DALTON`S ATOMIC THEORY - 1808: Publication of Dalton`s "A New
... Matter is composed of small, chemically indivisible ATOMS ELEMENTS are kinds of matter that contain only a single kind of atom. All the atoms of an element have identical chemical properties. COMPOUNDS are kinds of matter that are composed of atoms of two or more ELEMENTS which are combined in simpl ...
... Matter is composed of small, chemically indivisible ATOMS ELEMENTS are kinds of matter that contain only a single kind of atom. All the atoms of an element have identical chemical properties. COMPOUNDS are kinds of matter that are composed of atoms of two or more ELEMENTS which are combined in simpl ...
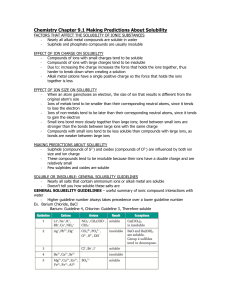
Chemistry Chapter 9.1 Making Predictions About Solubility
... - Compounds of ions with small charges tend to be soluble - Compounds of ions with large charges tend to be insoluble - Due to: increasing the charge increases the force that holds the ions together, thus harder to break down when creating a solution - Alkali metal cations have a single positive cha ...
... - Compounds of ions with small charges tend to be soluble - Compounds of ions with large charges tend to be insoluble - Due to: increasing the charge increases the force that holds the ions together, thus harder to break down when creating a solution - Alkali metal cations have a single positive cha ...
The Chemical Bond
... B2, C2, O2, F2, Ne2, and Ne2+. Give the term symbol for the C2 molecule in its ground state, assuming its electronic configuration is…(2pπ)2; i.e., that there is an electron in each of the degenerate orbitals 2pπx and 2pπy. 9. Sketch the MO energy diagrams of CO, NO, and CN¯. Compare your results to ...
... B2, C2, O2, F2, Ne2, and Ne2+. Give the term symbol for the C2 molecule in its ground state, assuming its electronic configuration is…(2pπ)2; i.e., that there is an electron in each of the degenerate orbitals 2pπx and 2pπy. 9. Sketch the MO energy diagrams of CO, NO, and CN¯. Compare your results to ...
Test - Regents
... powdered drinks is that they bubble and fizz when placed in water, forming an instant carbonated beverage. The fizz in Fizzies is caused by bubbles of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas that are released when the tablet is dropped into water. Careful observation reveals that these bubbles rise to the surface ...
... powdered drinks is that they bubble and fizz when placed in water, forming an instant carbonated beverage. The fizz in Fizzies is caused by bubbles of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas that are released when the tablet is dropped into water. Careful observation reveals that these bubbles rise to the surface ...
2. Covalent network
... o A cation is smaller than its parent atom Lattice energy: the change in energy when ions are packed together to form an ionic solid o Lattice energy=k(Q1 Q2/r) o K= constant o Q1, Q2 = charges on the ions ...
... o A cation is smaller than its parent atom Lattice energy: the change in energy when ions are packed together to form an ionic solid o Lattice energy=k(Q1 Q2/r) o K= constant o Q1, Q2 = charges on the ions ...
Syllabus - Harrison County BOE
... Big Idea 1: The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions Big Idea 2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and ...
... Big Idea 1: The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions Big Idea 2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and ...
Modeling and experimental studies of radical formation in RF discharges with etching gases
... producing the axial magnetic field, and a metal chamber of 350 . He gas is injected from the left end of the device as a buffer gas and c-C5F8 at the metal chamber as a material gas. The total gas pressure is 14.0 mTorr and RF power is 500W. The top half in Fig. 1 depicts the distribution of ne, wh ...
... producing the axial magnetic field, and a metal chamber of 350 . He gas is injected from the left end of the device as a buffer gas and c-C5F8 at the metal chamber as a material gas. The total gas pressure is 14.0 mTorr and RF power is 500W. The top half in Fig. 1 depicts the distribution of ne, wh ...
