Unusual deprotonated alkynyl hydrogen bonding in metal
... Understanding and controlling supported molecular architectures is of fundamental importance for fabricating molecular device elements through the bottom-up approach.1−7 Hydrogen bonding, which provides selectivity and directionality combined with error corrective processes, has been successfully em ...
... Understanding and controlling supported molecular architectures is of fundamental importance for fabricating molecular device elements through the bottom-up approach.1−7 Hydrogen bonding, which provides selectivity and directionality combined with error corrective processes, has been successfully em ...
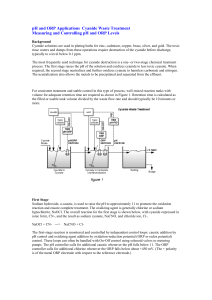
pH and ORP Applications Cyanide Waste Treatment
... oxidizing agent. In this application, chlorine accepts electrons from the cyanide to oxidize it, while simultaneously the chlorine is being reduced to chloride. ORP is a measure of the status of an oxidation-reduction reaction. The gold electrode detects the solution抯 ability to accept or donate ele ...
... oxidizing agent. In this application, chlorine accepts electrons from the cyanide to oxidize it, while simultaneously the chlorine is being reduced to chloride. ORP is a measure of the status of an oxidation-reduction reaction. The gold electrode detects the solution抯 ability to accept or donate ele ...
Presentation 3
... Express the concentrations of ligands in terms of [Al3+] and total concentration of each ligand to give, [Al3+] = [Al]T / { (cK1 KW / [H+]) + (cK2 [SO42-]T / {1 + cK2 [Al3+]}) + (cK3 [F-]T / {1 + cK3 [Al3+]}) + (cK4 [L-]T / {1 + cK4 [Al3+]})} and approximate a solution for [Al3+] (below). In turn, t ...
... Express the concentrations of ligands in terms of [Al3+] and total concentration of each ligand to give, [Al3+] = [Al]T / { (cK1 KW / [H+]) + (cK2 [SO42-]T / {1 + cK2 [Al3+]}) + (cK3 [F-]T / {1 + cK3 [Al3+]}) + (cK4 [L-]T / {1 + cK4 [Al3+]})} and approximate a solution for [Al3+] (below). In turn, t ...
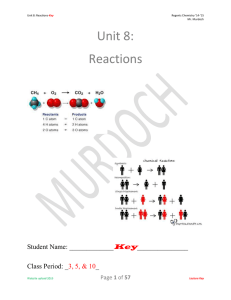
Chapter 4: Reaction Stoichiometry Reaction Stoichiometry
... 3. Swap the cations to form a new compound - this will be one of your products. 4. Take the remaining cation and convert it to an element this will be the other product. 5. Write the new compounds with balanced formulas. 6. Determine the phases of the new products - are the new compounds soluble or ...
... 3. Swap the cations to form a new compound - this will be one of your products. 4. Take the remaining cation and convert it to an element this will be the other product. 5. Write the new compounds with balanced formulas. 6. Determine the phases of the new products - are the new compounds soluble or ...
Mock Examination (2016/2017) CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 SECTION B
... “Zinc and copper are both located in area for transition metals in the Periodic Table. However, zinc is usually not regarded as a transition metals but copper is regarded as a transition metal.” Using Zn and copper reacts with conc H2SO4(l), different colour of the solutions were observed. 1M The co ...
... “Zinc and copper are both located in area for transition metals in the Periodic Table. However, zinc is usually not regarded as a transition metals but copper is regarded as a transition metal.” Using Zn and copper reacts with conc H2SO4(l), different colour of the solutions were observed. 1M The co ...
unit iii kinetics and mechanism of reactions in metal complexes
... [Pt(NH3)3Cl]+ changes only by a factor of 2 whereas the charge of the complex changes from -2 to +1. This suggests that both bond breaking and bond making are important, which is characteristic of an associative SN2 mechanism. 4. Nature of the entering ligand greatly affects the rate of substitution ...
... [Pt(NH3)3Cl]+ changes only by a factor of 2 whereas the charge of the complex changes from -2 to +1. This suggests that both bond breaking and bond making are important, which is characteristic of an associative SN2 mechanism. 4. Nature of the entering ligand greatly affects the rate of substitution ...
