FAN6961 Boundary Mode PFC Controller FAN6961 —Boundary Mode PFC Controller Features
... controller IC intended for controlling PFC preregulators. The FAN6961 provides a controlled on-time to regulate the output DC voltage and achieve natural power factor correction. The maximum on-time of the external switch is programmable to ensure safe operation during AC brownouts. An innovative mu ...
... controller IC intended for controlling PFC preregulators. The FAN6961 provides a controlled on-time to regulate the output DC voltage and achieve natural power factor correction. The maximum on-time of the external switch is programmable to ensure safe operation during AC brownouts. An innovative mu ...
Homework 1 Solution
... source? How much? Ans: Since the 1A from the current source is gone, the 5V would have to supply this current to maintain KVL in the right mesh. The current would flow OUT from the source: P5v Source=5V(-1A)= -5W, generating. 9) In the circuit below, the voltage source, V1, will burn up if it has to ...
... source? How much? Ans: Since the 1A from the current source is gone, the 5V would have to supply this current to maintain KVL in the right mesh. The current would flow OUT from the source: P5v Source=5V(-1A)= -5W, generating. 9) In the circuit below, the voltage source, V1, will burn up if it has to ...
SILICON DESIGNS, INC.
... The model 2266 accelerometer module combines an integrated SDI low noise accelerometer with high drive, low impedance buffering for measuring acceleration in commercial/industrial environments. It is tailored for zero to medium frequency instrumentation applications. The anodized aluminum case is ep ...
... The model 2266 accelerometer module combines an integrated SDI low noise accelerometer with high drive, low impedance buffering for measuring acceleration in commercial/industrial environments. It is tailored for zero to medium frequency instrumentation applications. The anodized aluminum case is ep ...
Pro-Series Strobe Kit Instructions
... Erratic behavior (and/or) shutdown: 1) The power supply will shut down if there is a short circuit condition on any one of the strobe heads. If the electrical conductors connecting the power supply to the strobe heads are exposed to water, a short circuit will result. The first sign is intermittent ...
... Erratic behavior (and/or) shutdown: 1) The power supply will shut down if there is a short circuit condition on any one of the strobe heads. If the electrical conductors connecting the power supply to the strobe heads are exposed to water, a short circuit will result. The first sign is intermittent ...
Mechatronics I Laboratory Exercise 5
... 4. Build the circuit you just designed. Refer to Figures 7 and 8 to help with wiring the circuit and to help pay attention to the pin out. Use the ground from the bench power supply for the appropriate non-inverting inputs. You will use the bench ground as your common ground. All equipment and circu ...
... 4. Build the circuit you just designed. Refer to Figures 7 and 8 to help with wiring the circuit and to help pay attention to the pin out. Use the ground from the bench power supply for the appropriate non-inverting inputs. You will use the bench ground as your common ground. All equipment and circu ...
Leakage Biased PMOS Sleep Switch Dynamic Circuits
... high- pMOS transistor at high and low die temperatures, reof a low- nMOS transistor spectively. Similarly, the of a highis 4.3 and 198.9 higher than the nMOS transistor at high and low die temperatures, respectively. Gate tunneling is, therefore, the dominant leakage mechanism in a dual- domino gate ...
... high- pMOS transistor at high and low die temperatures, reof a low- nMOS transistor spectively. Similarly, the of a highis 4.3 and 198.9 higher than the nMOS transistor at high and low die temperatures, respectively. Gate tunneling is, therefore, the dominant leakage mechanism in a dual- domino gate ...
AD7545A: CMOS 12-Bit Buffered Multiplying DAC Data Sheet (Rev C, 03/2000)
... about a “pseudo-analog ground” of 5 V. This voltage range would allow operation from a single VDD of +10 V to +15 V. The AD584 pin-programmable reference fixes AGND at +5 V. VIN is set at +2 V by means of the series resistors R1 and R2. ...
... about a “pseudo-analog ground” of 5 V. This voltage range would allow operation from a single VDD of +10 V to +15 V. The AD584 pin-programmable reference fixes AGND at +5 V. VIN is set at +2 V by means of the series resistors R1 and R2. ...
DN142 - Ultralow Quiescent Current DC/DC Converters for Light Load Applications
... 100Hz, 95% to 98% duty cycle signal to the SHDN pin ensures that the circuit of Figure 1 comes out of shutdown frequently enough to maintain regulation during no-load or low-load conditions. Since the part spends nearly all of its time in shutdown, the no-load quiescent current (see Figure 4) is ap ...
