Speciation of asexual protists – periodic selection
... • Our findings clearly contradict the assumptions of Finlay (1999) and Fenchel and Finlay (2006) that the genetic variation in molecular markers only reflects the accumulation of neutral mutations. • The phenotypic data should be combined with molecular background and ecological ...
... • Our findings clearly contradict the assumptions of Finlay (1999) and Fenchel and Finlay (2006) that the genetic variation in molecular markers only reflects the accumulation of neutral mutations. • The phenotypic data should be combined with molecular background and ecological ...
The Origin of Species
... • Morphological species concept - emphasis is on unique structural features • Phylogenetic species concept - emphasis is on ancestor-descendent relationships • Pluralistic species concept - acknowledges that, where species concepts are concerned, one size may not fit all! ...
... • Morphological species concept - emphasis is on unique structural features • Phylogenetic species concept - emphasis is on ancestor-descendent relationships • Pluralistic species concept - acknowledges that, where species concepts are concerned, one size may not fit all! ...
B chromosomes
... The essential features of Bs are: (i) they are dispensable; (ii) they pair only among themselves at meiosis (in species where they do pair) and do not recombine with the As; (iii) their inheritance is irregular, due to their polysomic nature and to the occurrence and elimination of univalents, all o ...
... The essential features of Bs are: (i) they are dispensable; (ii) they pair only among themselves at meiosis (in species where they do pair) and do not recombine with the As; (iii) their inheritance is irregular, due to their polysomic nature and to the occurrence and elimination of univalents, all o ...
Biological Species Concept
... – Weaknesses: geographically widespread populations that don’t actually interbreed may be considered the same species ...
... – Weaknesses: geographically widespread populations that don’t actually interbreed may be considered the same species ...
Review Sheet NYS Regents Lab Activity #1 Relationships and Biodiversity
... 3. Botana curus shares the most characteristics with Sample Z, making this sample the most closely related. These characteristics included the presence of Enzyme M, the same pigments blue, yellow, and pink, scattered bundles, no difference in the amino acid sequences, and the same DNA banding patter ...
... 3. Botana curus shares the most characteristics with Sample Z, making this sample the most closely related. These characteristics included the presence of Enzyme M, the same pigments blue, yellow, and pink, scattered bundles, no difference in the amino acid sequences, and the same DNA banding patter ...
GBE 214 TECNIQUES IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
... describe the correct way for experiments design, sampling, collection of results, their analysis and interpretation, error detection and correction. The techniques presented in this course would provide students with an excellent resume for future career opportunities in biotechnology. The laborator ...
... describe the correct way for experiments design, sampling, collection of results, their analysis and interpretation, error detection and correction. The techniques presented in this course would provide students with an excellent resume for future career opportunities in biotechnology. The laborator ...
3-10
... Subject: The structure and replication of DNA. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 8: The structure and replication of DNA. ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts and keywords: DNA: the genetic materi ...
... Subject: The structure and replication of DNA. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 8: The structure and replication of DNA. ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts and keywords: DNA: the genetic materi ...
Taxonomic Issues in Conservation and Using Phylogenies to
... Loyauté. Although they found evidence of genetic structure among islands in both of these groups, the lack of strong morphological differences among populations within each group, probably does not warrant separate management at this time, with one exception. Since they did not have morphologic ...
... Loyauté. Although they found evidence of genetic structure among islands in both of these groups, the lack of strong morphological differences among populations within each group, probably does not warrant separate management at this time, with one exception. Since they did not have morphologic ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... The more alike the DNA sequences of two organisms, the more closely related they are evolutionarily. Early phylogenetic tree of ...
... The more alike the DNA sequences of two organisms, the more closely related they are evolutionarily. Early phylogenetic tree of ...
2559 P Ramsfield
... harknessii) is a serious threat to exotic Pinus radiata forests in New Zealand. As the pathogen is not present in New Zealand and because of the long period of time between infection and spore production, a DNA based marker has been developed that is able to detect the presence of pathogen DNA withi ...
... harknessii) is a serious threat to exotic Pinus radiata forests in New Zealand. As the pathogen is not present in New Zealand and because of the long period of time between infection and spore production, a DNA based marker has been developed that is able to detect the presence of pathogen DNA withi ...
3.5 billion years ago.
