Joystick Controllers
... The analogue output can be factory configured to provide signals for fault detection circuits and a center tap provides an accurate voltage reference for the center position or a zero point for a bipolar supply voltage. An electrically independent switch operates with separate contacts each side of ...
... The analogue output can be factory configured to provide signals for fault detection circuits and a center tap provides an accurate voltage reference for the center position or a zero point for a bipolar supply voltage. An electrically independent switch operates with separate contacts each side of ...
DAC7558 - Texas Instruments
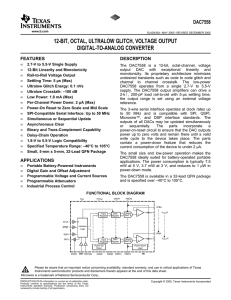
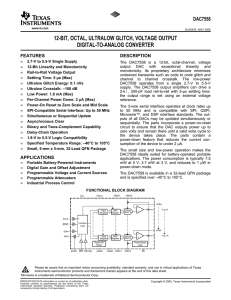
... monotonicity. Its proprietary architecture minimizes undesired transients such as code to code glitch and channel to channel crosstalk. The low-power DAC7558 operates from a single 2.7-V to 5.5-V supply. The DAC7558 output amplifiers can drive a 2-kΩ, 200-pF load rail-to-rail with 5-µs settling time ...
... monotonicity. Its proprietary architecture minimizes undesired transients such as code to code glitch and channel to channel crosstalk. The low-power DAC7558 operates from a single 2.7-V to 5.5-V supply. The DAC7558 output amplifiers can drive a 2-kΩ, 200-pF load rail-to-rail with 5-µs settling time ...
Electrical Circuits
... source. Ground is typically any major metal part of a vehicle. You can think of ground as a zero voltage reference. Ground provides a common connection that all circuits can use so that they do not have to be wired all the way back to the battery. The circuit type is determined by how the power sour ...
... source. Ground is typically any major metal part of a vehicle. You can think of ground as a zero voltage reference. Ground provides a common connection that all circuits can use so that they do not have to be wired all the way back to the battery. The circuit type is determined by how the power sour ...
Example Temperature Measurement
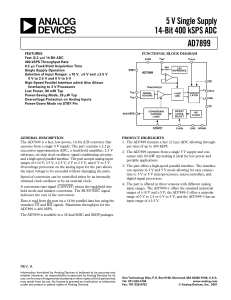
... IDAC current in this topology. This ratiometric approach ensures a greater effective number of bits (ENOB) because the noise in the IDAC reflects in the reference as well as in the input, and thus tends to cancel off. The effect of the IDAC current temperature drift is also cancelled out in this rat ...
... IDAC current in this topology. This ratiometric approach ensures a greater effective number of bits (ENOB) because the noise in the IDAC reflects in the reference as well as in the input, and thus tends to cancel off. The effect of the IDAC current temperature drift is also cancelled out in this rat ...
MAX517/MAX518/MAX519 2-Wire Serial 8-Bit DACs with Rail
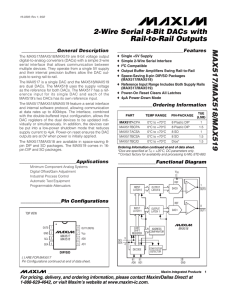
... the timing diagram for signals on the 2-wire bus. Figure 3 shows a typical application. The 2-wire bus can have several devices (in addition to the MAX517/ MAX518/MAX519) attached. The two bus lines (SDA and SCL) must be high when the bus is not in use. When in use, the port bits are toggled to gene ...
... the timing diagram for signals on the 2-wire bus. Figure 3 shows a typical application. The 2-wire bus can have several devices (in addition to the MAX517/ MAX518/MAX519) attached. The two bus lines (SDA and SCL) must be high when the bus is not in use. When in use, the port bits are toggled to gene ...
On-chip optical interconnect for low-power
... modulation scheme for high-speed operation. The source always has to be biased above its threshold current by a MOS current sink to eliminate turn-on delays, which is why low-threshold sources are so important (figures of the order of 40µA [7] have been reported). A switched current sink modulates t ...
... modulation scheme for high-speed operation. The source always has to be biased above its threshold current by a MOS current sink to eliminate turn-on delays, which is why low-threshold sources are so important (figures of the order of 40µA [7] have been reported). A switched current sink modulates t ...
2,4 GHz Power Amplifier with Cartesian Feedback for WLAN Maria Hofvendahl 2002-09-03 LiTH-ISY-EX-3254-2002
... linearisation. The next subchapter is about different types of distortion in amplifiers and it will be followed by how these distortions can be measured. The last part is about different linearisation techniques and the main part will be about the Cartesian feedback. ...
... linearisation. The next subchapter is about different types of distortion in amplifiers and it will be followed by how these distortions can be measured. The last part is about different linearisation techniques and the main part will be about the Cartesian feedback. ...
