III. MATERIAL AND METHODS The present study was undertaken
... Taqpolymerase enzyme (Genei, India), two concentrations each of DNA (5, 10 ng) and dNTP (0.1, 0.2 mM, Eppendorf, USA) were varied in different combinations and the combination that gave good amplification was selected and used for further experiments. Amplifications were performed in a final volume ...
... Taqpolymerase enzyme (Genei, India), two concentrations each of DNA (5, 10 ng) and dNTP (0.1, 0.2 mM, Eppendorf, USA) were varied in different combinations and the combination that gave good amplification was selected and used for further experiments. Amplifications were performed in a final volume ...
DNA ppt
... 1. Enzyme (helicase) unzips the DNA. 2. DNA polymerase (enzyme) matches the correct nucleotide to each side of the unzipped DNA. 3. DNA polymerase – proofreads their replication to make sure they did not make any mistakes. ...
... 1. Enzyme (helicase) unzips the DNA. 2. DNA polymerase (enzyme) matches the correct nucleotide to each side of the unzipped DNA. 3. DNA polymerase – proofreads their replication to make sure they did not make any mistakes. ...
Gene Regulation
... if bacterium has enough tryptophan then it doesn’t need to make enzymes used to build tryptophan • turn genes ON example if bacterium encounters new sugar (energy source), like lactose, then it needs to start making enzymes used to digest lactose ...
... if bacterium has enough tryptophan then it doesn’t need to make enzymes used to build tryptophan • turn genes ON example if bacterium encounters new sugar (energy source), like lactose, then it needs to start making enzymes used to digest lactose ...
DNA Replication Paper Lab
... alive, there must be a way to make sure every new cell gets these instructions. A new cell is made by already existing cells, therefore, there is a mechanism to copy these “life instructions” into new cells. DNA has the instructions for life coded by the order in which the nucleotides occur in a chr ...
... alive, there must be a way to make sure every new cell gets these instructions. A new cell is made by already existing cells, therefore, there is a mechanism to copy these “life instructions” into new cells. DNA has the instructions for life coded by the order in which the nucleotides occur in a chr ...
Linkage
... Terminology in microbial genetics • Prototroph: “original” and “feed”, a wild type strain, one able to synthesize all needed compounds from a simple carbon source such as glucose. • Auxotroph: a mutant that has lost the ability to make some necessary organic compound; it must be added to the cultur ...
... Terminology in microbial genetics • Prototroph: “original” and “feed”, a wild type strain, one able to synthesize all needed compounds from a simple carbon source such as glucose. • Auxotroph: a mutant that has lost the ability to make some necessary organic compound; it must be added to the cultur ...
Phylogenetic analysis of phytoplasmas based on sequences
... Previous analysis based primarily on the 16S rDNA gene has indicated that the aster yellows group phytoplasmas (16SrI) form a distinct subclade within the phytoplasma clade, and further analyses of this subclade using genes such as secY and tuf have subdivided this group into distinct lineages (Lee ...
... Previous analysis based primarily on the 16S rDNA gene has indicated that the aster yellows group phytoplasmas (16SrI) form a distinct subclade within the phytoplasma clade, and further analyses of this subclade using genes such as secY and tuf have subdivided this group into distinct lineages (Lee ...
Vocabulary List
... 5. Nitrogenous Bases – the parts of DNA and RNA that pair (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 6. DNA Replication – the process of making another copy of the genetic code by a semi-conservative process. Occurs within the nucleus 7. DNA Polymerase – enzyme that links DNA nucleotides together during ...
... 5. Nitrogenous Bases – the parts of DNA and RNA that pair (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 6. DNA Replication – the process of making another copy of the genetic code by a semi-conservative process. Occurs within the nucleus 7. DNA Polymerase – enzyme that links DNA nucleotides together during ...
Unzipping Genes - HiMedia Laboratories
... Salmonella is a gram-negative, rod-shaped, facultative intracellular pathogen. Salmonellae live in the intestinal tracts of warm- and cold-blooded animals. Some species are ubiquitous while other species are specifically adapted to a particular host. In humans, Salmonella are the cause of two diseas ...
... Salmonella is a gram-negative, rod-shaped, facultative intracellular pathogen. Salmonellae live in the intestinal tracts of warm- and cold-blooded animals. Some species are ubiquitous while other species are specifically adapted to a particular host. In humans, Salmonella are the cause of two diseas ...
chap-4 - Workforce3One
... end recognizing each enzyme • The insert DNA is placed into the vector in only 1 orientation • Vector religation is also prevented as the two restriction sites are incompatible ...
