Biology I ECA Review Standard 7 Genetics
... allelic and polygenic traits and illustrate their inheritance patterns over multiple generations. 7.3 Determine the likelihood of the appearance of a specific trait in an offspring given the genetic make-up of the parents. 7.4 Explain the process by which a cell copies its DNA and identify facto ...
... allelic and polygenic traits and illustrate their inheritance patterns over multiple generations. 7.3 Determine the likelihood of the appearance of a specific trait in an offspring given the genetic make-up of the parents. 7.4 Explain the process by which a cell copies its DNA and identify facto ...
Single Cell DNA Damage/Repair Assay Using HaloChip
... double strand break) to be repaired, or damaged DNAs have to be involved in cell functions before they can be repaired, the damages will be inherited and accumulated,3 leading to mutations that can eventually cause diseases such as cancers and central neuron system diseases, etc.4−6 Although a panel ...
... double strand break) to be repaired, or damaged DNAs have to be involved in cell functions before they can be repaired, the damages will be inherited and accumulated,3 leading to mutations that can eventually cause diseases such as cancers and central neuron system diseases, etc.4−6 Although a panel ...
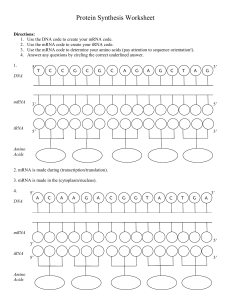
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 11. Transcription takes place in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 12. tRNA is used in (translation/transcription). 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus ...
... 11. Transcription takes place in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 12. tRNA is used in (translation/transcription). 13. tRNA uses (anticodons/codons) to match to the mRNA. 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus ...
slg mock midterm – for practice only
... b. Each strand of both daughter molecules contains a mixture of old and newly synthesized DNA. c. The two strands of the parental molecule separate, and each functions as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. d. DNA Polymerase III carries out synthesis by extending from the RNA pr ...
... b. Each strand of both daughter molecules contains a mixture of old and newly synthesized DNA. c. The two strands of the parental molecule separate, and each functions as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. d. DNA Polymerase III carries out synthesis by extending from the RNA pr ...
Assessing the biocompatibility of click
... that instead of enzymes, uses highly efficient chemical reactions for the ligation of oligonucleotides (5–7). Such an approach would not only eliminate the need for enzymatic ligation and cloning during gene synthesis to enable the full automation of large-scale gene synthesis, but also readily allow ...
... that instead of enzymes, uses highly efficient chemical reactions for the ligation of oligonucleotides (5–7). Such an approach would not only eliminate the need for enzymatic ligation and cloning during gene synthesis to enable the full automation of large-scale gene synthesis, but also readily allow ...
Decoding the message_2 - Molecular-Biology-Resource
... F F PART B Answer the questions below. 1) Several codons code for “spc”. Explain why this is an advantage or disadvantage for the organism. A change in a single base may not necessarily result in a change in amino acid. Therefore, it would be an advantage for the organism to have multiple codons for ...
... F F PART B Answer the questions below. 1) Several codons code for “spc”. Explain why this is an advantage or disadvantage for the organism. A change in a single base may not necessarily result in a change in amino acid. Therefore, it would be an advantage for the organism to have multiple codons for ...
Quiz 3 Solutions
... No. You need a selection marker on your second plasmid, but you would not want it to be the same marker as your first plasmid. If you used the same marker, you would never know if your bacteria had the second plasmid. You could only be sure that the bacteria had the first plasmid. Therefore, you wou ...
... No. You need a selection marker on your second plasmid, but you would not want it to be the same marker as your first plasmid. If you used the same marker, you would never know if your bacteria had the second plasmid. You could only be sure that the bacteria had the first plasmid. Therefore, you wou ...
DNA Replication and Telomere Maintenance
... Bacterial DNA polymerases have multiple functions DNA polymerase I • Primer removal, gap filling between Okazaki fragments, and nucleotide excision repair pathway. • Two subunits: Klenow fragment has 5′→3′ polymerase activity; other subunit has both 3′→5′ and 5′→3′ exonuclease activity. • Unique ab ...
... Bacterial DNA polymerases have multiple functions DNA polymerase I • Primer removal, gap filling between Okazaki fragments, and nucleotide excision repair pathway. • Two subunits: Klenow fragment has 5′→3′ polymerase activity; other subunit has both 3′→5′ and 5′→3′ exonuclease activity. • Unique ab ...
Understanding Our Environment - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... - Gene Expression - Use of information in DNA to direct production of particular proteins. Transcription - mRNA molecule is synthesized from gene within DNA. Translation - mRNA used to direct protein production. Johnson - The Living World: 3rd Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies ...
... - Gene Expression - Use of information in DNA to direct production of particular proteins. Transcription - mRNA molecule is synthesized from gene within DNA. Translation - mRNA used to direct protein production. Johnson - The Living World: 3rd Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies ...
The dnrM gene in Streptomyces peucetius contains a
... vector pGEX-4 was obtained from Pharmacia. The high-copy number E. coli-Streptomyces shuttle vector pWHM3 was from Vara e t al. (1989). M13 phage-derived mp18 and mp19 vectors (Yanisch-Perron e t al., 1985) were used for sequencing by previously published methods (Summers e t a/., 1992). The pUC4-KI ...
... vector pGEX-4 was obtained from Pharmacia. The high-copy number E. coli-Streptomyces shuttle vector pWHM3 was from Vara e t al. (1989). M13 phage-derived mp18 and mp19 vectors (Yanisch-Perron e t al., 1985) were used for sequencing by previously published methods (Summers e t a/., 1992). The pUC4-KI ...