... b. The above experiments show that polymers could easily form under the conditions found on Earth years ago. 3. What was the original process of copying hereditary info? a. In lab, short RNA molecules copy themselves in solutions containing nucleotides without enzymes or cells present (maybe the fir ...
... b. The above experiments show that polymers could easily form under the conditions found on Earth years ago. 3. What was the original process of copying hereditary info? a. In lab, short RNA molecules copy themselves in solutions containing nucleotides without enzymes or cells present (maybe the fir ...
NAME
... other humans visit Mars for 200 years. Any changes in the gene pool observed after 200 years are due to A. mutation pressure. B. a founder effect C. polymorphism D. gene flow 26. Which of the following could not be a barrier to gene flow between populations? A. geographic features such as oceans, ri ...
... other humans visit Mars for 200 years. Any changes in the gene pool observed after 200 years are due to A. mutation pressure. B. a founder effect C. polymorphism D. gene flow 26. Which of the following could not be a barrier to gene flow between populations? A. geographic features such as oceans, ri ...
NAME
... individuals with light hair. The term that best describes this situation is A. neutral variation. B. natural selection. C. random mating. D. random selection. 2. Which of the following concepts was presented in the BBC Video entitled "Blue Planet: The Deep?" A. all deep sea organisms produce light. ...
... individuals with light hair. The term that best describes this situation is A. neutral variation. B. natural selection. C. random mating. D. random selection. 2. Which of the following concepts was presented in the BBC Video entitled "Blue Planet: The Deep?" A. all deep sea organisms produce light. ...
File
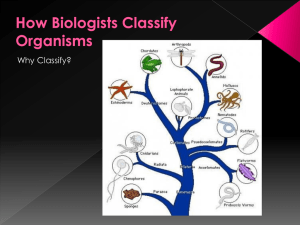
... •! Molecular data may lead scientists to propose a new classification. Molecular data can include: •! Proteins •! Mitochondrial DNA •! Ribosomal RNA •! Nuclear DNA Domains are above the kingdom level. •! Proposed by Carl Woese based on rRNA studies of prokaryotes. •! Domain model more clearly shows ...
... •! Molecular data may lead scientists to propose a new classification. Molecular data can include: •! Proteins •! Mitochondrial DNA •! Ribosomal RNA •! Nuclear DNA Domains are above the kingdom level. •! Proposed by Carl Woese based on rRNA studies of prokaryotes. •! Domain model more clearly shows ...
PCR Study Questions
... 3. DNA strands can come apart and go back together. Why is this important? ...
... 3. DNA strands can come apart and go back together. Why is this important? ...
S6. Phylogenetic results: complementary analyses Bayesian
... partitions (each codon position of the combined nuclear genes defined as separate partition; S6c) and one with 12 partitions (each codon position of each nuclear gene defined as separate partition; S6d). We furthermore used *BEAST 1.7.4 (Drummond et al. 2012) to calculate coalescence-based species t ...
... partitions (each codon position of the combined nuclear genes defined as separate partition; S6c) and one with 12 partitions (each codon position of each nuclear gene defined as separate partition; S6d). We furthermore used *BEAST 1.7.4 (Drummond et al. 2012) to calculate coalescence-based species t ...
Notes 3
... Q4. The Pongidae is not a monophyletic family because A. Bonobos and chimps are in different genera. B. There is more than one species of Pongidae. C. Humans are classified as being in a different family. D. The divergence of different species in the Pongidae was very recent. E. Some species of Pong ...
... Q4. The Pongidae is not a monophyletic family because A. Bonobos and chimps are in different genera. B. There is more than one species of Pongidae. C. Humans are classified as being in a different family. D. The divergence of different species in the Pongidae was very recent. E. Some species of Pong ...
phylogeny
... Q4. The Pongidae is not a monophyletic family because A. Bonobos and chimps are in different genera. B. There is more than one species of Pongidae. C. Humans are classified as being in a different family. D. The divergence of different species in the Pongidae was very recent. E. Some species of Pong ...
... Q4. The Pongidae is not a monophyletic family because A. Bonobos and chimps are in different genera. B. There is more than one species of Pongidae. C. Humans are classified as being in a different family. D. The divergence of different species in the Pongidae was very recent. E. Some species of Pong ...