Chemical Equilibrium - Request a Spot account
... making cheese sandwiches and breaking them back down into bread and cheese. 2 slices of bread + 1 slice of cheese → ← 1 cheese sandwich Many chemical systems establish chemical equilibrium in a similar manner: reactants create products which in turn create reactants. On a macroscopic scale, it appea ...
... making cheese sandwiches and breaking them back down into bread and cheese. 2 slices of bread + 1 slice of cheese → ← 1 cheese sandwich Many chemical systems establish chemical equilibrium in a similar manner: reactants create products which in turn create reactants. On a macroscopic scale, it appea ...
Chapter Seven - U of L Class Index
... Carbocation rearrangments are often promoted by the presence of Lewis Acids. In this case, the intermediates are said to be “carbocation-like” if not carbocations. ...
... Carbocation rearrangments are often promoted by the presence of Lewis Acids. In this case, the intermediates are said to be “carbocation-like” if not carbocations. ...
Band Gap Extraction from Individual Two
... the redoxactive sites by photolabeling.19 They also showed that high angle annular dark field−scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) is an excellent tool for characterizing the nanosheets loaded with metal and metal oxide nanoparticles.19 In addition, they used the sheets as an electr ...
... the redoxactive sites by photolabeling.19 They also showed that high angle annular dark field−scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) is an excellent tool for characterizing the nanosheets loaded with metal and metal oxide nanoparticles.19 In addition, they used the sheets as an electr ...
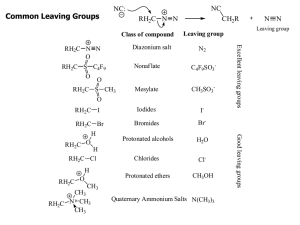
Common Leaving Groups
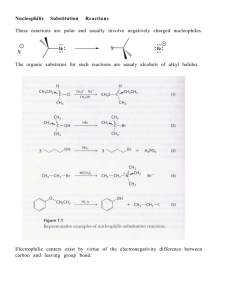
... atom. •A substrate that can form a relatively stable carbocation. The difference between E1 and SN1 reactions is in the type species which reacts with the substrate. E1 reactions are favoured with: •Bases that are poor nucleophiles (good nucleophiles will favour substitution reactions). ...
... atom. •A substrate that can form a relatively stable carbocation. The difference between E1 and SN1 reactions is in the type species which reacts with the substrate. E1 reactions are favoured with: •Bases that are poor nucleophiles (good nucleophiles will favour substitution reactions). ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions - An Introduction to Chemistry
... the electrons and be reduced. In other words, oxidation (loss of electrons) must be accompanied by reduction (gain of electrons). In the reaction that forms ZnO from Zn and O2, the uncharged zinc atoms cannot easily lose electrons and be oxidized unless something such as oxygen is there to gain the ...
... the electrons and be reduced. In other words, oxidation (loss of electrons) must be accompanied by reduction (gain of electrons). In the reaction that forms ZnO from Zn and O2, the uncharged zinc atoms cannot easily lose electrons and be oxidized unless something such as oxygen is there to gain the ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Analyze: We are given several chemical formulas and asked to classify each substance as a strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or nonelectrolyte. Plan: The approach we take is outlined in Table 4.3. We can predict whether a substance is ionic or molecular, based on its composition. As we saw in Sec ...
... Analyze: We are given several chemical formulas and asked to classify each substance as a strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, or nonelectrolyte. Plan: The approach we take is outlined in Table 4.3. We can predict whether a substance is ionic or molecular, based on its composition. As we saw in Sec ...
Chapter 14 Notes
... • Because of the polarity of the C=O group, these groups can interact, but the attraction is not as strong as hydrogen ...
... • Because of the polarity of the C=O group, these groups can interact, but the attraction is not as strong as hydrogen ...
Stoichiometry, Lab Basics, Reactions
... CaCl2. What is the minimum number of moles of AgNO3 that must be added to the solution in order to precipitate all of the Cl- as AgCl (s)? (Assume all AgCl is insoluble.) A) 0.10 mol B) 0.20 mol C) 0.30 mol D) 0.40 mol E) 0.60 mol ____ 21. A 40.0 mL sample of 0.25 M KOH is added to 60.0 mL of 0.15 M ...
... CaCl2. What is the minimum number of moles of AgNO3 that must be added to the solution in order to precipitate all of the Cl- as AgCl (s)? (Assume all AgCl is insoluble.) A) 0.10 mol B) 0.20 mol C) 0.30 mol D) 0.40 mol E) 0.60 mol ____ 21. A 40.0 mL sample of 0.25 M KOH is added to 60.0 mL of 0.15 M ...
幻灯片 1 - Sun Yat-sen University
... Classification of Alcohols • Primary Alcohols: OH is on a C that is bonded to at least two H's. That is, the OH is on an end carbon. Examples: CH3OH, CH3CH2OH • Secondary Alcohols: OH is on a C that is bonded to one H. That is, the C is bonded to two other carbons. Examples: CH3CH(OH)CH3 isopropano ...
... Classification of Alcohols • Primary Alcohols: OH is on a C that is bonded to at least two H's. That is, the OH is on an end carbon. Examples: CH3OH, CH3CH2OH • Secondary Alcohols: OH is on a C that is bonded to one H. That is, the C is bonded to two other carbons. Examples: CH3CH(OH)CH3 isopropano ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... The next step in writing a correct chemical equation is to replace the names of the reactants and products with appropriate symbols and formulas. Methane is a molecular compound composed of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. Its chemical formula is CH4. Recall that oxygen exists in nature as d ...
... The next step in writing a correct chemical equation is to replace the names of the reactants and products with appropriate symbols and formulas. Methane is a molecular compound composed of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. Its chemical formula is CH4. Recall that oxygen exists in nature as d ...
Chapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides
... elimination products without any by-products formed from an SN1 reaction. • Clean elimination takes place because the reaction mixture contains no good nucleophile to react with the intermediate carbocation, so no competing SN1 reaction occurs. • This makes the E1 dehydration of alcohols much more s ...
... elimination products without any by-products formed from an SN1 reaction. • Clean elimination takes place because the reaction mixture contains no good nucleophile to react with the intermediate carbocation, so no competing SN1 reaction occurs. • This makes the E1 dehydration of alcohols much more s ...
1. Define the following term: system. A) The part of the universe that
... 19. Define the following term: endothermic process. A) The study of heat change in chemical reactions B) The process of transferring thermal energy from a system to the surroundings. C) The process of transferring thermal energy from the surroundings to a system. D) The transfer of thermal energy b ...
... 19. Define the following term: endothermic process. A) The study of heat change in chemical reactions B) The process of transferring thermal energy from a system to the surroundings. C) The process of transferring thermal energy from the surroundings to a system. D) The transfer of thermal energy b ...