Chemical Bonding in the Ternary Transition Metal Bismuthides
... immediately followed by the Bi(s)-Bi(s) antibonding one. The same “S-shape pattern” is observed for the Bi(p) orbitals starting above the band gap at -11.3 eV. Such “S-shape patterns” below Ef are the result of a filled, pretty much non-interacting (with other orbitals) bands (cf. ref 8, pp 42 ff). ...
... immediately followed by the Bi(s)-Bi(s) antibonding one. The same “S-shape pattern” is observed for the Bi(p) orbitals starting above the band gap at -11.3 eV. Such “S-shape patterns” below Ef are the result of a filled, pretty much non-interacting (with other orbitals) bands (cf. ref 8, pp 42 ff). ...
The SimSoup Guide - Chris Gordon
... Atoms are of different types. These types are called elements. An atom has a mass and a number of electrons that orbit a nucleus. Some of these are valence electrons that can participate in bonds with other atoms. ...
... Atoms are of different types. These types are called elements. An atom has a mass and a number of electrons that orbit a nucleus. Some of these are valence electrons that can participate in bonds with other atoms. ...
P-BLOCK ELEMENTS
... (a) Action of oxygen: All members when heated in oxygen form oxides. CO2, SiO2 and GeO2 are acidic whereas SnO2 and PbO2 are amphoteric. (b) Action of water: Only tin decomposes steam to form stannic dioxide and dihydrogen. Sn + 2H2O SnO2 + 2H2 (c) Action of halogen: All the elements form halide w ...
... (a) Action of oxygen: All members when heated in oxygen form oxides. CO2, SiO2 and GeO2 are acidic whereas SnO2 and PbO2 are amphoteric. (b) Action of water: Only tin decomposes steam to form stannic dioxide and dihydrogen. Sn + 2H2O SnO2 + 2H2 (c) Action of halogen: All the elements form halide w ...
101
... To assign oxidation numbers to the atoms in a water molecule, you can consider all the bonding electrons to be “owned” by the more electronegative oxygen atom, as shown in Figure 10.4B. Thus, each hydrogen atom in a water molecule is considered to have no electrons, as hydrogen would in a hydrogen ...
... To assign oxidation numbers to the atoms in a water molecule, you can consider all the bonding electrons to be “owned” by the more electronegative oxygen atom, as shown in Figure 10.4B. Thus, each hydrogen atom in a water molecule is considered to have no electrons, as hydrogen would in a hydrogen ...
Chemistry-Maths-Student-Guide
... reaction gone. Two of these – calculations involving reacting quantities (or moles) and calculations involving reaction rates are ones that you’ll have come across at GCSE. The last one – the idea of reactions at equilibrium – is an idea you may have seen at GCSE, but you’ve yet to put numbers into ...
... reaction gone. Two of these – calculations involving reacting quantities (or moles) and calculations involving reaction rates are ones that you’ll have come across at GCSE. The last one – the idea of reactions at equilibrium – is an idea you may have seen at GCSE, but you’ve yet to put numbers into ...
A study on the nickel(II)
... N(2) or N(3), are the most likely binding sites. Since at this pH proton dissociation from the ligand does not occur, two anions of ClO 2 4 bind to Ni(II) to compensate for the positive charge of the complex. Moreover, we suggest that two water molecules bind to a Ni(II) ion to fulfil the octahedral ...
... N(2) or N(3), are the most likely binding sites. Since at this pH proton dissociation from the ligand does not occur, two anions of ClO 2 4 bind to Ni(II) to compensate for the positive charge of the complex. Moreover, we suggest that two water molecules bind to a Ni(II) ion to fulfil the octahedral ...
Chemistry Spell check on
... Reference may be made to the Chemistry Higher and Advanced Higher Data Booklet. Write your answers clearly in the spaces provided in this booklet. Additional space for answers and rough work is provided at the end of this booklet. If you use this space you must clearly identify the question number y ...
... Reference may be made to the Chemistry Higher and Advanced Higher Data Booklet. Write your answers clearly in the spaces provided in this booklet. Additional space for answers and rough work is provided at the end of this booklet. If you use this space you must clearly identify the question number y ...
Document
... Reference may be made to the Chemistry Higher and Advanced Higher Data Booklet. Write your answers clearly in the spaces provided in this booklet. Additional space for answers and rough work is provided at the end of this booklet. If you use this space you must clearly identify the question number y ...
... Reference may be made to the Chemistry Higher and Advanced Higher Data Booklet. Write your answers clearly in the spaces provided in this booklet. Additional space for answers and rough work is provided at the end of this booklet. If you use this space you must clearly identify the question number y ...