... 100Hz, 95% to 98% duty cycle signal to the SHDN pin ensures that the circuit of Figure 1 comes out of shutdown frequently enough to maintain regulation during no-load or low-load conditions. Since the part spends nearly all of its time in shutdown, the no-load quiescent current (see Figure 4) is ap ...
www.BDTIC.com/TI Designing With Logic SDYA009C June 1997
... 2.1 Behavior With the Supply Voltage Switched Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1.1 Bipolar Circuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... 2.1 Behavior With the Supply Voltage Switched Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1.1 Bipolar Circuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Series Cicuit Lab
... Objectives: The purpose of this lab exercise will be to reinforce concepts learned in the classroom segment of Electricity/Electronics. These concepts include: series connected resistance is additive, voltage drop is additive, and current measurements through-out the circuit is the same. . Students ...
... Objectives: The purpose of this lab exercise will be to reinforce concepts learned in the classroom segment of Electricity/Electronics. These concepts include: series connected resistance is additive, voltage drop is additive, and current measurements through-out the circuit is the same. . Students ...
DC Slides
... We continue our exploration or DC circuits. There is a WebAssign which you should be able to answer later in the week. Feel free to actually read the textbook and start sooner! There will be a QUIZ on Friday. ...
... We continue our exploration or DC circuits. There is a WebAssign which you should be able to answer later in the week. Feel free to actually read the textbook and start sooner! There will be a QUIZ on Friday. ...
In this new setup, the current flowing across the Pt100/polysilicon...
... resistance during a 95 ºC - 0 s Æ 53 ºC - 0 s Æ 72 ºC - 0 s cycle. Two different slopes (green and blue boxes) can be distinctly observed during cooling (no actuator current) and heating periods, with punctuated transitions in between. The current-dependant effect is most marked at 72 ºC (black circ ...
... resistance during a 95 ºC - 0 s Æ 53 ºC - 0 s Æ 72 ºC - 0 s cycle. Two different slopes (green and blue boxes) can be distinctly observed during cooling (no actuator current) and heating periods, with punctuated transitions in between. The current-dependant effect is most marked at 72 ºC (black circ ...
Click Here (.doc)
... For this step we had to build the circuit of figure 10 and then use the triple output power supply for Vin and the other power supply for Vdc = 1.5V. Then we connected the com of the triple output power supply to the negative terminal of the other power supply. Then We measured Vout while varying Vi ...
... For this step we had to build the circuit of figure 10 and then use the triple output power supply for Vin and the other power supply for Vdc = 1.5V. Then we connected the com of the triple output power supply to the negative terminal of the other power supply. Then We measured Vout while varying Vi ...
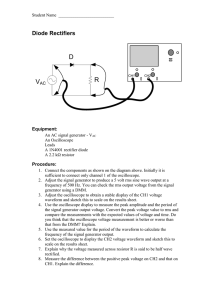
Diode Rectifiers
... Student Name __________________________ 9. Disconnect the diode D and instead connect the bridge rectifier module between VAC and R. 10. Measure and sketch the new voltage waveform across R to scale. Comment on the peak value of the new voltage waveform. 11. Suggest a reason why the bridge rectifie ...
... Student Name __________________________ 9. Disconnect the diode D and instead connect the bridge rectifier module between VAC and R. 10. Measure and sketch the new voltage waveform across R to scale. Comment on the peak value of the new voltage waveform. 11. Suggest a reason why the bridge rectifie ...
A Low-Impedance, Sub-Bandgap 0.6μm CMOS Reference with 0.84
... ultimately presenting a PTAT voltage across R13, the same one assumed and used in Eq. 2, where R12 is the series combination of R14 and R15. In the end, coefficients A, B, and C (i.e., R11-R15) from Eqs. (2) and (4) are designed to cancel and balance the CTAT behavior of diode voltage VD with the PT ...
... ultimately presenting a PTAT voltage across R13, the same one assumed and used in Eq. 2, where R12 is the series combination of R14 and R15. In the end, coefficients A, B, and C (i.e., R11-R15) from Eqs. (2) and (4) are designed to cancel and balance the CTAT behavior of diode voltage VD with the PT ...
Series-Parallel and More Self Test
... A: The first source converts to 10V/1k=10mA in parallel with 1k. The second converts to 20V/2k=10mA in parallel with 2k. This leaves a complete parallel-only circuit consisting of 20mA feeding 1k||2k||3k=545.5. The parallel voltage is 20mA*545.5=10.91V B: For superposition, consider each source by i ...
... A: The first source converts to 10V/1k=10mA in parallel with 1k. The second converts to 20V/2k=10mA in parallel with 2k. This leaves a complete parallel-only circuit consisting of 20mA feeding 1k||2k||3k=545.5. The parallel voltage is 20mA*545.5=10.91V B: For superposition, consider each source by i ...
Designreview2
... Currently, we have examined three separate methods to reduce total leakage in a circuit—input vector control, MTCMOS and variable threshold CMOS design. The input vector control method was motivated by the fact that in stacked circuits gate leakage has a much greater contribution to the overall leak ...
... Currently, we have examined three separate methods to reduce total leakage in a circuit—input vector control, MTCMOS and variable threshold CMOS design. The input vector control method was motivated by the fact that in stacked circuits gate leakage has a much greater contribution to the overall leak ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.