Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing a Pyridyl-Supported Pyrazolyl
... of the imidazole moiety in 5. It is noteworthy that the intermediate 5 did not react with 1-iodoheptane to form N-nheptylimidazoliun iodide. In a fashion similar to the preparation of the 16-electron ruthenium(II) complex of a pyridyl-pyrazolylimidazolyl ligand,10 complex 7 was successfully transfor ...
... of the imidazole moiety in 5. It is noteworthy that the intermediate 5 did not react with 1-iodoheptane to form N-nheptylimidazoliun iodide. In a fashion similar to the preparation of the 16-electron ruthenium(II) complex of a pyridyl-pyrazolylimidazolyl ligand,10 complex 7 was successfully transfor ...
Standard - Santee Education Complex
... There are two main types of bonding discussed here. A COVALENT BOND results when two atoms "share" valence electrons between them. An IONIC BOND occurs when one atom gains a valence electron from a different atom, forming a negative ion (ANION) and a positive ion (CATION), respectively. These opposi ...
... There are two main types of bonding discussed here. A COVALENT BOND results when two atoms "share" valence electrons between them. An IONIC BOND occurs when one atom gains a valence electron from a different atom, forming a negative ion (ANION) and a positive ion (CATION), respectively. These opposi ...
PDF Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics
... 2. They must collide with enough energy to overcome an energy barrier to reaction called the activation energy. 3. They must collide in an orientation that allows the necessary bond‐breaking and forming needed to transform the reactants to the products. ...
... 2. They must collide with enough energy to overcome an energy barrier to reaction called the activation energy. 3. They must collide in an orientation that allows the necessary bond‐breaking and forming needed to transform the reactants to the products. ...
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
... • Working backward, the alkene precursor can be found by removing the oxygen from each product and joining the two carbon atoms to form a double bond ...
... • Working backward, the alkene precursor can be found by removing the oxygen from each product and joining the two carbon atoms to form a double bond ...
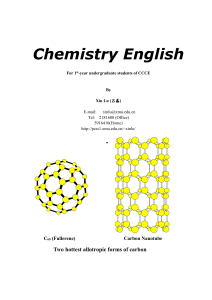
Chemistry English
... Atomic theory: if the matter were divided a sufficient number of times, it could eventually be reduced to the indivisible, indestructible particles called atom. The atomic theory was presented by the British chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) in the early 1800s. It is one of the greatest advances in th ...
... Atomic theory: if the matter were divided a sufficient number of times, it could eventually be reduced to the indivisible, indestructible particles called atom. The atomic theory was presented by the British chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) in the early 1800s. It is one of the greatest advances in th ...
PPT - Gmu
... adjacent Carbon atoms that produces a stabilizing affect on the Carbocation (Hyperconjugation). Electron density shifts toward the positive charge The C-H & C-C orbitals adjacent to the unfilled p orbital of the Carbocation are filled. Sharing of the electron density Delocalizes the positive c ...
... adjacent Carbon atoms that produces a stabilizing affect on the Carbocation (Hyperconjugation). Electron density shifts toward the positive charge The C-H & C-C orbitals adjacent to the unfilled p orbital of the Carbocation are filled. Sharing of the electron density Delocalizes the positive c ...
chem equation Pkt Student2
... 3) Write a balanced chemical equation by adding_____________________, NOT subscripts (this will require trial and error, the following guidelines may be helpful) a) balance the different types of atoms ________________ b) first, balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only _ ...
... 3) Write a balanced chemical equation by adding_____________________, NOT subscripts (this will require trial and error, the following guidelines may be helpful) a) balance the different types of atoms ________________ b) first, balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only _ ...
Today Kinetics How fast are reactions? What are the rates?
... Compares Free energy of reactants and products This is the ideal case assuming everything can find its lowest energy state (time is irrelevant) ...
... Compares Free energy of reactants and products This is the ideal case assuming everything can find its lowest energy state (time is irrelevant) ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... indicated that it is 92. 23% C and 7.82% H. The mass spectrum indicated the molar mass is 78 g/mol. What is the molecular formula of this unknown compound? ...
... indicated that it is 92. 23% C and 7.82% H. The mass spectrum indicated the molar mass is 78 g/mol. What is the molecular formula of this unknown compound? ...
Prelab Assignment: The lodination of Acetone
... Repeat the experiment, using as a reference the reacted solution instead of distilled water. The amount of time required in the two runs should agree within about 20 seconds. The rate of the reaction equals the initial concentration of 1, in the reaction mixture divided by the elapsed time. Since t ...
... Repeat the experiment, using as a reference the reacted solution instead of distilled water. The amount of time required in the two runs should agree within about 20 seconds. The rate of the reaction equals the initial concentration of 1, in the reaction mixture divided by the elapsed time. Since t ...
Electrochemical Investigations of W(CO) (L) and W(CO) (L) Complexes:
... Complexes such as that shown above, in which the bridging ligand is 4,4'-bpy, will show redox-tunable properties only if the non-emissive fragment can undergo one or more chemically reversible electrontransfer processes. We therefore undertook a systematic study of the oxidative electrochemistry of ...
... Complexes such as that shown above, in which the bridging ligand is 4,4'-bpy, will show redox-tunable properties only if the non-emissive fragment can undergo one or more chemically reversible electrontransfer processes. We therefore undertook a systematic study of the oxidative electrochemistry of ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... something is. Proteins denature if the environment is too acid or too basic (3) ENZYME AND SUBSTRATE CONCENTRATION The rate of a chemical reaction is affected by the total number of enzymes as well as the concentration of substrates. (4) INHIBITORS: Inhibitors either slow down or stop the activity o ...
... something is. Proteins denature if the environment is too acid or too basic (3) ENZYME AND SUBSTRATE CONCENTRATION The rate of a chemical reaction is affected by the total number of enzymes as well as the concentration of substrates. (4) INHIBITORS: Inhibitors either slow down or stop the activity o ...
Chapter 14
... 61) The rate constant for a second-order reaction is 0.13 M-1s-1. If the initial concentration of reactant is 0.26 mol/L, it takes __________ s for the concentration to decrease to 0.11 mol/L. A) 0.017 B) 0.68 C) 9.1 D) 40. E) 5.2 Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium 1) At equilibrium, __________. A) all ...
... 61) The rate constant for a second-order reaction is 0.13 M-1s-1. If the initial concentration of reactant is 0.26 mol/L, it takes __________ s for the concentration to decrease to 0.11 mol/L. A) 0.017 B) 0.68 C) 9.1 D) 40. E) 5.2 Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium 1) At equilibrium, __________. A) all ...
View PDF
... ____ 17. In the reaction A + B → C + D, if the quantity of B is insufficient to react with all of A, a. A is the limiting reactant. c. there is no limiting reactant. b. B is the limiting reactant. d. no product can be formed. ____ 18. What is the maximum possible amount of product obtained in a che ...
... ____ 17. In the reaction A + B → C + D, if the quantity of B is insufficient to react with all of A, a. A is the limiting reactant. c. there is no limiting reactant. b. B is the limiting reactant. d. no product can be formed. ____ 18. What is the maximum possible amount of product obtained in a che ...