Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), l ...
... calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), l ...
Lewis Acids and Bases - Screenshot for timg.co.il
... Complex Ion Formation • A complex ion consists of a central metal atom or ion, with other groups called ligands bonded to it. – The metal ion accepts electron pairs (Lewis acid). – Ligands act donate electron pairs (Lewis base). – Common ligands: ...
... Complex Ion Formation • A complex ion consists of a central metal atom or ion, with other groups called ligands bonded to it. – The metal ion accepts electron pairs (Lewis acid). – Ligands act donate electron pairs (Lewis base). – Common ligands: ...
Document
... never involved in the bond as they are too close to their own nucleus. 2 He atoms will never form a bond because Energy of He2 > 2 He. ...
... never involved in the bond as they are too close to their own nucleus. 2 He atoms will never form a bond because Energy of He2 > 2 He. ...
2014MSC(ORGANIC(CHEMISTRY!
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
12/06/05
... Recall why we have FM in metals: • Band structure leads to enhanced exchange interactions between (relatively) localized spins (d- or f-shell electrons). • Conduction electrons can play a very important role. In semiconductors, • Carriers present are only there because of doping, and at much lower c ...
... Recall why we have FM in metals: • Band structure leads to enhanced exchange interactions between (relatively) localized spins (d- or f-shell electrons). • Conduction electrons can play a very important role. In semiconductors, • Carriers present are only there because of doping, and at much lower c ...
electron configuration
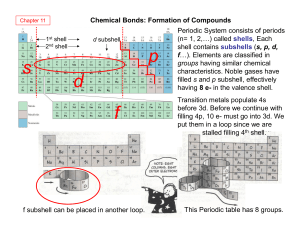
... better help you understand chemical reactivity and predict an atom’s reaction behavior. • We know when n=1 (1st EL), there are 2 e- (2n2); n=2, 8 e-, n=3, 18 e-, etc. … BUT what SUBLEVEL and ORBITAL are these electrons in? ...
... better help you understand chemical reactivity and predict an atom’s reaction behavior. • We know when n=1 (1st EL), there are 2 e- (2n2); n=2, 8 e-, n=3, 18 e-, etc. … BUT what SUBLEVEL and ORBITAL are these electrons in? ...
Types of Reactions and Solution Chemistry
... ability to react with each other. According to the Arrhenius theory, pure water dissociates to some extent to produce hydrogen ions, H+ and hydroxide ions, OH-. When this occurs, equal amounts of H+ and OH- ions are produced: H2O(l) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) An acid, according to Arrhenius, is any substanc ...
... ability to react with each other. According to the Arrhenius theory, pure water dissociates to some extent to produce hydrogen ions, H+ and hydroxide ions, OH-. When this occurs, equal amounts of H+ and OH- ions are produced: H2O(l) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) An acid, according to Arrhenius, is any substanc ...
Question 2
... Predict if a precipitation reaction will occur in each of the following cases. If it does, write the full, balanced equation AND the net ionic equation (including state symbols) to show the formation of the precipitate. If there is no reaction, say so, and indicate why. (9) a) CuSO4(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) ...
... Predict if a precipitation reaction will occur in each of the following cases. If it does, write the full, balanced equation AND the net ionic equation (including state symbols) to show the formation of the precipitate. If there is no reaction, say so, and indicate why. (9) a) CuSO4(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) ...
Lecture 21 revised (Slides) October 12
... Transition Metal Configurations • The unexpected electron configurations found experimentally for Cu and Cr are often rationalized in terms of a special stability (low energy) associated with a half full (3d5) and full (3d10) d subshell. Similar issues arise with transition metal ions. The large nu ...
... Transition Metal Configurations • The unexpected electron configurations found experimentally for Cu and Cr are often rationalized in terms of a special stability (low energy) associated with a half full (3d5) and full (3d10) d subshell. Similar issues arise with transition metal ions. The large nu ...
A2 Chemistry key word list
... double bond carries the same atom or group: the cis isomer (Z isomer) has that group on each carbon on the same side; the trans isomer (E isomer) has that group on each carbon on different ...
... double bond carries the same atom or group: the cis isomer (Z isomer) has that group on each carbon on the same side; the trans isomer (E isomer) has that group on each carbon on different ...
Chemistry
... Balanced chemical equations to represent relative numbers of particles in chemical reactions. States of substances and use of symbols (s), (l), (g) and (aq) for solid, liquid, gas and aqueous ...
... Balanced chemical equations to represent relative numbers of particles in chemical reactions. States of substances and use of symbols (s), (l), (g) and (aq) for solid, liquid, gas and aqueous ...
2.5 THE NAMES AND FORMULAS OF COMPOUNDS
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
Instructions for AP/IB 2 Chem Summer Assignment Note
... Learn the general formula for each type of reaction. If the reaction occurs in water solution, you must give the net ionic equation. If it doesn't occur in aqueous solution, the atoms/molecules do not exist as ions. ...