BD4157MUV
... With an input of 2.0 volts or higher, this terminal goes HIGH to activate the circuit, and goes LOW to deactivate the circuit (with the standby circuit current of 40 μA), It discharges each output and lowers output voltage when the input falls to 0.8 volts or less. V3_IN, V15_IN, and V3AUX_IN These ...
... With an input of 2.0 volts or higher, this terminal goes HIGH to activate the circuit, and goes LOW to deactivate the circuit (with the standby circuit current of 40 μA), It discharges each output and lowers output voltage when the input falls to 0.8 volts or less. V3_IN, V15_IN, and V3AUX_IN These ...
Multi-mode controller for SMPS
... Control input for loop regulation. The pin will be driven by the phototransistor (emitter-grounded) of an optocoupler to modulate its voltage by modulating the current sunk. A capacitor placed between the pin and GND (3), as close to the IC as possible to reduce noise pick-up, sets a pole in the out ...
... Control input for loop regulation. The pin will be driven by the phototransistor (emitter-grounded) of an optocoupler to modulate its voltage by modulating the current sunk. A capacitor placed between the pin and GND (3), as close to the IC as possible to reduce noise pick-up, sets a pole in the out ...
4 - Binus Repository
... sources can be replaced by the Thevenin or Norton equivalent circuits shown in Fig. 8-24. The general concept of Thevenin's and Norton's theorems and their restrictions are the same as in the resistive circuit studied in Chapter 3. The important difference here is that the signals VT, IN, V, and I a ...
... sources can be replaced by the Thevenin or Norton equivalent circuits shown in Fig. 8-24. The general concept of Thevenin's and Norton's theorems and their restrictions are the same as in the resistive circuit studied in Chapter 3. The important difference here is that the signals VT, IN, V, and I a ...
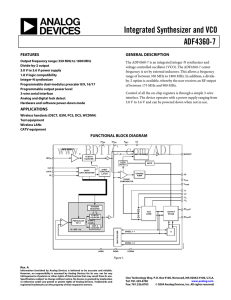
Integrated Synthesizer and VCO ADF4360-7 FEATURES
... VCO Output. The output level is programmable from −5 dBm to −14 dBm. See the Output Matching section for a description of the various output stages. VCO Complementary Output. The output level is programmable from −5 dBm to −14 dBm. See the Output Matching section for a description of the various out ...
... VCO Output. The output level is programmable from −5 dBm to −14 dBm. See the Output Matching section for a description of the various output stages. VCO Complementary Output. The output level is programmable from −5 dBm to −14 dBm. See the Output Matching section for a description of the various out ...
calculation of tms320c5x power dissipation
... second (MIPS) to handle the requirements of today’s high performance applications. In addition to its performance capabilities, the device is designed to exhibit very low power dissipation, and features flexible power management modes which allow further savings on power requirments. The TMS320C5x d ...
... second (MIPS) to handle the requirements of today’s high performance applications. In addition to its performance capabilities, the device is designed to exhibit very low power dissipation, and features flexible power management modes which allow further savings on power requirments. The TMS320C5x d ...
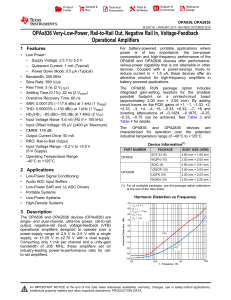
DC-AC Power Inverter Pure Sine Wave PST-1500-12 PST-1500
... effect is a tendency to cancel each other. Hence, in a circuit containing both inductances and capacitances, the net Reactance (X) will be equal to the difference between the values of the inductive and capacitive reactances. The net Reactance (X) will be inductive if XL > XC and capacitive if XC > ...
... effect is a tendency to cancel each other. Hence, in a circuit containing both inductances and capacitances, the net Reactance (X) will be equal to the difference between the values of the inductive and capacitive reactances. The net Reactance (X) will be inductive if XL > XC and capacitive if XC > ...
Exeltech User Manual - Alternative Energy, Inc.
... These inverters can supply twice their rated output power for 3 seconds, in order to start motors or supply in-rush currents to electronic loads. If output power is exceeded for greater than 3 seconds, output voltage is reduced to a level which will provide the inverter’s rated power to the load by ...
... These inverters can supply twice their rated output power for 3 seconds, in order to start motors or supply in-rush currents to electronic loads. If output power is exceeded for greater than 3 seconds, output voltage is reduced to a level which will provide the inverter’s rated power to the load by ...
A Ammeter V Voltmeter
... The readout of an instrument labeled “voltmeter” is intended by the manufacturer to tell you the electric pressure difference between any two points on a circuit to which it is connected. In this investigation you will investigate the actual behavior of your voltmeter. 6.2 Activity: Testing the volt ...
... The readout of an instrument labeled “voltmeter” is intended by the manufacturer to tell you the electric pressure difference between any two points on a circuit to which it is connected. In this investigation you will investigate the actual behavior of your voltmeter. 6.2 Activity: Testing the volt ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.