DNA Methylation studies
... DNA methylation is one of the several post-synthetic modifications that normal DNA goes through after each replication. Methylation does not alter the DNA sequence but alters its function, and it plays an important role by interfering DNA-protein interactions such as during transcription. DNA methyl ...
... DNA methylation is one of the several post-synthetic modifications that normal DNA goes through after each replication. Methylation does not alter the DNA sequence but alters its function, and it plays an important role by interfering DNA-protein interactions such as during transcription. DNA methyl ...
Exploring Mutant Organisms Teacher Extended Background
... is also mutated. The cell can no longer do the job it was meant for and it cannot destroy itself. It can only make more cells just like itself continuously. Cancer is also understood to be associated with an accumulation of mutations in the cell. That is, the cell requires a certain number of mutati ...
... is also mutated. The cell can no longer do the job it was meant for and it cannot destroy itself. It can only make more cells just like itself continuously. Cancer is also understood to be associated with an accumulation of mutations in the cell. That is, the cell requires a certain number of mutati ...
document
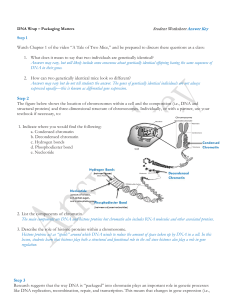
... explains how it can be replicated, or copied. • Each side, or strand, can make another copy. • DNA begins replication at one point and proceeds in both directions until replication is complete. ...
... explains how it can be replicated, or copied. • Each side, or strand, can make another copy. • DNA begins replication at one point and proceeds in both directions until replication is complete. ...
Central Dogma WebQuest - Life Science
... Answer each of the questions as you travel to the webpages below. Links can be found here: mvhslifescience.weebly.com → Biology → DNA → WebQuest (bottom of the page) From Gene to Protein: Transcription Complete the tutorial by clicking “Next Concept” and reading each page. Answer the questions and f ...
... Answer each of the questions as you travel to the webpages below. Links can be found here: mvhslifescience.weebly.com → Biology → DNA → WebQuest (bottom of the page) From Gene to Protein: Transcription Complete the tutorial by clicking “Next Concept” and reading each page. Answer the questions and f ...
Introduction to Genetics - Course ON-LINE
... Alleles are formed by mutations • Mutation is a change of the nucleotide sequence of DNA. • It may be positive, negative, or neutral. • There are many reasons for mutation. These can be classified as internal and external factors. ...
... Alleles are formed by mutations • Mutation is a change of the nucleotide sequence of DNA. • It may be positive, negative, or neutral. • There are many reasons for mutation. These can be classified as internal and external factors. ...
No Slide Title
... have multiple copies of plasmids, and when the bacterium dies, its plasmids are released into the environment where they can be incorporated into a different bacterium. Recombination in bacteria is common. Bacterial recombination can also take place by transduction, a process involving virus vectors ...
... have multiple copies of plasmids, and when the bacterium dies, its plasmids are released into the environment where they can be incorporated into a different bacterium. Recombination in bacteria is common. Bacterial recombination can also take place by transduction, a process involving virus vectors ...
Statement of purpose
... the metabolic genes. The basic molecular mechanism through which DNA recognition by AraR is abolished on arabinose binding is still unknown. This project aims to understand the mechanism of gene repression by AraR and release of this repression at the molecular level. I have determined crystal struc ...
... the metabolic genes. The basic molecular mechanism through which DNA recognition by AraR is abolished on arabinose binding is still unknown. This project aims to understand the mechanism of gene repression by AraR and release of this repression at the molecular level. I have determined crystal struc ...
Bacterial DNA Insert
... • How can you discriminate between bacteria that have taken up plasmid (either +/- insert) and the other 99.9% of the bacteria? – Take advantage of the drug resistance gene in the plasmid vector. • Ampr = gene that codes for an enzyme that breaks down ampicillin, a drug that stops bacterial cell div ...
... • How can you discriminate between bacteria that have taken up plasmid (either +/- insert) and the other 99.9% of the bacteria? – Take advantage of the drug resistance gene in the plasmid vector. • Ampr = gene that codes for an enzyme that breaks down ampicillin, a drug that stops bacterial cell div ...