... Learn the general formula for each type of reaction. If the reaction occurs in water solution, you must give the net ionic equation. If it doesn't occur in aqueous solution, the atoms/molecules do not exist as ions. ...
Chemistry
... Balanced chemical equations to represent relative numbers of particles in chemical reactions. States of substances and use of symbols (s), (l), (g) and (aq) for solid, liquid, gas and aqueous ...
... Balanced chemical equations to represent relative numbers of particles in chemical reactions. States of substances and use of symbols (s), (l), (g) and (aq) for solid, liquid, gas and aqueous ...
chemistry final - Madison Public Schools
... 38. The law of constant composition applies to: A. homogeneous mixtures. B. compounds. ...
... 38. The law of constant composition applies to: A. homogeneous mixtures. B. compounds. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Study Guide
... Orbital: Regions of probability where electrons are located. Each orbital can contain up to 2 electrons Oxidation Number: A charge assigned to an atom that represents that charge it would have if it contained and ionic bond. Oxidation numbers are written as charge value, +4, -6, +2 Oxidation: Proces ...
... Orbital: Regions of probability where electrons are located. Each orbital can contain up to 2 electrons Oxidation Number: A charge assigned to an atom that represents that charge it would have if it contained and ionic bond. Oxidation numbers are written as charge value, +4, -6, +2 Oxidation: Proces ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS 1
... Balanced chemical equations to represent relative numbers of particles in chemical reactions. States of substances and use of symbols (s), (l), (g) and (aq) for solid, liquid, gas and aqueous ...
... Balanced chemical equations to represent relative numbers of particles in chemical reactions. States of substances and use of symbols (s), (l), (g) and (aq) for solid, liquid, gas and aqueous ...
Chapter 7
... Uncertainty Principle – location and momentum of particle are complimentary; can’t both be known simultaneously with precision; can’t specify precise location of particle if it behaves like a wave Developed an equation that describes the wavelike properties of matter, we use the wave function to exp ...
... Uncertainty Principle – location and momentum of particle are complimentary; can’t both be known simultaneously with precision; can’t specify precise location of particle if it behaves like a wave Developed an equation that describes the wavelike properties of matter, we use the wave function to exp ...
chapter
... • There are three basic types of subatomic particles: • An electron carries a unit of negative electric charge • A proton carries a unit of positive charge • A neutron is an uncharged particle • Protons and neutrons compose the atomic nucleus • Electrons move rapidly around the atomic nucleus • In a ...
... • There are three basic types of subatomic particles: • An electron carries a unit of negative electric charge • A proton carries a unit of positive charge • A neutron is an uncharged particle • Protons and neutrons compose the atomic nucleus • Electrons move rapidly around the atomic nucleus • In a ...
Study Guide for Exam 2_old
... You should be able to answer the following questions, solve problems involving the following concepts, or understand the following concepts so that you can describe them and answer questions about them. Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence electrons? What is ion ...
... You should be able to answer the following questions, solve problems involving the following concepts, or understand the following concepts so that you can describe them and answer questions about them. Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence electrons? What is ion ...
Honors Chemistry
... 2. In single and double replacement reactions, reactants that are compounds are always aqueous. 3. In single and double replacement reactions, products that are compounds should have their phases identified using a solubility chart (aqueous vs. precipitate) 4. In synthesis and decomposition reaction ...
... 2. In single and double replacement reactions, reactants that are compounds are always aqueous. 3. In single and double replacement reactions, products that are compounds should have their phases identified using a solubility chart (aqueous vs. precipitate) 4. In synthesis and decomposition reaction ...
topic 3: periodicity
... Metallic bonds become stronger as the number of delocalised/valence electrons per atom increases and the size of the ions decreases which explains Na Mg Al (in Na there is only 1 delocalized electron per 1 Na atom; also the greater the number of delocalized electrons, the greater the charge on t ...
... Metallic bonds become stronger as the number of delocalised/valence electrons per atom increases and the size of the ions decreases which explains Na Mg Al (in Na there is only 1 delocalized electron per 1 Na atom; also the greater the number of delocalized electrons, the greater the charge on t ...
Final Exam Review Guide
... ________ 1. Ionic bonds are formed between metals and non-metals ________ 2. Covalent bonds are formed between non-metals and other non-metals. ________ 3. Metals do not form bonds with other metals ________ 4. The transition metals lose electrons to form ions. ________ 5. When comparing degree of p ...
... ________ 1. Ionic bonds are formed between metals and non-metals ________ 2. Covalent bonds are formed between non-metals and other non-metals. ________ 3. Metals do not form bonds with other metals ________ 4. The transition metals lose electrons to form ions. ________ 5. When comparing degree of p ...
How many molecules?
... substitute readily if electrical neutrality is maintained – if charge differs by more than one, substitution is minimal ...
... substitute readily if electrical neutrality is maintained – if charge differs by more than one, substitution is minimal ...