Download Pdf Article
... cm-1). Though three transitions are expected in this case (dxy→ dx2-y2, dz2 →dx-y2 and ,dxz, dyz → dx2-y2) they are very close in energy and often appear in the form of one broad band envelope [18]. These three transitions are characteristic to Cu 2+ (d9) ion present in a tetragonal ...
... cm-1). Though three transitions are expected in this case (dxy→ dx2-y2, dz2 →dx-y2 and ,dxz, dyz → dx2-y2) they are very close in energy and often appear in the form of one broad band envelope [18]. These three transitions are characteristic to Cu 2+ (d9) ion present in a tetragonal ...
Chemistry of CHLORINE
... -Electron affinity is the energy required to gain an electron in an atom of an element in gaseous state. It involves the process: X(g) + e → X-(g) Electronegativity is the ease/tendency of gaining/ acquiring electrons by an element during chemical reactions. It does not involve use of energy but the ...
... -Electron affinity is the energy required to gain an electron in an atom of an element in gaseous state. It involves the process: X(g) + e → X-(g) Electronegativity is the ease/tendency of gaining/ acquiring electrons by an element during chemical reactions. It does not involve use of energy but the ...
Regular article A valence-bond-based complete-active-space
... contributes to the Pijab elements for the six carbon–carbon p bonds. However, there are six more covalent determinants (coefficient 0.146 each) with parallel spins on neighboring carbon atoms that only contribute to four Pijab elements each. Finally, there are 12 ionic terms (coefficient 0.142 each) tha ...
... contributes to the Pijab elements for the six carbon–carbon p bonds. However, there are six more covalent determinants (coefficient 0.146 each) with parallel spins on neighboring carbon atoms that only contribute to four Pijab elements each. Finally, there are 12 ionic terms (coefficient 0.142 each) tha ...
Computational Study of protonation of ozone
... of ozone is 0.69 D; dipole moment of the structure Ia is 11.84D, structure Ib 12.08D, structure Ic 9.89 D, the structure Id 1.39D. The third and fourth minima are structures of protonated ozone in which the proton is coordinated to the second oxygen atom of ozone (structure Ib) and all three atoms o ...
... of ozone is 0.69 D; dipole moment of the structure Ia is 11.84D, structure Ib 12.08D, structure Ic 9.89 D, the structure Id 1.39D. The third and fourth minima are structures of protonated ozone in which the proton is coordinated to the second oxygen atom of ozone (structure Ib) and all three atoms o ...
Gas Laws
... strong or relatively weak? Explain. LDF are created by a momentary polarity due to a valence electron moving out of its normal orbit. Nonpolar molecules are the only type of molecules in which LDF is the major intermolecular force of attraction. LDF are the weakest force of attraction. 9. What cause ...
... strong or relatively weak? Explain. LDF are created by a momentary polarity due to a valence electron moving out of its normal orbit. Nonpolar molecules are the only type of molecules in which LDF is the major intermolecular force of attraction. LDF are the weakest force of attraction. 9. What cause ...
Gas Laws
... strong or relatively weak? Explain. LDF are created by a momentary polarity due to a valence electron moving out of its normal orbit. Nonpolar molecules are the only type of molecules in which LDF is the major intermolecular force of attraction. LDF are the weakest force of attraction. 9. What cause ...
... strong or relatively weak? Explain. LDF are created by a momentary polarity due to a valence electron moving out of its normal orbit. Nonpolar molecules are the only type of molecules in which LDF is the major intermolecular force of attraction. LDF are the weakest force of attraction. 9. What cause ...
Homework extension
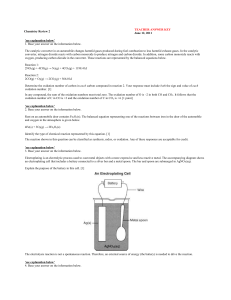
... zinc chloride zinc + chlorine ZnCl2(aq) Zn(s) + Cl2(g) At the electrodes: The ions become atoms by either gaining or losing electrons. Zinc ions need to gain electrons Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn Chloride ions need to lose electrons. (Chlorine gas (Cl2) is formed so we need 2 ions): 2 Cl- Cl2 + 2 ehttp:/ ...
... zinc chloride zinc + chlorine ZnCl2(aq) Zn(s) + Cl2(g) At the electrodes: The ions become atoms by either gaining or losing electrons. Zinc ions need to gain electrons Zn2+ + 2 e- Zn Chloride ions need to lose electrons. (Chlorine gas (Cl2) is formed so we need 2 ions): 2 Cl- Cl2 + 2 ehttp:/ ...
