Constructing a Model of Protein Synthesis
... a. What is the order of bases on the complementary strand of mRNA? b. What is the sequence of amino acids that would result from this molecule? 17. How might one change in a DNA nucleotide change the formation of the protein? What is this change called? ...
... a. What is the order of bases on the complementary strand of mRNA? b. What is the sequence of amino acids that would result from this molecule? 17. How might one change in a DNA nucleotide change the formation of the protein? What is this change called? ...
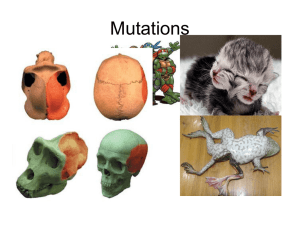
MUTATIONS
... - alters codon changing it to a STOP codon and only part of the protein is translated - lead to non-functional proteins ...
... - alters codon changing it to a STOP codon and only part of the protein is translated - lead to non-functional proteins ...
What is Biotechnology?
... ● DNA is made in a test tube for the first time. ● Sickle cell disease is shown to occur due to a change in one amino acid. ...
... ● DNA is made in a test tube for the first time. ● Sickle cell disease is shown to occur due to a change in one amino acid. ...
Transduction
... Terminology in microbial genetics • Prototroph: “original” and “feed”, a wild type strain, one able to synthesize all needed compounds from a simple carbon source such as glucose. • Auxotroph: a mutant that has lost the ability to make some necessary organic compound; it must be added to the cultur ...
... Terminology in microbial genetics • Prototroph: “original” and “feed”, a wild type strain, one able to synthesize all needed compounds from a simple carbon source such as glucose. • Auxotroph: a mutant that has lost the ability to make some necessary organic compound; it must be added to the cultur ...
CHAPTER 21
... E11. In general terms, what is a polymorphism? Explain the molecular basis for a restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). How is an RFLP detected experimentally? Why are RFLPs useful in physical mapping studies? How can they be used to clone a particular gene? Answer: A polymorphism refers t ...
... E11. In general terms, what is a polymorphism? Explain the molecular basis for a restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). How is an RFLP detected experimentally? Why are RFLPs useful in physical mapping studies? How can they be used to clone a particular gene? Answer: A polymorphism refers t ...
Introduction to DNA Computing
... Recombinant DNA Technology •Cleavage DNA at specific sites by restriction enzymes,which greatly facilitates the isolation and manipulation of individual DNA. •Rapid sequencing of all the nucleotides in a purified DNA fragment, which makes it possible to determine the boundaries of a gene and the am ...
... Recombinant DNA Technology •Cleavage DNA at specific sites by restriction enzymes,which greatly facilitates the isolation and manipulation of individual DNA. •Rapid sequencing of all the nucleotides in a purified DNA fragment, which makes it possible to determine the boundaries of a gene and the am ...
Presentation - IAC 2016, New Delhi
... The ‘game-changer’ in microbiology Application of rRNA gene barcoding 16S rRNA gene, D1/D2 26S rRNA gene 18S rRNA gene ...
... The ‘game-changer’ in microbiology Application of rRNA gene barcoding 16S rRNA gene, D1/D2 26S rRNA gene 18S rRNA gene ...
The Molecule of Life: DNA
... Ethanol is less dense than water so it floats on top. All of the proteins we broke up in Step 4 will sink to the bottom; the DNA will float on top. ...
... Ethanol is less dense than water so it floats on top. All of the proteins we broke up in Step 4 will sink to the bottom; the DNA will float on top. ...
Document
... • Many antibiotics are the result of industrial production. – Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be produced on an industrial scale. – Antibiotic production can involve fermentation, producing natural antibiotics or semisynthetic drugs. ...
... • Many antibiotics are the result of industrial production. – Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be produced on an industrial scale. – Antibiotic production can involve fermentation, producing natural antibiotics or semisynthetic drugs. ...
--- The Language of Biotechnology
... – They are everywhere and shape our visible world – They have widest range of diversity – They have adapted to survive in extremely wide range of environments ...
... – They are everywhere and shape our visible world – They have widest range of diversity – They have adapted to survive in extremely wide range of environments ...
Recitation 4 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... will have the genoptye Aa. They will display whichever of the two phenotypes is dominant. If you cross two F1 organisms together (Aa x Aa), you create the F2 generation. The ratios of different genotypes and phenotypes within the F2 generation can be derived either by using the laws of basic probabi ...
... will have the genoptye Aa. They will display whichever of the two phenotypes is dominant. If you cross two F1 organisms together (Aa x Aa), you create the F2 generation. The ratios of different genotypes and phenotypes within the F2 generation can be derived either by using the laws of basic probabi ...
