Recrystallization: A Purification Technique
... used if there were a higher product to solvent ratio. When heated, the product dissolved in the water and reformed crystals with cooling. However, when the product was heated in hexanes, the product did not fully dissolve; therefore, the hexanes were also eliminated. A mass of the product was obtain ...
... used if there were a higher product to solvent ratio. When heated, the product dissolved in the water and reformed crystals with cooling. However, when the product was heated in hexanes, the product did not fully dissolve; therefore, the hexanes were also eliminated. A mass of the product was obtain ...
CH2C05/ PH2C05/ PO2C05 COORDINATION CHEMISTRY
... in allyl group. 16. Write a note on HFSCF Theory. 17. Draw a correlation diagram for the orbitals of a homonuclear diatomic molecule. How does it differ from that of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule? 18. Calculate the SALCs corresponding to the stretching vibrations of NO3- (D3h). 19. Describe any ...
... in allyl group. 16. Write a note on HFSCF Theory. 17. Draw a correlation diagram for the orbitals of a homonuclear diatomic molecule. How does it differ from that of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule? 18. Calculate the SALCs corresponding to the stretching vibrations of NO3- (D3h). 19. Describe any ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... The possession or use of any communications device is strictly prohibited when taking this examination. If you have or use any communications device, no matter how briefly, your examination will be invalidated and no score will be calculated for you. This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Us ...
... The possession or use of any communications device is strictly prohibited when taking this examination. If you have or use any communications device, no matter how briefly, your examination will be invalidated and no score will be calculated for you. This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Us ...
Redox Introduction
... Type I: ions or molecules react with no apparent change in the electronic structure of the particles. Type II: ions or atoms undergo changes of electronic structure. Electrons may be transferred from one particle to another. On the other hand, the sharing of the electrons may be somewhat changed. Ty ...
... Type I: ions or molecules react with no apparent change in the electronic structure of the particles. Type II: ions or atoms undergo changes of electronic structure. Electrons may be transferred from one particle to another. On the other hand, the sharing of the electrons may be somewhat changed. Ty ...
Physical Chemistry 1.pdf
... often place more emphasis on speeding up the rate of a reaction than on its percentage yield. Organic chemists use kinetic studies to determine the mechanisms of reactions and to tell how fast products will be formed. ...
... often place more emphasis on speeding up the rate of a reaction than on its percentage yield. Organic chemists use kinetic studies to determine the mechanisms of reactions and to tell how fast products will be formed. ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... To calculate how much oxygen is required to make 144 grams of water, begin with a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 2H2 + O2 2H2O • Determine how many moles of water you are trying to ...
... To calculate how much oxygen is required to make 144 grams of water, begin with a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 2H2 + O2 2H2O • Determine how many moles of water you are trying to ...
Slide 1
... To calculate how much oxygen is required to make 144 grams of water, begin with a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 2H2 + O2 2H2O • Determine how many moles of water you are trying to ...
... To calculate how much oxygen is required to make 144 grams of water, begin with a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 2H2 + O2 2H2O • Determine how many moles of water you are trying to ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... To calculate how much oxygen is required to make 144 grams of water, begin with a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 2H2 + O2 2H2O • Determine how many moles of water you are trying to ...
... To calculate how much oxygen is required to make 144 grams of water, begin with a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 2H2 + O2 2H2O • Determine how many moles of water you are trying to ...
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
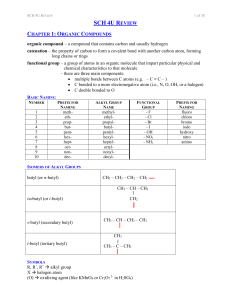
... F, Cl, Br, I fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo CH2CH2CH3 propyl CH2CH3 ethyl CH3 methyl ...
... F, Cl, Br, I fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo CH2CH2CH3 propyl CH2CH3 ethyl CH3 methyl ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... To calculate how much oxygen is required to make 144 grams of water, begin with a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 2H2 + O2 2H2O • Determine how many moles of water you are trying to ...
... To calculate how much oxygen is required to make 144 grams of water, begin with a balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 2H2 + O2 2H2O • Determine how many moles of water you are trying to ...
Redox
... definitions can only be used when a chemical reaction involves hydrogen and oxygen, and therefore their usefulness is limited. ...
... definitions can only be used when a chemical reaction involves hydrogen and oxygen, and therefore their usefulness is limited. ...
3C95 Chemistry 12 2015-2016 (Lockwood)
... 5. predict the effect (or lack of effect) on the value of Keq of changes in the following factors: temperature, pressure, concentration, surface area, and catalyst Page 6 of 16 ...
... 5. predict the effect (or lack of effect) on the value of Keq of changes in the following factors: temperature, pressure, concentration, surface area, and catalyst Page 6 of 16 ...
Document
... • Two Alkyl Groups of Alcohol Correspond to Grignard Reagent • Grignard Reactions Quite Useful in Wide Range of Alcohol Syntheses (w/ Varying Degrees of Substitution) ...
... • Two Alkyl Groups of Alcohol Correspond to Grignard Reagent • Grignard Reactions Quite Useful in Wide Range of Alcohol Syntheses (w/ Varying Degrees of Substitution) ...
Skill Practice 1
... 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allows you to tell? 4. Assuming that the temperature scales for both phase diagrams are the same, which c ...
... 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allows you to tell? 4. Assuming that the temperature scales for both phase diagrams are the same, which c ...