System Definition Document
... These switches control the flow of electrical power around the payload. They require a 5V logic to work, so they always have a level shifting circuit between them and the OBDH. Level shifter (in house) This circuit takes a 3.3V logic and steps it to a level that the power FET switches can use. It ha ...
... These switches control the flow of electrical power around the payload. They require a 5V logic to work, so they always have a level shifting circuit between them and the OBDH. Level shifter (in house) This circuit takes a 3.3V logic and steps it to a level that the power FET switches can use. It ha ...
In Problems 1 and 2, find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent
... b. Find the impedance for Zmatch that will force the voltage vR to be 180o out of phase with the current iR. In phase is a condition where the phase angle of the voltage is equal to the phase angle of the current. Note that this does not mean that the phase angle will be equal to 0o. This will never ...
... b. Find the impedance for Zmatch that will force the voltage vR to be 180o out of phase with the current iR. In phase is a condition where the phase angle of the voltage is equal to the phase angle of the current. Note that this does not mean that the phase angle will be equal to 0o. This will never ...
Single Stage Amplifiers (2)
... Av changes quite about. So there is quite a bit of nonlinearity. ...
... Av changes quite about. So there is quite a bit of nonlinearity. ...
Lab: " Ohm`s Law "
... B. Choose three resistors. R1 = _________ Ω R2 = __________ Ω R3 = __________ Ω. Connect one of the resistors to the power supply. Turn on the voltmeter and adjust it to read DCV 20. Connect it in parallel (across) the resistor. Turn on the ammeter and adjust it to read 10 A. Place it in series with ...
... B. Choose three resistors. R1 = _________ Ω R2 = __________ Ω R3 = __________ Ω. Connect one of the resistors to the power supply. Turn on the voltmeter and adjust it to read DCV 20. Connect it in parallel (across) the resistor. Turn on the ammeter and adjust it to read 10 A. Place it in series with ...
Low drop - Low supply voltage, Low ESR capacitor compatible
... The Thermal over load protection limits total power dissipation in the device. When the junction temperature (TJ) exceeds +140°C, the thermal sensor sends a signal to the shutdown logic, turning off the pass transistor and allowing the device to cool. The pass transistor turns on again after the dev ...
... The Thermal over load protection limits total power dissipation in the device. When the junction temperature (TJ) exceeds +140°C, the thermal sensor sends a signal to the shutdown logic, turning off the pass transistor and allowing the device to cool. The pass transistor turns on again after the dev ...
AN532 : Common Questions Concerning CMOS Analog Switches
... four layer SCR found in JI technology does not exist. This circuit is intended to protect the device from high current levels which result from the forward biasing of the parasitic transistors which are inherent in all FET structures. If for some reason the resistor-diode protection circuit cannot b ...
... four layer SCR found in JI technology does not exist. This circuit is intended to protect the device from high current levels which result from the forward biasing of the parasitic transistors which are inherent in all FET structures. If for some reason the resistor-diode protection circuit cannot b ...
Design of Low-Voltage, Low-Power FGMOS Based Voltage Buffer
... processing chain of a design. It is capable of shifting the signal levels and incorporating tunable mechanisms due to its programmable threshold voltage. It operates normally below the operational limits of supply voltage levels for a particular technology and thus consumes less power than the minim ...
... processing chain of a design. It is capable of shifting the signal levels and incorporating tunable mechanisms due to its programmable threshold voltage. It operates normally below the operational limits of supply voltage levels for a particular technology and thus consumes less power than the minim ...
Activity 6.2.6 Transistors
... 21. Name the two scientists who created the first integrated circuit. ...
... 21. Name the two scientists who created the first integrated circuit. ...
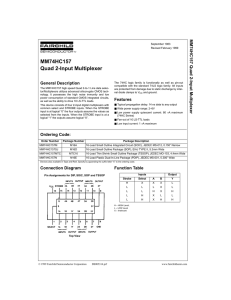
74HC157 pdf
... The MM74HC157 high speed Quad 2-to-1 Line data selector/Multiplexers utilizes advanced silicon-gate CMOS technology. It possesses the high noise immunity and low power consumption of standard CMOS integrated circuits, as well as the ability to drive 10 LS-TTL loads. This device consists of four 2-in ...
... The MM74HC157 high speed Quad 2-to-1 Line data selector/Multiplexers utilizes advanced silicon-gate CMOS technology. It possesses the high noise immunity and low power consumption of standard CMOS integrated circuits, as well as the ability to drive 10 LS-TTL loads. This device consists of four 2-in ...
Power-Gated MOS Current Mode Logic (PG
... have been implemented in various demanding applications such as high-speed ring oscillators, frequency dividers, and multi-channel data multiplexing [13, 4, 5, 7]. Since the power consumption depends less strongly on the particular switching activity or the operating frequency, when used in multi-GH ...
... have been implemented in various demanding applications such as high-speed ring oscillators, frequency dividers, and multi-channel data multiplexing [13, 4, 5, 7]. Since the power consumption depends less strongly on the particular switching activity or the operating frequency, when used in multi-GH ...
CMOS VLSI Design 4th Ed.
... 3-input NAND Gate Y pulls low if ALL inputs are 1 Y pulls high if ANY input is 0 ...
... 3-input NAND Gate Y pulls low if ALL inputs are 1 Y pulls high if ANY input is 0 ...
Power Estimation at the architectural level
... VLSI has its beginning back in the early 60's with SSI, small scale integration, when a few bipolar transistors and resistors were fabricated on the same chip. Today chips are both simpler and more complex. They typically only contain two active elements (NMOS and PMOS transistors) and wires. But th ...
... VLSI has its beginning back in the early 60's with SSI, small scale integration, when a few bipolar transistors and resistors were fabricated on the same chip. Today chips are both simpler and more complex. They typically only contain two active elements (NMOS and PMOS transistors) and wires. But th ...
HT9170 DTMF Receiver
... The information appearing in this Data Sheet is believed to be accurate at the time of publication. However, Holtek assumes no responsibility arising from the use of the specifications described. The applications mentioned herein are used solely for the purpose of illustration and Holtek makes no wa ...
... The information appearing in this Data Sheet is believed to be accurate at the time of publication. However, Holtek assumes no responsibility arising from the use of the specifications described. The applications mentioned herein are used solely for the purpose of illustration and Holtek makes no wa ...
Principle of Transformer Action
... – Output power cannot exceed input power! – power in = power out ...
... – Output power cannot exceed input power! – power in = power out ...
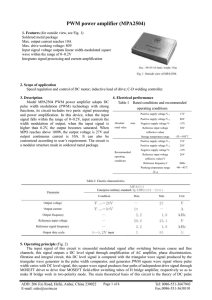
PWM power amplifier (MPA2504) 1. Features (for outside view, see
... Speed regulation and control of DC motor; inductive load of drive; C-D welding controller. 3. Description Model MPA2504 PWM power amplifier adopts DC pulse width modulation (PWM) technology with strong functions, its circuit includes two parts: signal processing and power amplification. In this devi ...
... Speed regulation and control of DC motor; inductive load of drive; C-D welding controller. 3. Description Model MPA2504 PWM power amplifier adopts DC pulse width modulation (PWM) technology with strong functions, its circuit includes two parts: signal processing and power amplification. In this devi ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.