5.DNA - Colorado State University
... We are going to take the first steps done in DNA fingerprinting by forensic scientists—isolating the DNA. DNA has a charge, like electricity, and it can stick to water. We want to neutralize that charge before we isolate our DNA, so we add salt. Our DNA is located inside a membrane-bound nucleus tha ...
... We are going to take the first steps done in DNA fingerprinting by forensic scientists—isolating the DNA. DNA has a charge, like electricity, and it can stick to water. We want to neutralize that charge before we isolate our DNA, so we add salt. Our DNA is located inside a membrane-bound nucleus tha ...
the language of biology - Gonzaga College High School
... and control the sythesis (making) of other biomolecules (carbohydrates, fats and lipids, and nucleic acids) hormones regulate various processes in the organism, such as growth and the menstrual cycle. other proteins are structural molecules, such as keratin (which forms fingernails and hair) and col ...
... and control the sythesis (making) of other biomolecules (carbohydrates, fats and lipids, and nucleic acids) hormones regulate various processes in the organism, such as growth and the menstrual cycle. other proteins are structural molecules, such as keratin (which forms fingernails and hair) and col ...
2017 PUERTO RICO PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY ANNUAL
... Characterization of the rhizosphere microbiome of Tabebuia heterophylla, a tree native to the West Indies, in order to understand how the microbes may contribute to the plasticity of the tree and enable its growth in poor nutrient, heavy-metal rich and disturbed soils; 2) Mining for lignocellulose c ...
... Characterization of the rhizosphere microbiome of Tabebuia heterophylla, a tree native to the West Indies, in order to understand how the microbes may contribute to the plasticity of the tree and enable its growth in poor nutrient, heavy-metal rich and disturbed soils; 2) Mining for lignocellulose c ...
Document
... A plasmid is an extrachromosomal DNA molecule separate from the chromosomal DNA which is capable of replicating independently of the chromosomal DNA. In many cases, it is circular and doublestranded. Plasmids usually occur naturally in bacteria, but are sometimes found in eukaryotic organisms. ...
... A plasmid is an extrachromosomal DNA molecule separate from the chromosomal DNA which is capable of replicating independently of the chromosomal DNA. In many cases, it is circular and doublestranded. Plasmids usually occur naturally in bacteria, but are sometimes found in eukaryotic organisms. ...
Pretest and Post Test Questions
... SC.912.L.16.9: Explain how and why the genetic code is universal and is common to almost all organisms. SC 912.L.16.3: Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. 1) DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus is used in ...
... SC.912.L.16.9: Explain how and why the genetic code is universal and is common to almost all organisms. SC 912.L.16.3: Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. 1) DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus is used in ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... Explain why people are screened for certain genetic conditions. Explain the difference between curing a medical problem and managing or treating the ...
... Explain why people are screened for certain genetic conditions. Explain the difference between curing a medical problem and managing or treating the ...
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
... into single stranded DNA. This can be done by denaturing the double stranded DNA with NaOH. A Sanger reaction consists of the following: a strand to be sequenced (one of the single strands which was denatured using NaOH), DNA primers (short pieces of DNA that are both complementary to the strand whi ...
... into single stranded DNA. This can be done by denaturing the double stranded DNA with NaOH. A Sanger reaction consists of the following: a strand to be sequenced (one of the single strands which was denatured using NaOH), DNA primers (short pieces of DNA that are both complementary to the strand whi ...
I Preparation of Metaphase Chromosomes
... Buffer solution, providing a suitable chemical environment for optimum activity and stability of the DNA polymerase. Divalent cations; generally Mg2+ is used 2.Denaturation step: This step is the first regular cycling event and consists of heating the reaction to 94–98 °C for 20–30 seconds. It cause ...
... Buffer solution, providing a suitable chemical environment for optimum activity and stability of the DNA polymerase. Divalent cations; generally Mg2+ is used 2.Denaturation step: This step is the first regular cycling event and consists of heating the reaction to 94–98 °C for 20–30 seconds. It cause ...
Document
... b. reduced functioning of the skin cell c. no change in functioning of the skin cell d. the person's offspring have mutated skin 7. The pairing of _____ in DNA is the key feature that allows DNA to be copied. a. nucleotides c. chromosomes b. nitrogen bases d. codons 8. The process by which a DNA mol ...
... b. reduced functioning of the skin cell c. no change in functioning of the skin cell d. the person's offspring have mutated skin 7. The pairing of _____ in DNA is the key feature that allows DNA to be copied. a. nucleotides c. chromosomes b. nitrogen bases d. codons 8. The process by which a DNA mol ...