Section 4.9 Oxidation–Reduction Reactions
... Types of Aqueous Solutions and Solubility Dissolution of an Molecular Solid in Water • Sucrose is a molecular solid. Not composed of ions. • How does is dissolve in water? • Sugar molecules have areas that are polar – just like water • The partial positive and negative charges on the sugar interact ...
... Types of Aqueous Solutions and Solubility Dissolution of an Molecular Solid in Water • Sucrose is a molecular solid. Not composed of ions. • How does is dissolve in water? • Sugar molecules have areas that are polar – just like water • The partial positive and negative charges on the sugar interact ...
ION-SELECTIVE ELECTRODES - Clayton State University
... - Electrochemical processes involve the transfer of electrons from one substance to another ...
... - Electrochemical processes involve the transfer of electrons from one substance to another ...
Unit 8: Reactions
... i. 35.0 g of N2(g) + X g of H2(g) = 42.5 of NH3(g), therefore you first solve for 42.5 g– 35.0 g = 7.5 g, so 7.5 g of H2(g) was used making 42.5 of NH3(g). 2. How many grams of aluminum are formed when 45.0 g of Al2O3(s) are decomposed into Al(s) and 21.1 g of O2(g)? i. 45.0 g of Al2O3 = 21.1 g of O ...
... i. 35.0 g of N2(g) + X g of H2(g) = 42.5 of NH3(g), therefore you first solve for 42.5 g– 35.0 g = 7.5 g, so 7.5 g of H2(g) was used making 42.5 of NH3(g). 2. How many grams of aluminum are formed when 45.0 g of Al2O3(s) are decomposed into Al(s) and 21.1 g of O2(g)? i. 45.0 g of Al2O3 = 21.1 g of O ...
Threshold Collision-Induced Dissociation Determination and
... Some ionophores (e.g., monensin A) display remarkable selectivity for Na+, whereas others (e.g., nonactin) are selective for K+. Polypeptides such as gramicidin A form ion channels through which Na+ can be transported.1-3 The Ag+ ion has long been used as a bactericide in newborns;4,5 some silver co ...
... Some ionophores (e.g., monensin A) display remarkable selectivity for Na+, whereas others (e.g., nonactin) are selective for K+. Polypeptides such as gramicidin A form ion channels through which Na+ can be transported.1-3 The Ag+ ion has long been used as a bactericide in newborns;4,5 some silver co ...
4 Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... aqueous reactions. Modern medical practice depends heavily on analyses of blood and other body fluids. In addition to the common tests for sugar, cholesterol, and iron, analyses for specific chemical markers allow detection of many diseases before more obvious symptoms occur. Aqueous chemistry is al ...
... aqueous reactions. Modern medical practice depends heavily on analyses of blood and other body fluids. In addition to the common tests for sugar, cholesterol, and iron, analyses for specific chemical markers allow detection of many diseases before more obvious symptoms occur. Aqueous chemistry is al ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... TOPIC 1. REACTION RATES - COLLISION THEORY ...
... TOPIC 1. REACTION RATES - COLLISION THEORY ...
Chemical Reaction
... involves the rearrangement of atoms. produces one or more new substances. can be observed by the appearance of new physical properties. A chemical reaction forms new products with different properties. An antacid (NaHCO3) tablet in water forms bubbles of carbon dioxide (CO2). © 2013 Pearson Ed ...
... involves the rearrangement of atoms. produces one or more new substances. can be observed by the appearance of new physical properties. A chemical reaction forms new products with different properties. An antacid (NaHCO3) tablet in water forms bubbles of carbon dioxide (CO2). © 2013 Pearson Ed ...
Module 1 Predictor Questions
... Pay special attention to the unit factors provided as they are what will be used in converting one unit to another. Note that each unit factor may be written in two equivalent ways. The one you use depends on what units you are trying to cancel in a dimensional analysis problem (see examples below). ...
... Pay special attention to the unit factors provided as they are what will be used in converting one unit to another. Note that each unit factor may be written in two equivalent ways. The one you use depends on what units you are trying to cancel in a dimensional analysis problem (see examples below). ...
bond
... electrons occupy: • The Aufbau principle: an electron always goes to the available orbital with the lowest energy • The Pauli exclusion principle: only two electrons can occupy one atomic orbital and the two electrons have opposite spin • Hund’s rule: electrons will occupy empty degenerated orbitals ...
