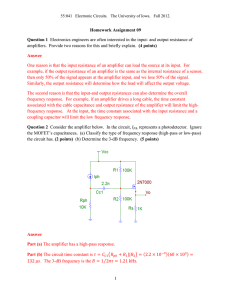
Transducers
... transducer is placed in the field and a known current is passed through it, resulting in a Hall voltage proportional to the field strength. It is otherwise surprisingly difficult to measure constant magnetic fields -- alternating ones are easier as we can insert a coil and measure the alternating vo ...
... transducer is placed in the field and a known current is passed through it, resulting in a Hall voltage proportional to the field strength. It is otherwise surprisingly difficult to measure constant magnetic fields -- alternating ones are easier as we can insert a coil and measure the alternating vo ...
7408
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
Trends of Semiconductor Technology for Total
... method of avoiding these problems, but then leakage current increases. It thus becomes necessary to employ a method of holding down the leakage current in mobile devices to reduce power consumption during standby. The typical method used is the technique of increasing the transistor substrate voltag ...
... method of avoiding these problems, but then leakage current increases. It thus becomes necessary to employ a method of holding down the leakage current in mobile devices to reduce power consumption during standby. The typical method used is the technique of increasing the transistor substrate voltag ...
DM7408 Quad 2-Input AND Gates
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
Paper Title (use style: paper title)
... switching of the capacitor. Thus dynamic power consumption reduced, because the main source of dynamic power consumption is capacitance switching. Leakage current occurs due to unnecessary flow of current between the drain and the source of the transistor. This leakage current can be avoided by the ...
... switching of the capacitor. Thus dynamic power consumption reduced, because the main source of dynamic power consumption is capacitance switching. Leakage current occurs due to unnecessary flow of current between the drain and the source of the transistor. This leakage current can be avoided by the ...
ece2201_lab4
... IMPROVED AUDIO MUTE SWITCH (CMOS TRANSMISSION GATE) L16. As in Lab 3, our goal is a switch with two states: one state that passes an audio signal undistorted to a speaker, another state that blocks the signal completely. In lab 3, with only an N-channel device, significant distortion was observed s ...
... IMPROVED AUDIO MUTE SWITCH (CMOS TRANSMISSION GATE) L16. As in Lab 3, our goal is a switch with two states: one state that passes an audio signal undistorted to a speaker, another state that blocks the signal completely. In lab 3, with only an N-channel device, significant distortion was observed s ...
DM74LS09 Quad 2-Input AND Gates with Open
... performs the logic AND function. The open-collector outputs require external pull-up resistors for proper logical operation. ...
... performs the logic AND function. The open-collector outputs require external pull-up resistors for proper logical operation. ...
lecture1430873751
... logic gate to produce a false output. The CMOS 4000 logic family uses different levels of voltages compared to the TTL types as they are designed using field effect transistors, or FET’s. In CMOS technology a logic “1” level operates between 3.0 volts and 18 volts and a logic “0” level is below 1.5 ...
... logic gate to produce a false output. The CMOS 4000 logic family uses different levels of voltages compared to the TTL types as they are designed using field effect transistors, or FET’s. In CMOS technology a logic “1” level operates between 3.0 volts and 18 volts and a logic “0” level is below 1.5 ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.