I.5. Periodic properties of the elements
... I.5. Periodic properties of the elements The elements of Group 18, rare gases, have the configuration ns2 np6, except helium, whose configuration is 1s2. That means the outer shells of the atoms are full. These prove to be very stable configurations and they can be altered with great difficulty. As ...
... I.5. Periodic properties of the elements The elements of Group 18, rare gases, have the configuration ns2 np6, except helium, whose configuration is 1s2. That means the outer shells of the atoms are full. These prove to be very stable configurations and they can be altered with great difficulty. As ...
(1) Dissolves, accompanied by evolution of flammable gas (2
... Account for each of the following in terms of principles of atomic structure, including the number, properties, and arrangements of subatomic particles. (a) The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. (b) The difference between ...
... Account for each of the following in terms of principles of atomic structure, including the number, properties, and arrangements of subatomic particles. (a) The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. (b) The difference between ...
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
... Molecular spectra are much more complex than atomic spectra, even for hydrogen (a) Molecular hydrogen ...
... Molecular spectra are much more complex than atomic spectra, even for hydrogen (a) Molecular hydrogen ...
uplift luna ap chemistry
... CnH2n+1OH; Do not be fooled—this looks like a hydroxide ion, but is not! It does not make this hydrocarbon an alkaline or basic compound. Do not name these as a hydroxide! C2H6 is ethane while C2H5OH is ethanol. NAMING BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS How do I know it is ionic? The chemical formula will begin ...
... CnH2n+1OH; Do not be fooled—this looks like a hydroxide ion, but is not! It does not make this hydrocarbon an alkaline or basic compound. Do not name these as a hydroxide! C2H6 is ethane while C2H5OH is ethanol. NAMING BINARY IONIC COMPOUNDS How do I know it is ionic? The chemical formula will begin ...
RULES OF CHEMICAL NOMENCLATURE I. Elements (periodic
... inside the “( )” is multiplied by the subscript. B. All atoms have oxidation numbers (valence). This is the combining power of the atom. C. Polyatomic ions or “radicals” are groups of atoms that behave as if they are single atoms. They also have oxidation numbers. ( we will show these later). D. We ...
... inside the “( )” is multiplied by the subscript. B. All atoms have oxidation numbers (valence). This is the combining power of the atom. C. Polyatomic ions or “radicals” are groups of atoms that behave as if they are single atoms. They also have oxidation numbers. ( we will show these later). D. We ...
29.2 Chemical Bonds
... In chemical reactions you start with reactants that are combined into products. The reactants and products may include atoms, molecules, and energy. ...
... In chemical reactions you start with reactants that are combined into products. The reactants and products may include atoms, molecules, and energy. ...
Document
... In chemical reactions you start with reactants that are combined into products. The reactants and products may include atoms, molecules, and energy. ...
... In chemical reactions you start with reactants that are combined into products. The reactants and products may include atoms, molecules, and energy. ...
CHAPTER 2: ATOMS, MOLECULES AND IONS ULES AND IONS
... Molecules: Two or more atoms (same or different type of atoms) join together by chemical force to form molecules. ...
... Molecules: Two or more atoms (same or different type of atoms) join together by chemical force to form molecules. ...
Name - Quia
... 40. Describe how temperature relates to kinetic energy. If the temperature goes up or down, what happens to kinetic energy? 41. Name several factors that determine the speed of the atoms and molecules of a particular substance. 42. What are the four states of matter? Describe them each in terms of h ...
... 40. Describe how temperature relates to kinetic energy. If the temperature goes up or down, what happens to kinetic energy? 41. Name several factors that determine the speed of the atoms and molecules of a particular substance. 42. What are the four states of matter? Describe them each in terms of h ...
Fall Final Rev 2014
... 20 a. Covalent bonding: nonmetals share valence electrons w other nonmetals so each atom is surrounded by 8 (or 2, for H). Atoms stay w their valence e– to form molecules. Molecule has no charge, so it does not conduct electricity in any state. Ionic bonding: metals transfer e– to nonmetals; metals ...
