Schottky_Diode_Poste..
... The time of response for these devices are measured to be 15ns or less. This time is RC limited. We expect the actual time of response to be in the order of 10-100 ps. Use of Silicon Dioxide helps further to reduce the leakage and this proves that the surface between the two films are perfect. The u ...
... The time of response for these devices are measured to be 15ns or less. This time is RC limited. We expect the actual time of response to be in the order of 10-100 ps. Use of Silicon Dioxide helps further to reduce the leakage and this proves that the surface between the two films are perfect. The u ...
TDA2050 - STMicroelectronics
... Short-circuit protection The TDA2050 has an original circuit which limits the current of the output transistors. The maximum output current is a function of the collector emitter voltage, hence the output transistors work within their safe operating area. This function can therefore be considered as ...
... Short-circuit protection The TDA2050 has an original circuit which limits the current of the output transistors. The maximum output current is a function of the collector emitter voltage, hence the output transistors work within their safe operating area. This function can therefore be considered as ...
Document
... available with features such as a programmable output, currentvoltage boosting, internal short-circuit current limiting, thermal shutdown, and floating operation for high voltage applications ...
... available with features such as a programmable output, currentvoltage boosting, internal short-circuit current limiting, thermal shutdown, and floating operation for high voltage applications ...
PDF [FULL TEXT]
... it is being turned ON. It doesn’t depend upon frequency. It can be further classified under the banner as: Efficient charge recovery logic (ECRL). 2N-2N 2P logic. Positive feed back adiabatic logic (PFAL). NMOS energy recovery logic (NERL). Clocked adiabatic logic (CAL). Fully adiabatic lo ...
... it is being turned ON. It doesn’t depend upon frequency. It can be further classified under the banner as: Efficient charge recovery logic (ECRL). 2N-2N 2P logic. Positive feed back adiabatic logic (PFAL). NMOS energy recovery logic (NERL). Clocked adiabatic logic (CAL). Fully adiabatic lo ...
R09 SET-1 Code No: R09221902
... Explain how the deficiencies of weighted resister type DAC can be overcome through an R-2R ladder type network. Explain the conversion procedure in R-2R ladder type DAC. Define the terms ‘Resolution’, ‘Conversion time’ and ‘Linearity’ of an Analog to Digital converter. What is the resolution of a 11 ...
... Explain how the deficiencies of weighted resister type DAC can be overcome through an R-2R ladder type network. Explain the conversion procedure in R-2R ladder type DAC. Define the terms ‘Resolution’, ‘Conversion time’ and ‘Linearity’ of an Analog to Digital converter. What is the resolution of a 11 ...
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS INSTAL
... system errors etc. typically 10% of the span of the control concerned. ...
... system errors etc. typically 10% of the span of the control concerned. ...
University of California, Berkeley Spring 2013 EE 42/100 Prof. K
... VCube/Cord = I x (2RCord + 2RCable + RCar) = I x 2RCord + I x (2RCable + RCar) = I x 2RCord + VCord/Cable 114V = 12A x 2RCord + 111V RCord = 0.125 Ω The measured RCord is 45% greater than what we initially calculated. The increased resistance value could be due to the rising temperature of the wir ...
... VCube/Cord = I x (2RCord + 2RCable + RCar) = I x 2RCord + I x (2RCable + RCar) = I x 2RCord + VCord/Cable 114V = 12A x 2RCord + 111V RCord = 0.125 Ω The measured RCord is 45% greater than what we initially calculated. The increased resistance value could be due to the rising temperature of the wir ...
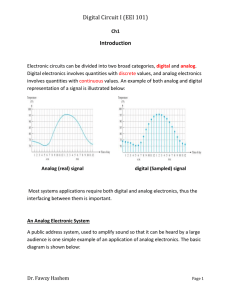
Digital Circuit I (EEI 101)
... on a single chip. Medium-scale integration (MSI), compromises from more than 10 to 100 equivalent gate circuits on a single chip. Large-scale integration (LSI), compromises from more than 100 to 10,000 equivalent gate circuits on a single chip. Very large-scale integration (VLSI), compromises ...
... on a single chip. Medium-scale integration (MSI), compromises from more than 10 to 100 equivalent gate circuits on a single chip. Large-scale integration (LSI), compromises from more than 100 to 10,000 equivalent gate circuits on a single chip. Very large-scale integration (VLSI), compromises ...
AC Circuits
... Clock oscillator: Most digital circuits require a clock signal. This is simply a periodic digital waveform, which alternates between 0 and 1 states at some chosen frequency. (When a personal computer is advertised as having a 66 MHz CPU, for example, the 66 MHz refers to the clock frequency used in ...
... Clock oscillator: Most digital circuits require a clock signal. This is simply a periodic digital waveform, which alternates between 0 and 1 states at some chosen frequency. (When a personal computer is advertised as having a 66 MHz CPU, for example, the 66 MHz refers to the clock frequency used in ...
PGA103 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in such safety-critical applications. TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI produ ...
... provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in such safety-critical applications. TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI produ ...
hxlvdsr - Honeywell
... The HXLVDSR is a radiation hardened quad differential line receiver designed for applications requiring low power dissipation and high data rates. The HXLVDSR accepts low voltage differential input signals and translates them to 3.3V CMOS output levels. The receiver includes tristate output capabili ...
... The HXLVDSR is a radiation hardened quad differential line receiver designed for applications requiring low power dissipation and high data rates. The HXLVDSR accepts low voltage differential input signals and translates them to 3.3V CMOS output levels. The receiver includes tristate output capabili ...
ADM209 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Internally Generated Positive Supply (10 V nominal) on all parts, except ADM209 . The ADM209 requires an external 9 V to 13.2 V supply. Internally Generated Negative Supply (–10 V Nominal). Ground Pin. Must be connected to 0 V. (ADM209 only) External capacitor (+ terminal) is connected to this pin. ...
... Internally Generated Positive Supply (10 V nominal) on all parts, except ADM209 . The ADM209 requires an external 9 V to 13.2 V supply. Internally Generated Negative Supply (–10 V Nominal). Ground Pin. Must be connected to 0 V. (ADM209 only) External capacitor (+ terminal) is connected to this pin. ...
Fairchild’s Process Enhancements Eliminate the CMOS SCR Latch-Up Problem In 74HC Logic
... example, a poly-silicon resistor is used for electrostatic protection, and this enables larger voltages to be applied to the circuit pins without causing latchup. This is because the poly resistor actually forms a current limit resistor in series with the diodes. In most applications the designer is ...
... example, a poly-silicon resistor is used for electrostatic protection, and this enables larger voltages to be applied to the circuit pins without causing latchup. This is because the poly resistor actually forms a current limit resistor in series with the diodes. In most applications the designer is ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.






![PDF [FULL TEXT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015018175_1-0620b69520c9bf1d46146ee7338be05c-300x300.png)