondria. d. ATP synthases ...
... 30. Which statement about ATP synthesis is FALSE? a. ATP is synthesized only in chloroplasts and mitochondria. b. ATP synthesis in the chloroplast occurs in the thylakoid region of this organelle. c. Proton motive force (proton gradient) drives the formation of ATP in mitochondria. d. ATP synthases ...
File
... • The structure of the ATP synthase: – The F1 particle is the catalytic subunit, and contains three catalytic sites for ATP synthesis. – The F0 particle attaches to the F1 and is embedded in the inner membrane. – The F0 base contains a channel through which protons are conducted from the intermembra ...
... • The structure of the ATP synthase: – The F1 particle is the catalytic subunit, and contains three catalytic sites for ATP synthesis. – The F0 particle attaches to the F1 and is embedded in the inner membrane. – The F0 base contains a channel through which protons are conducted from the intermembra ...
GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS – I: Brief Review of: AEROBIC
... • When blood flow is inadequate: Example: • Heavy Exercise of Skeletal Muscle, or • An Attack of Angina Pectoris in case of the Heart, • The H+ ions cannot escape from the cells fast enough, • The need for ATP within the cells, because of lack of Oxygen, may partially over-ride the Allosteric Inhib ...
... • When blood flow is inadequate: Example: • Heavy Exercise of Skeletal Muscle, or • An Attack of Angina Pectoris in case of the Heart, • The H+ ions cannot escape from the cells fast enough, • The need for ATP within the cells, because of lack of Oxygen, may partially over-ride the Allosteric Inhib ...
Topic 3: Periodicity
... increased nuclear charge makes it more difficult to remove a third electron). In the higher oxidation states the elements usually not exist as a free metal ions, but covalently bonded or as a oxyanions (MnO4-). ...
... increased nuclear charge makes it more difficult to remove a third electron). In the higher oxidation states the elements usually not exist as a free metal ions, but covalently bonded or as a oxyanions (MnO4-). ...
Photosynthesis chapt07
... Excited electrons enter an ETC to make ATP and NADPH. NADPH has a the same function and similar structure to NADH - NADP+ is reduced to NADPH ...
... Excited electrons enter an ETC to make ATP and NADPH. NADPH has a the same function and similar structure to NADH - NADP+ is reduced to NADPH ...
Photo Notes - Intro
... Occurs in a cycle, called the Calvin Cycle, due to the series of chemical reactions starting and ending with the same molecule. (draw picture) All steps are enzyme driven Calvin Cycle takes place in a liquid filled area of the chloroplasts called the stoma It takes 6 “turns” of the cycle to ...
... Occurs in a cycle, called the Calvin Cycle, due to the series of chemical reactions starting and ending with the same molecule. (draw picture) All steps are enzyme driven Calvin Cycle takes place in a liquid filled area of the chloroplasts called the stoma It takes 6 “turns” of the cycle to ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... For Questions 9–14, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words. 9. In eukaryotes, the electron transport chain is composed of a series of electron carriers located in the INNER MEMBRANE of the mitochondrion. 10. In prokaryotes, the electron transport chain is in the CELL MEMBRANE. ...
... For Questions 9–14, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words. 9. In eukaryotes, the electron transport chain is composed of a series of electron carriers located in the INNER MEMBRANE of the mitochondrion. 10. In prokaryotes, the electron transport chain is in the CELL MEMBRANE. ...