Genetic Control of Cell Function
... of the structural proteins and enzymes needed for protein synthesis. As with the other types of RNA, rRNA is synthesized in the nucleus. Unlike other RNAs, ribosomal RNA is produced in a specialized nuclear structure called the nucleolus. The formed rRNA combines with ribosomal proteins in the nucle ...
... of the structural proteins and enzymes needed for protein synthesis. As with the other types of RNA, rRNA is synthesized in the nucleus. Unlike other RNAs, ribosomal RNA is produced in a specialized nuclear structure called the nucleolus. The formed rRNA combines with ribosomal proteins in the nucle ...
File
... they could plant their own crops and breed their own animals, they learned to use biotechnology. The discovery that fruit juices fermented into wine, or that milk could be converted into cheese or yogurt, or that beer could be made by fermenting solutions of malt and hops began the study of biotec ...
... they could plant their own crops and breed their own animals, they learned to use biotechnology. The discovery that fruit juices fermented into wine, or that milk could be converted into cheese or yogurt, or that beer could be made by fermenting solutions of malt and hops began the study of biotec ...
Geometrical ordering of DNA in bacteria
... chromosome is represented by a self-avoiding random walk on this lattice. (3) Each step of the random walk represents a compacted unit of the chromosome. Compaction is the key ingredient of our model that is required to obtain the experimentally observed linear correlation. The specific scenario tha ...
... chromosome is represented by a self-avoiding random walk on this lattice. (3) Each step of the random walk represents a compacted unit of the chromosome. Compaction is the key ingredient of our model that is required to obtain the experimentally observed linear correlation. The specific scenario tha ...
The BCM Microarray Core Facility
... The Microarray Core Facility (MCF) at Baylor College of Medicine provides investigators with access to a variety of state-of-the-art technologies and approaches that will enhance discovery for their genomic research. We house instrumentation supporting Affymetrix, Agilent, NimbleGen, Luminex, and Il ...
... The Microarray Core Facility (MCF) at Baylor College of Medicine provides investigators with access to a variety of state-of-the-art technologies and approaches that will enhance discovery for their genomic research. We house instrumentation supporting Affymetrix, Agilent, NimbleGen, Luminex, and Il ...
Tracking bacterial DNA replication forks in vivo by pulsed field gel
... Intact chromosomal DNA was prepared in agarose and digested with the restriction enzyme Not I. The resulting Not I fragments were fractionated by PFG electrophoresis. Exposure of this gel to X-ray film revealed the time-dependent incorporation of 14C-thymidine into various Not I fragments (Figure 2) ...
... Intact chromosomal DNA was prepared in agarose and digested with the restriction enzyme Not I. The resulting Not I fragments were fractionated by PFG electrophoresis. Exposure of this gel to X-ray film revealed the time-dependent incorporation of 14C-thymidine into various Not I fragments (Figure 2) ...
History of Biotech and Biotech Applications
... they could plant their own crops and breed their own animals, they learned to use biotechnology. The discovery that fruit juices fermented into wine, or that milk could be converted into cheese or yogurt, or that beer could be made by fermenting solutions of malt and hops began the study of biotec ...
... they could plant their own crops and breed their own animals, they learned to use biotechnology. The discovery that fruit juices fermented into wine, or that milk could be converted into cheese or yogurt, or that beer could be made by fermenting solutions of malt and hops began the study of biotec ...
Newsletter 1
... common male ancestor. A similar test for a common female ancestor is also available using ‘mitochondrial’ DNA, but as names in our society pass down the male line, this is less useful for many family history purposes. Specific parts of the Y-chromosome known as ‘markers’ are used to make such compar ...
... common male ancestor. A similar test for a common female ancestor is also available using ‘mitochondrial’ DNA, but as names in our society pass down the male line, this is less useful for many family history purposes. Specific parts of the Y-chromosome known as ‘markers’ are used to make such compar ...
cDNA Sequences of Three Kinds of /3
... 100th amino acid residue of /3-tubulin, since isoleucine or valine instead of asparagine at the 100th residue in yeast results in a resistant phenotype.9 For the progress in breeding new types of rice which have resistance to seedling blight disease using genetic engineering, characterization of /3- ...
... 100th amino acid residue of /3-tubulin, since isoleucine or valine instead of asparagine at the 100th residue in yeast results in a resistant phenotype.9 For the progress in breeding new types of rice which have resistance to seedling blight disease using genetic engineering, characterization of /3- ...
Unoshan_project
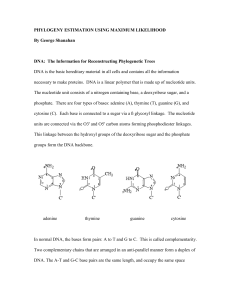
... directions, and the bases of the individual nucleotides are on the inside of the helix, stacked on top of each other. The larger base shape shown in the picture above depicts the purines (adenine and guanine). The other base shape in the illustration represents the pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) ...
... directions, and the bases of the individual nucleotides are on the inside of the helix, stacked on top of each other. The larger base shape shown in the picture above depicts the purines (adenine and guanine). The other base shape in the illustration represents the pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) ...
How Relevant is the Escherichia coli UvrABC Model for Excision
... DNA helicases operate in eukaryotic nucleotide excision. In addition, a striking sequence conservation is noted between human and yeast repair proteins. But no eukaryotic homologs of the UvrABC proteins have been identified. In this Commentary the parallels and differences between the prokaryotic an ...