... electrons occupy: • The Aufbau principle: an electron always goes to the available orbital with the lowest energy • The Pauli exclusion principle: only two electrons can occupy one atomic orbital and the two electrons have opposite spin • Hund’s rule: electrons will occupy empty degenerated orbitals ...
POGIL - Basic Skills Supplement - The Mole-1
... 3. There are an equal number of nitrogen atoms in one mole of NH3 and one mole of N2. 4. The number of Cu atoms in 100 grams of pure copper metal is the same as the number of atoms in 100 grams of cupric oxide. 5. The number of Ni atoms in 100 moles of pure nickel metal is the same as the number of ...
... 3. There are an equal number of nitrogen atoms in one mole of NH3 and one mole of N2. 4. The number of Cu atoms in 100 grams of pure copper metal is the same as the number of atoms in 100 grams of cupric oxide. 5. The number of Ni atoms in 100 moles of pure nickel metal is the same as the number of ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... Therefore, cluster calculations represent an alternative way of describing localised bonds at surfaces as well as defects in ionic crystals. The problem is how to introduce the effect of the rest of the crystal. Completely different strategies can be adopted to “embed” clusters of largely covalent o ...
... Therefore, cluster calculations represent an alternative way of describing localised bonds at surfaces as well as defects in ionic crystals. The problem is how to introduce the effect of the rest of the crystal. Completely different strategies can be adopted to “embed” clusters of largely covalent o ...
Chemistry
... molecular substances, e.g. poly(ethene); sand (silicon dioxide); diamond; graphite in order to deduce their properties (c) compare the bonding and structures of diamond and graphite in order to deduce their properties such as electrical conductivity, lubricating or cutting action (candidates will no ...
... molecular substances, e.g. poly(ethene); sand (silicon dioxide); diamond; graphite in order to deduce their properties (c) compare the bonding and structures of diamond and graphite in order to deduce their properties such as electrical conductivity, lubricating or cutting action (candidates will no ...
ض ( ا ء ا ط ك ا رر 108 1) -
... What is the ion symbol for an atom with twenty (20) protons and eighteen (18) electrons? ...
... What is the ion symbol for an atom with twenty (20) protons and eighteen (18) electrons? ...
Qsp Ksp Qsp > Ksp
... Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compounds, alkalis (group 1) have oxidation number +1; alkaline earths (group 2) have oxidation number +2. f. In compounds, flu ...
... Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compounds, alkalis (group 1) have oxidation number +1; alkaline earths (group 2) have oxidation number +2. f. In compounds, flu ...
Hydration Water Dynamics in Undercooled Aqueous Solutions of
... heavy water at the concentrations c = 1,2, and 3 m corresponding to compositionsR = (moles of DzO)/(mole of salt) = 50,25, and 17, respectively. The 2 m solution corresponds to a composition where there is just enough water to hydrate the Me4N+ cations according to an estimated coordination number N ...
... heavy water at the concentrations c = 1,2, and 3 m corresponding to compositionsR = (moles of DzO)/(mole of salt) = 50,25, and 17, respectively. The 2 m solution corresponds to a composition where there is just enough water to hydrate the Me4N+ cations according to an estimated coordination number N ...
Redox reactions - SALEM-Immanuel Lutheran College
... The bond pair in any polar covalent bond (including ionic bond) between two unlike atoms is presumed to belong to the more electronegative atom. ...
... The bond pair in any polar covalent bond (including ionic bond) between two unlike atoms is presumed to belong to the more electronegative atom. ...
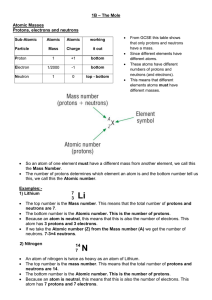
The Mole
... We can make solutions of known concentration using volumetric flasks. The easiest way of learning this is to try an example. We need 250cm3 of 0.1 mol dm3 solution of sodium hydroxide. Use the formula to calculate the No. of moles of sodium hydroxide – No. of moles = Concentration (Mol dm3) x ...
... We can make solutions of known concentration using volumetric flasks. The easiest way of learning this is to try an example. We need 250cm3 of 0.1 mol dm3 solution of sodium hydroxide. Use the formula to calculate the No. of moles of sodium hydroxide – No. of moles = Concentration (Mol dm3) x ...