DNA
... – When a gene coding for a human protein (like a hormone or enzyme) is inserted into bacteria, the new recombinant cells may produce LARGE amounts of the protein. – The human growth hormone, a hormone required for growth and development, was incredibly rare before genetic engineering. – Now these tr ...
... – When a gene coding for a human protein (like a hormone or enzyme) is inserted into bacteria, the new recombinant cells may produce LARGE amounts of the protein. – The human growth hormone, a hormone required for growth and development, was incredibly rare before genetic engineering. – Now these tr ...
In-Fusion HD Cloning Kit - Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
... After 1 hr of growth in 450 μl of SOC medium, 50 μl of the transformation culture was plated onto an LB Amp 100/Xgal/IPTG plate. At least 500 white colonies were observed for the cloning reaction. Notice to Purchaser Clontech products are to be used for research purposes only. They may not be used f ...
... After 1 hr of growth in 450 μl of SOC medium, 50 μl of the transformation culture was plated onto an LB Amp 100/Xgal/IPTG plate. At least 500 white colonies were observed for the cloning reaction. Notice to Purchaser Clontech products are to be used for research purposes only. They may not be used f ...
document
... Read the authors’ conclusions below, and with a partner discuss how these conclusions could be relevant for humans and summarize in your own words below. “In the present study, we observed a statistically significant shift in coat-color phenotype and adult body weight distribution among genetically ...
... Read the authors’ conclusions below, and with a partner discuss how these conclusions could be relevant for humans and summarize in your own words below. “In the present study, we observed a statistically significant shift in coat-color phenotype and adult body weight distribution among genetically ...
Biotechnology - clevengerscience
... bacteria • Insert new gene into plasmid • Insert plasmid into bacteria = vector • bacteria now expresses new gene and makes new protein transformed gene from other organism ...
... bacteria • Insert new gene into plasmid • Insert plasmid into bacteria = vector • bacteria now expresses new gene and makes new protein transformed gene from other organism ...
Genetics
... All living forms are closely related Genomes are modular, allowing rapid evolution Genetic techniques permit dissection of biological complexity Focus of this course is on human genetics ...
... All living forms are closely related Genomes are modular, allowing rapid evolution Genetic techniques permit dissection of biological complexity Focus of this course is on human genetics ...
Recombinant Expression of PDI in E. coli
... Gene Clonig of PDI 1 -PDI 1 Gene is attained from RT-PCR and has Ndel and BamHI sticky ends. -pET-15b Vector is cut at the BamHI and Ndel sites -This ensures that the correct reading frame is preserved so that proteins will be translated correctly. ...
... Gene Clonig of PDI 1 -PDI 1 Gene is attained from RT-PCR and has Ndel and BamHI sticky ends. -pET-15b Vector is cut at the BamHI and Ndel sites -This ensures that the correct reading frame is preserved so that proteins will be translated correctly. ...
DNA
... During this process, DNA fragments will migrate across a gelcoated plate – fragments are chemically treated so that the strands separate from each other RFLP DNA typing- used in impeachment trial of President Bill Clinton – semen stained dress of Ms. Lewinsky pg 372 ...
... During this process, DNA fragments will migrate across a gelcoated plate – fragments are chemically treated so that the strands separate from each other RFLP DNA typing- used in impeachment trial of President Bill Clinton – semen stained dress of Ms. Lewinsky pg 372 ...
DNA Fingerprinting
... Polymerase Chain Reaction - PCR • Invented by K.B Mullis in 1983 • Allows in vitro amplification of ANY DNA sequence in large numbers ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction - PCR • Invented by K.B Mullis in 1983 • Allows in vitro amplification of ANY DNA sequence in large numbers ...
advances in genetics
... females) with SIMILAR genes mate to produce offspring with similar traits • Possible problems: “bad” genes are also passed to the new generation ...
... females) with SIMILAR genes mate to produce offspring with similar traits • Possible problems: “bad” genes are also passed to the new generation ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.