Chapter 12-1 Part 2
... 3. Bacteria Extract + Carb destroying enzymes = transformation occurred (mouse alive or dead?) 4. Bacteria Extract + RNA destroying enzymes = transformation occurred (mouse alive or dead?) 5. Bacteria Extract + DNA destroying enzymes = transformation DID NOT OCCUR (mouse alive or dead?) ...
... 3. Bacteria Extract + Carb destroying enzymes = transformation occurred (mouse alive or dead?) 4. Bacteria Extract + RNA destroying enzymes = transformation occurred (mouse alive or dead?) 5. Bacteria Extract + DNA destroying enzymes = transformation DID NOT OCCUR (mouse alive or dead?) ...
DNA Replication
... How does mRNA tell the cell what to do? • mRNA is a message that codes for a protein • Proteins are made in the cytoplasm (at the – ...
... How does mRNA tell the cell what to do? • mRNA is a message that codes for a protein • Proteins are made in the cytoplasm (at the – ...
HONORS BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2015
... Cell Division and DNA: 1. A cell with 64 chromosomes undergoes meiotic division. What is the chromosome number in the daughter cell? 2. A cell with 88 chromosomes undergoes mitotic division. What is the chromosome number in the daughter cell? Draw a diagram of the steps the parent cell would have ta ...
... Cell Division and DNA: 1. A cell with 64 chromosomes undergoes meiotic division. What is the chromosome number in the daughter cell? 2. A cell with 88 chromosomes undergoes mitotic division. What is the chromosome number in the daughter cell? Draw a diagram of the steps the parent cell would have ta ...
ibbiochapter3geneticsppt(1)
... of 1st fragment(we’ll call it fragment 1).It will start to add free nucleotides by ____________________________ 2 kinds of nucleotides added • 3-Some nucleotides standard,but some special dideoxynucleotide triphosphates(ddNTP labeled ddA,ddT,ddC,ddG-figure 3.7-p.123)-added as DNA chain terminators-m ...
... of 1st fragment(we’ll call it fragment 1).It will start to add free nucleotides by ____________________________ 2 kinds of nucleotides added • 3-Some nucleotides standard,but some special dideoxynucleotide triphosphates(ddNTP labeled ddA,ddT,ddC,ddG-figure 3.7-p.123)-added as DNA chain terminators-m ...
Select one of your Biology instructors from another class and look
... 8.1 What are the translation initiation and stop codons in the genetic code? In a random sequence of four ribonucleotides, all with equal frequency, what is the probability that any three adjacent nucleotides will be a start codon? A stop codon? In an mRNA molecule of random sequence, what is the av ...
... 8.1 What are the translation initiation and stop codons in the genetic code? In a random sequence of four ribonucleotides, all with equal frequency, what is the probability that any three adjacent nucleotides will be a start codon? A stop codon? In an mRNA molecule of random sequence, what is the av ...
lay-person-summary
... blocks, A, T, G, and C, which are contained within a long strand. It is the specific sequence of these that controls cell development – this is known as ‘genetics’. Abnormal changes in the sequence are called mutations. DNA also has markers attached to it called methyl groups: These can regulate how ...
... blocks, A, T, G, and C, which are contained within a long strand. It is the specific sequence of these that controls cell development – this is known as ‘genetics’. Abnormal changes in the sequence are called mutations. DNA also has markers attached to it called methyl groups: These can regulate how ...
AP Biology - APBioKorzwiki
... After you have cloned & amplified DNA (genes), you can then tackle more ...
... After you have cloned & amplified DNA (genes), you can then tackle more ...
Protein Synthesis Activity
... DNA and RNA, the two types of nucleic acids found in cells, determine which protein molecules a cell makes, or synthesizes. Protein molecules, formed by sequencing twenty different amino acids in various combinations, are important to living things because they control biological pathways, direct th ...
... DNA and RNA, the two types of nucleic acids found in cells, determine which protein molecules a cell makes, or synthesizes. Protein molecules, formed by sequencing twenty different amino acids in various combinations, are important to living things because they control biological pathways, direct th ...
Framework for Teachable Unit
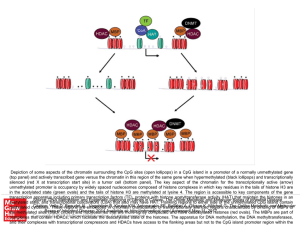
... _ increase in the recruitment of gene silencing proteins to the histone tail If a patient with cancer is found to have unusual patterns of methylation, then treating with HDAC inhibitors would have which effect(s)? Mark all that are true. _ decrease in the gene expression of gene X _ no change in ge ...
... _ increase in the recruitment of gene silencing proteins to the histone tail If a patient with cancer is found to have unusual patterns of methylation, then treating with HDAC inhibitors would have which effect(s)? Mark all that are true. _ decrease in the gene expression of gene X _ no change in ge ...
Midterm Practice Test
... 59) Where does Glycolysis occur in the cell? 60) In passive transport, molecules prefer to move from areas of __________ concentration to areas of __________ concentration. In active transport, molecules are passed in the opposite direction, from areas of __________ concentration to areas of _______ ...
... 59) Where does Glycolysis occur in the cell? 60) In passive transport, molecules prefer to move from areas of __________ concentration to areas of __________ concentration. In active transport, molecules are passed in the opposite direction, from areas of __________ concentration to areas of _______ ...
Electrical Biosensors in Microfluidic for High Throughput Genomics and Proteomics
... Electrical Biosensors in Microfluidic for High Throughput Genomics and Proteomics ...
... Electrical Biosensors in Microfluidic for High Throughput Genomics and Proteomics ...
Supplementary Information (doc 36K)
... centrifuged for 60 min at 15230 × g and the supernatant discarded. The pellet was washed twice by shaking the tube with the pellet and with 600 μl of 80% ethanol for 15 s, centrifuging for 5 min at maximum speed (17135 × g), and discarding the supernatant each time. The pellet in the tube was then ...
... centrifuged for 60 min at 15230 × g and the supernatant discarded. The pellet was washed twice by shaking the tube with the pellet and with 600 μl of 80% ethanol for 15 s, centrifuging for 5 min at maximum speed (17135 × g), and discarding the supernatant each time. The pellet in the tube was then ...
Activity--Extracting DNA - Challenger Learning Center
... The damage that may occur to the DNA contained in the cells may result in mutations that get passed along when the cell divides to form a new cell. A mutation is a random change in a gene or chromosome that results in a new trait. Mutations can alter the way the cell works and may have dangerous con ...
... The damage that may occur to the DNA contained in the cells may result in mutations that get passed along when the cell divides to form a new cell. A mutation is a random change in a gene or chromosome that results in a new trait. Mutations can alter the way the cell works and may have dangerous con ...
Slide 1
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) makes several copies of the same gene by repeated heating and cooling ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) makes several copies of the same gene by repeated heating and cooling ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.