... 20 a. Covalent bonding: nonmetals share valence electrons w other nonmetals so each atom is surrounded by 8 (or 2, for H). Atoms stay w their valence e– to form molecules. Molecule has no charge, so it does not conduct electricity in any state. Ionic bonding: metals transfer e– to nonmetals; metals ...
PRACTICE EXAM for FALL 2013 FINAL EXAM (Unit 6 + review) 1
... 20 a. Covalent bonding: nonmetals share valence electrons w other nonmetals so each atom is surrounded by 8 (or 2, for H). Atoms stay w their valence e– to form molecules. Molecule has no charge, so it does not conduct electricity in any state. Ionic bonding: metals transfer e– to nonmetals; metals ...
... 20 a. Covalent bonding: nonmetals share valence electrons w other nonmetals so each atom is surrounded by 8 (or 2, for H). Atoms stay w their valence e– to form molecules. Molecule has no charge, so it does not conduct electricity in any state. Ionic bonding: metals transfer e– to nonmetals; metals ...
Zn + HCl → ZnCl 2 + H2 NaOH + H3PO4 → Na3PO4 + H2O N2 +
... 1) Write all the reactant and product formulas on the left and right side of the equation, respectively. Make sure you have all and that you have written the formulas correctly. Now, never touch the subscripts in the formulas again. Different subscripts = different molecules 2) Balance the equat ...
... 1) Write all the reactant and product formulas on the left and right side of the equation, respectively. Make sure you have all and that you have written the formulas correctly. Now, never touch the subscripts in the formulas again. Different subscripts = different molecules 2) Balance the equat ...
26. Applications of Magnetic Force on Moving Charges
... Devices that use magnetic force on a moving charge (22.4) LORENTZ FORCE: expression for total magnetic and electric force on a charge • In space containing electric and magnetic field together: o force on moving charge is ...
... Devices that use magnetic force on a moving charge (22.4) LORENTZ FORCE: expression for total magnetic and electric force on a charge • In space containing electric and magnetic field together: o force on moving charge is ...
單選題共 33 題,每題 4 分
... a) The complex ion contains Co(I). b) The complex ion exhibits cis and trans geometric isomers, but no optical isomers. c) The complex ion exhibits two geometric isomers (cis and trans) and two optical isomers. d) Since en is a strong field ligand (large ), the complex ion is paramagnetic. e) The g ...
... a) The complex ion contains Co(I). b) The complex ion exhibits cis and trans geometric isomers, but no optical isomers. c) The complex ion exhibits two geometric isomers (cis and trans) and two optical isomers. d) Since en is a strong field ligand (large ), the complex ion is paramagnetic. e) The g ...
Introductory Chemistry I
... 4. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 3d orbitals is a. 5 b. 6 c. 10 d. 14 e. 18 5. Let’s say that you are examining the outermost electrons in a ground-state germanium atom. Which of the following sets of values for the four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms) could you use to descr ...
... 4. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 3d orbitals is a. 5 b. 6 c. 10 d. 14 e. 18 5. Let’s say that you are examining the outermost electrons in a ground-state germanium atom. Which of the following sets of values for the four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms) could you use to descr ...
Active Reading 3.1: Matter and Substances
... in the proportion of 1:2:1. 2 Carbohydrates are a key source of energy, and they are found in most foods—especially fruits, vegetables, and grains. 3 The building blocks of carbohydrates are single sugars called monosaccharides, such as glucose (C6H12O6) and fructose. 4 Glucose is a major source of ...
... in the proportion of 1:2:1. 2 Carbohydrates are a key source of energy, and they are found in most foods—especially fruits, vegetables, and grains. 3 The building blocks of carbohydrates are single sugars called monosaccharides, such as glucose (C6H12O6) and fructose. 4 Glucose is a major source of ...
answer
... cis-dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III) chloride Although the structural formula above gives rise to cis and trans isomers, only the cis form is optically active. Draw the structure of the metal complex component of the compound. ...
... cis-dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III) chloride Although the structural formula above gives rise to cis and trans isomers, only the cis form is optically active. Draw the structure of the metal complex component of the compound. ...