... DNA helicases operate in eukaryotic nucleotide excision. In addition, a striking sequence conservation is noted between human and yeast repair proteins. But no eukaryotic homologs of the UvrABC proteins have been identified. In this Commentary the parallels and differences between the prokaryotic an ...
DNA, Inheritance, and Genetic Variation
... replication and protein synthesis. First, they model how one DNA molecule copies itself during DNA replication to produce two identical daughter molecules. Next, they explore how a gene works and model the process of protein synthesis. ...
... replication and protein synthesis. First, they model how one DNA molecule copies itself during DNA replication to produce two identical daughter molecules. Next, they explore how a gene works and model the process of protein synthesis. ...
Rice 5 S Ribosomal RNA and Its Binding Protein Genes: Structure
... signals than the others because they presumably contain more copies of the 5 S ribosomal RNA gene. Restriction enzyme analysis and Southern blot hybridization by using [ 32PHabeled flax 5 S ribosomal DNA showed that these three plaques are identical. A 5.0 kb EcoRl fragment from the phage DNA that c ...
... signals than the others because they presumably contain more copies of the 5 S ribosomal RNA gene. Restriction enzyme analysis and Southern blot hybridization by using [ 32PHabeled flax 5 S ribosomal DNA showed that these three plaques are identical. A 5.0 kb EcoRl fragment from the phage DNA that c ...
BIOT 3 Lecture 4 Gel Electrophoresis
... • composition of the buffer in the gels, wells and chambers are similar • Gel pore size and molecular charge density are the only factors that have any effect on stacking • Limited in separating smaller molecules, smaller molecules have less of a difference between their mobility Discontinuous buffe ...
... • composition of the buffer in the gels, wells and chambers are similar • Gel pore size and molecular charge density are the only factors that have any effect on stacking • Limited in separating smaller molecules, smaller molecules have less of a difference between their mobility Discontinuous buffe ...
Challenging traditional approaches to
... computers will hopefully integrate into biological systems. Because these machines are capable of a biological output, this project is literally cutting-edge science. These devices are unlikely to replace the common computer. Instead, due to their capability for direct interface, the importance of b ...
... computers will hopefully integrate into biological systems. Because these machines are capable of a biological output, this project is literally cutting-edge science. These devices are unlikely to replace the common computer. Instead, due to their capability for direct interface, the importance of b ...
Probabilities and Probabilistic Models
... • a one-pass algorithm based on approximate matching • For a given input string w, assume that a part v has already been compressed and the remaining part is u, with w = vu. The algorithm finds an “optimal prefix” p of u that approximately matches some substring of v such that p can be encoded econo ...
... • a one-pass algorithm based on approximate matching • For a given input string w, assume that a part v has already been compressed and the remaining part is u, with w = vu. The algorithm finds an “optimal prefix” p of u that approximately matches some substring of v such that p can be encoded econo ...
Transcription and Translation ppt
... determine the phenotypical characteristics of organisms. Genes also direct the production of other physiologically essential proteins such as antibodies and hormones. Proteins drive cellular processes such as metabolism; determining physical characteristics and producing genetic disorders by their a ...
... determine the phenotypical characteristics of organisms. Genes also direct the production of other physiologically essential proteins such as antibodies and hormones. Proteins drive cellular processes such as metabolism; determining physical characteristics and producing genetic disorders by their a ...
Classification of Microorganisms
... DNA fingerprinting: Number and sizes of DNA fragments (fingerprints) produced by RE digests are used to determine genetic similarities. Ribotyping: rRNA sequencing ...
... DNA fingerprinting: Number and sizes of DNA fragments (fingerprints) produced by RE digests are used to determine genetic similarities. Ribotyping: rRNA sequencing ...
PowerPoint file
... DNA fingerprinting: Number and sizes of DNA fragments (fingerprints) produced by RE digests are used to determine genetic similarities. Ribotyping: rRNA sequencing Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can be used to amplify a small amount of microbial DNA in a sample. The Fig 10.14: Electrophoresis ...
... DNA fingerprinting: Number and sizes of DNA fragments (fingerprints) produced by RE digests are used to determine genetic similarities. Ribotyping: rRNA sequencing Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can be used to amplify a small amount of microbial DNA in a sample. The Fig 10.14: Electrophoresis ...
Fly-FISHing: A protocol to localize single copy genes inside the
... Nurminsky, R. Jones, and E. Lozovskaya 1994, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 6824-6829; Hiraoka, Y., A.F. Dernburg, S.J. Parmelee, M.C. Rykowski, D.A. Agard, and J.W. Sedat 1993, J. Cell Biol. 120: 591-600; Risau, W., H. Saumweber, and P. Symmons 1981, Exp. Cell Res. 33: 529-541; Tautz, D., and ...
... Nurminsky, R. Jones, and E. Lozovskaya 1994, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 6824-6829; Hiraoka, Y., A.F. Dernburg, S.J. Parmelee, M.C. Rykowski, D.A. Agard, and J.W. Sedat 1993, J. Cell Biol. 120: 591-600; Risau, W., H. Saumweber, and P. Symmons 1981, Exp. Cell Res. 33: 529-541; Tautz, D., and ...
... would like to characterize these altered reverse transcriptases to understand the reduced binding of the drug as well as to perhaps design new drugs to target the mutant viruses. These mutant enzymes would be produced in E. Coli. In this problem you must do both Parts i and ii. You have a choice wit ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.