CRISPR| Cas Gene Editing - Federation of American Societies for
... invaders. Illustration: © Michael Linkinhoker, Link Studio, LLC. ...
... invaders. Illustration: © Michael Linkinhoker, Link Studio, LLC. ...
PDF version
... made by commercial genotyping labs. The NBCEC is a group of researchers at some of the land-grant universities who work in quantitative and molecular genetics. Validation is initiated when a commercial lab request the NBCEC validates their marker claim. The NBCEC organizes a resource population to t ...
... made by commercial genotyping labs. The NBCEC is a group of researchers at some of the land-grant universities who work in quantitative and molecular genetics. Validation is initiated when a commercial lab request the NBCEC validates their marker claim. The NBCEC organizes a resource population to t ...
Tech Notes Mutagenesis of Amplified DNA Sequences Using Ampligase
... relies on the absence of strand displacement activity of the thermostable polymerase which allows annealing of an internal mutagenic primer to the template strand. Phosphorylation of the 5´-end of the mutagenic primer allows thermostable ligase-mediated incorporation into the final full-length ampli ...
... relies on the absence of strand displacement activity of the thermostable polymerase which allows annealing of an internal mutagenic primer to the template strand. Phosphorylation of the 5´-end of the mutagenic primer allows thermostable ligase-mediated incorporation into the final full-length ampli ...
2.4 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... make up subunits –Each ribosome contains 2 subunits: large and small and associate to form 2 grooves A (aminoacyl) and P (peptidyl) site into which tRNA molecules bind and also E (exit) site which tRNA molecules leave the ...
... make up subunits –Each ribosome contains 2 subunits: large and small and associate to form 2 grooves A (aminoacyl) and P (peptidyl) site into which tRNA molecules bind and also E (exit) site which tRNA molecules leave the ...
περισσότερες πληροφορίες
... 3β. ….συνέχεια However, some eukaryotic proteins are processed after translation. This is the case for insulin, which is initially translated as pre-pro-insulin and through subsequent passages of maturation reaches the final sequence and conformation. In bacteria, such maturation processes do not t ...
... 3β. ….συνέχεια However, some eukaryotic proteins are processed after translation. This is the case for insulin, which is initially translated as pre-pro-insulin and through subsequent passages of maturation reaches the final sequence and conformation. In bacteria, such maturation processes do not t ...
II. The selected examples
... II. The selected examples - Phage T7 5. In fact, transcription of the late genes by the gene 1 product may help pull the DNA into the cell, causing sequential gene expression. 6. The specificity of phage RNA polymerase for their own promoter has been exploited in many applications in molecular gene ...
... II. The selected examples - Phage T7 5. In fact, transcription of the late genes by the gene 1 product may help pull the DNA into the cell, causing sequential gene expression. 6. The specificity of phage RNA polymerase for their own promoter has been exploited in many applications in molecular gene ...
Frequently Asked Questions about Red/ET Cloning
... A bacterial strain expressing Red/ET proteins directly from the chromosome like YZ2000 shows comparable efficiency to a bacterial strain electroporated with a Red/ET proficiency plasmid. In the latter case, the recombination system is only active for a short period of time so that the integrity of t ...
... A bacterial strain expressing Red/ET proteins directly from the chromosome like YZ2000 shows comparable efficiency to a bacterial strain electroporated with a Red/ET proficiency plasmid. In the latter case, the recombination system is only active for a short period of time so that the integrity of t ...
Drug resistance of bacteria commensal with Drosophila
... size-classes of ampicillin-resistance plasmids were recovered from supposedly cloned bacteria. Since each of these was isolated from the same contaminating bacteria and expressed the same antibiotic resistance pattern, it is likely that they represent derivatives from a single plasmid in the contami ...
... size-classes of ampicillin-resistance plasmids were recovered from supposedly cloned bacteria. Since each of these was isolated from the same contaminating bacteria and expressed the same antibiotic resistance pattern, it is likely that they represent derivatives from a single plasmid in the contami ...
Section 14. Pedigree Analysis and Molecular Markers
... appear before individuals reach reproductive maturity. Show incomplete penetrance = failure to be expressed in all individuals of the appropriate genotype. e.g. Huntington's disease (Huntington's chorea): age penetrance = proportion of individuals who are known to carry the genotype for the disease ...
... appear before individuals reach reproductive maturity. Show incomplete penetrance = failure to be expressed in all individuals of the appropriate genotype. e.g. Huntington's disease (Huntington's chorea): age penetrance = proportion of individuals who are known to carry the genotype for the disease ...
Section 6.3 Mutations
... even some vertebrates also use another system not present in humans. In these organisms, energy from light, enzymes, and other chemical molecules is used to change the DNA back into its original, undamaged shape. In another method of DNA repair, damage caused by free radicals and other cellular mole ...
... even some vertebrates also use another system not present in humans. In these organisms, energy from light, enzymes, and other chemical molecules is used to change the DNA back into its original, undamaged shape. In another method of DNA repair, damage caused by free radicals and other cellular mole ...
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Mendel and His Peas Lesson 2
... • In an insertion mutation, one or more nitrogen bases is added to the DNA. • In a substitution mutation, one nitrogen base is replaced by a different nitrogen base. ...
... • In an insertion mutation, one or more nitrogen bases is added to the DNA. • In a substitution mutation, one nitrogen base is replaced by a different nitrogen base. ...
Ch. 5 LEcture PPt
... • In a deletion mutation, one or more nitrogen base is left out of the DNA sequence. • In an insertion mutation, one or more nitrogen bases is added to the DNA. ...
... • In a deletion mutation, one or more nitrogen base is left out of the DNA sequence. • In an insertion mutation, one or more nitrogen bases is added to the DNA. ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.