Document
... • Uses: as fuels (e.g. Kerosine), solvents (e.g. hexane), chemical feedstock • Source: Primarily from the Crude oil which is a complicated mixture of many compounds. Some long hydrocarbons are broken up to produce smaller, often more useful hydrocarbons. ...
... • Uses: as fuels (e.g. Kerosine), solvents (e.g. hexane), chemical feedstock • Source: Primarily from the Crude oil which is a complicated mixture of many compounds. Some long hydrocarbons are broken up to produce smaller, often more useful hydrocarbons. ...
Wizard Test Maker
... (2) propanal (4) water 6856 Which Group 14 element is classified as a metal? (1) carbon (3) silicon (2) germanium (4) tin 6763 An element that has a low first ionization energy and good conductivity of heat and electricity is classified as a (3) nonmetal (1) metal (2) metalloid (4) noble gas 6709 A ...
... (2) propanal (4) water 6856 Which Group 14 element is classified as a metal? (1) carbon (3) silicon (2) germanium (4) tin 6763 An element that has a low first ionization energy and good conductivity of heat and electricity is classified as a (3) nonmetal (1) metal (2) metalloid (4) noble gas 6709 A ...
proline catalyzed direct asymmetric aldol and mannich reactions
... revealed no appreciably better catalysts. Direct proline catalysis was considered to be particularly favorable because, as the authors noted, the reactions have several advantages over normal enolate Copyright © 2005 by Mirth Hoyt ...
... revealed no appreciably better catalysts. Direct proline catalysis was considered to be particularly favorable because, as the authors noted, the reactions have several advantages over normal enolate Copyright © 2005 by Mirth Hoyt ...
Unit_4_Notes_
... found using t½ = 0.693 / k o Half-life of a second-order reaction can be found using t½ = 1 / k[A]0 14.5 Temperature and Rate Temperature causes the rate of a chemical reaction to increase because the temperature increase causes the rate constant to increase The collision model, which is based o ...
... found using t½ = 0.693 / k o Half-life of a second-order reaction can be found using t½ = 1 / k[A]0 14.5 Temperature and Rate Temperature causes the rate of a chemical reaction to increase because the temperature increase causes the rate constant to increase The collision model, which is based o ...
Chemical Energy
... The energy released in a chemical reaction raises the internal energy, E, and does work under constant pressure at the expense of energy stored in compounds. Thus, ...
... The energy released in a chemical reaction raises the internal energy, E, and does work under constant pressure at the expense of energy stored in compounds. Thus, ...
Chapter 8 Lecture
... Sulfonates are therefore excellent leaving groups. Hydroxide (HO-) is a very poor leaving group so transforming an alcohol into a sulfonate generates a good leaving group. ...
... Sulfonates are therefore excellent leaving groups. Hydroxide (HO-) is a very poor leaving group so transforming an alcohol into a sulfonate generates a good leaving group. ...
Understanding Electronic WaveFunctions
... experiments and theory are easier than is possible with extended solids since there are no finite size effects or pseudo-potentials to worry about. Let us try to generalize the Jastrow pair wavefunction of Eq.(5) to a molecule. The first problem is that the orbitals are not determined by translation ...
... experiments and theory are easier than is possible with extended solids since there are no finite size effects or pseudo-potentials to worry about. Let us try to generalize the Jastrow pair wavefunction of Eq.(5) to a molecule. The first problem is that the orbitals are not determined by translation ...
- dragicaminic.info
... Push-pull alkenes, consisting of one or two electron-donating groups (EDG) at the terminus of the C=C bond and one or two electron-withdrawing groups (EWG) at the other terminus, have been widely studied on the account of their low rotational barrier around the C-C double bond. This is attributed to ...
... Push-pull alkenes, consisting of one or two electron-donating groups (EDG) at the terminus of the C=C bond and one or two electron-withdrawing groups (EWG) at the other terminus, have been widely studied on the account of their low rotational barrier around the C-C double bond. This is attributed to ...
Topic Selection Menu - Pennsylvania State University
... Steric Factors in Nucleophilic Substitutions Influence of steric factors involving -C on SN1 vs SN2 Primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl halides Factors promoting backside attack vs carbocation formation carbon branching and rotation of branched substituents Steric hindrance due to nucleophile ...
... Steric Factors in Nucleophilic Substitutions Influence of steric factors involving -C on SN1 vs SN2 Primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl halides Factors promoting backside attack vs carbocation formation carbon branching and rotation of branched substituents Steric hindrance due to nucleophile ...
Topic Selection Menu - Pennsylvania State University
... – Influence of steric factors involving -C on SN1 vs SN2 – Primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl halides – Factors promoting backside attack vs carbocation formation – carbon branching and rotation of branched substituents – Steric hindrance due to nucleophile ...
... – Influence of steric factors involving -C on SN1 vs SN2 – Primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl halides – Factors promoting backside attack vs carbocation formation – carbon branching and rotation of branched substituents – Steric hindrance due to nucleophile ...
Organomet-2
... The bridging carbonyl has a (CO) stretch in the infra-red (IR) spectrum ~ 1800 cm-1 This is much lower than terminal carbonyls and more similar to an organic ketone R2C=O which has a (CO) stretch ~ 1750 cm-1 In solution Co2(CO)8 also has a structure with only terminal carbonyls, i.e. four per Co a ...
... The bridging carbonyl has a (CO) stretch in the infra-red (IR) spectrum ~ 1800 cm-1 This is much lower than terminal carbonyls and more similar to an organic ketone R2C=O which has a (CO) stretch ~ 1750 cm-1 In solution Co2(CO)8 also has a structure with only terminal carbonyls, i.e. four per Co a ...
MERIDIAN PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT
... how the nucleus changes during these reactions, and compare the resulting radiation with regard to penetrating ability. (DOK 1) ...
... how the nucleus changes during these reactions, and compare the resulting radiation with regard to penetrating ability. (DOK 1) ...
1 Inorganic Chemistry Chem 418 Syllabus, Winter 2011 Instructor
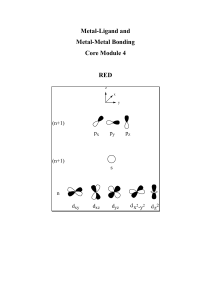
... 1. Understand the structure, bonding and chemistry (including reactions and mechanisms) of coordination compounds. 2. Understand the structure, bonding and chemistry (including reactions and catalysis) of organometallic complexes. 3. Understand the structure and bonding of cluster complexes. 4. Unde ...
... 1. Understand the structure, bonding and chemistry (including reactions and mechanisms) of coordination compounds. 2. Understand the structure, bonding and chemistry (including reactions and catalysis) of organometallic complexes. 3. Understand the structure and bonding of cluster complexes. 4. Unde ...
Thermochemistry1
... The enthalpy of a given chemical reaction is constant, regardless of the reaction happening in one step or many steps. If a chemical equation can be written as the sum of several other chemical equations (steps), the enthalpy change of the first chemical equation equals the sum of the enthalpy chang ...
... The enthalpy of a given chemical reaction is constant, regardless of the reaction happening in one step or many steps. If a chemical equation can be written as the sum of several other chemical equations (steps), the enthalpy change of the first chemical equation equals the sum of the enthalpy chang ...