9.2 Oxidation Numbers
... you can. (Table 9.2 provides a summary of these guidelines with examples.) The oxidation number for each atom in a pure element is zero. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. When fluorine atoms are combined with atoms of other elements, their oxidation number is ‒1. When o ...
... you can. (Table 9.2 provides a summary of these guidelines with examples.) The oxidation number for each atom in a pure element is zero. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. When fluorine atoms are combined with atoms of other elements, their oxidation number is ‒1. When o ...
Sulfur and iron surface states on fractured pyrite surfaces
... when pyrite is fractured. With each ruptured S-S bond, two mononuclear species (formally S12) are produced, one bound to one fracture surface and the second to the opposite fracture surface. This monomer is reduced to S22 (monosulfide) during relaxation through oxidation of surface Fe21 ions to Fe31 ...
... when pyrite is fractured. With each ruptured S-S bond, two mononuclear species (formally S12) are produced, one bound to one fracture surface and the second to the opposite fracture surface. This monomer is reduced to S22 (monosulfide) during relaxation through oxidation of surface Fe21 ions to Fe31 ...
Chemistry Review 2 answer key
... must equal 0, the oxidation number of the nitrogen must be +2. 'see explanation below' 23. Base your answer on the information below. Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and ex ...
... must equal 0, the oxidation number of the nitrogen must be +2. 'see explanation below' 23. Base your answer on the information below. Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and ex ...
Practice Question
... Tap water consists of water, sodium and chloride ions, and possibly bacteria, chlorine, and other ingredients. Which choice best defines what tap water is? ...
... Tap water consists of water, sodium and chloride ions, and possibly bacteria, chlorine, and other ingredients. Which choice best defines what tap water is? ...
Examination - SCSA - School Curriculum and Standards Authority
... adding solid sodium sulfate removing solid lead sulfate adding barium nitrate solution ...
... adding solid sodium sulfate removing solid lead sulfate adding barium nitrate solution ...
A* PLC Legacy GCSE Chemistry (all boards)
... Chloride ions are negative and so are attracted to the positive electrode/anode Lose 1 electron to become a chlorine atom Hydrogen ions (from water) are positive, attracted to negative electrode/cathode Gain one electron to become hydrogen atom Both diatomic and two atoms form the gases 4 marks ...
... Chloride ions are negative and so are attracted to the positive electrode/anode Lose 1 electron to become a chlorine atom Hydrogen ions (from water) are positive, attracted to negative electrode/cathode Gain one electron to become hydrogen atom Both diatomic and two atoms form the gases 4 marks ...
Atom
... b. Explain why the atoms of inert elements do not react with one another or combine with atoms of other elements. c. Explain how cations and anions form. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... b. Explain why the atoms of inert elements do not react with one another or combine with atoms of other elements. c. Explain how cations and anions form. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
APPENDIX 2 1 ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING BROAD
... In all of these separation methods, is the molecule being chemically altered? Are any chemical reactions occurring? Why is it necessary to frequently use more than one method to separate a mixture and what, if anything, determines the order of the methods? ...
... In all of these separation methods, is the molecule being chemically altered? Are any chemical reactions occurring? Why is it necessary to frequently use more than one method to separate a mixture and what, if anything, determines the order of the methods? ...
Sample chapter - Pharmaceutical Press
... In sp2 hybridisation the 2s and two of the 2p orbitals are combined to create three sp2 hybrid orbitals. The remaining 2p orbital remains unchanged by the hybridisation process. Each hybrid orbital has a 1/3 contribution from each of the three starting atomic orbitals. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals ...
... In sp2 hybridisation the 2s and two of the 2p orbitals are combined to create three sp2 hybrid orbitals. The remaining 2p orbital remains unchanged by the hybridisation process. Each hybrid orbital has a 1/3 contribution from each of the three starting atomic orbitals. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals ...
Unusual deprotonated alkynyl hydrogen bonding in metal
... Understanding and controlling supported molecular architectures is of fundamental importance for fabricating molecular device elements through the bottom-up approach.1−7 Hydrogen bonding, which provides selectivity and directionality combined with error corrective processes, has been successfully em ...
... Understanding and controlling supported molecular architectures is of fundamental importance for fabricating molecular device elements through the bottom-up approach.1−7 Hydrogen bonding, which provides selectivity and directionality combined with error corrective processes, has been successfully em ...