... end recognizing each enzyme • The insert DNA is placed into the vector in only 1 orientation • Vector religation is also prevented as the two restriction sites are incompatible ...
Microbes in nutrition Digestion vast majority of GI tract bacteria are
... d. certain hydrocarbons are optically active (known to occur only as a result of biological systems) e. data not conclusive - all features could have resulted from microbial activity after oil was formed C. Applied microbiology 1. the properties of specific microorganisms and ecosystems can be explo ...
... d. certain hydrocarbons are optically active (known to occur only as a result of biological systems) e. data not conclusive - all features could have resulted from microbial activity after oil was formed C. Applied microbiology 1. the properties of specific microorganisms and ecosystems can be explo ...
Protocols - BioMed Central
... d. Heat shock the cells by incubating them at 42 oC for 45 seconds, immediately afterward return the cells to ice and incubate for 2 minutes. e. Add 450 l SOC medium, mix by inverting the tubes a couple of times and incubate for 1 hour at 37 oC with 300 rpm. f. Pellet the cells in a table top centr ...
... d. Heat shock the cells by incubating them at 42 oC for 45 seconds, immediately afterward return the cells to ice and incubate for 2 minutes. e. Add 450 l SOC medium, mix by inverting the tubes a couple of times and incubate for 1 hour at 37 oC with 300 rpm. f. Pellet the cells in a table top centr ...
Cat Coat Color Genetics Part 2: Coat Patterns
... all cats, including solid colored cats. However, it is only when the cat has the dominant Agouti (A) gene that the Tabby pattern is seen. The only case where this is not true ...
... all cats, including solid colored cats. However, it is only when the cat has the dominant Agouti (A) gene that the Tabby pattern is seen. The only case where this is not true ...
When Mount Vesuvius erupted in 79 A
... material from Pleistocene specimens, presumably due to their ability to amplify damaged DNA. Ice age genomics is upon us. Largely, thanks to novel sequencing methods, such as the Roche /454 sequencer, which also utilize emulsion PCR, Polymerases such as those described here should benefit the recov ...
... material from Pleistocene specimens, presumably due to their ability to amplify damaged DNA. Ice age genomics is upon us. Largely, thanks to novel sequencing methods, such as the Roche /454 sequencer, which also utilize emulsion PCR, Polymerases such as those described here should benefit the recov ...
Genetic Engineering - Valhalla High School
... identify the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule make unlimited copies of DNA ...
... identify the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule make unlimited copies of DNA ...
Week 5
... Barr body: the form taken by one of the X chromosomes in each cell of females (XX). The chromosome appears as a clump in the nucleus. In this form it is inactive, thus providing dose compensation. CpG groups: portions of the DNA rich in the sequence Cytosine-Guanosine (as read from the 5’ end of the ...
... Barr body: the form taken by one of the X chromosomes in each cell of females (XX). The chromosome appears as a clump in the nucleus. In this form it is inactive, thus providing dose compensation. CpG groups: portions of the DNA rich in the sequence Cytosine-Guanosine (as read from the 5’ end of the ...
gelbank
... 2DE is a separation method for proteome-analysis. Proteins are separated according to their isoelectric piont (pI) and their molecular weight (MW). It’s a combination of 2 techniques: • Isoelectric focusing • SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis ...
... 2DE is a separation method for proteome-analysis. Proteins are separated according to their isoelectric piont (pI) and their molecular weight (MW). It’s a combination of 2 techniques: • Isoelectric focusing • SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis ...
Bio 211 Quiz 1 practice test answers
... 2. _________ is a process in which an organism incorporates genetic material from another organism without being the offspring of that organism a. Reductionism b. homeostasis c. horizontal gene transfer d. vertical gene transfer 3. Assemblage of populations of different species is considered to be a ...
... 2. _________ is a process in which an organism incorporates genetic material from another organism without being the offspring of that organism a. Reductionism b. homeostasis c. horizontal gene transfer d. vertical gene transfer 3. Assemblage of populations of different species is considered to be a ...
Editorial: Modulating Prokaryotic Lifestyle by DNA
... interest from the healthcare point of view. As it is well-known the antibiotic-resistance strains of pathogenic bacteria are a major world problem, so that there is an urgent need of innovative approaches to tackle it. Human and animal infectious diseases impose staggering costs worldwide in terms o ...
... interest from the healthcare point of view. As it is well-known the antibiotic-resistance strains of pathogenic bacteria are a major world problem, so that there is an urgent need of innovative approaches to tackle it. Human and animal infectious diseases impose staggering costs worldwide in terms o ...
Slajd 1
... Divergent trends in the number of genes across clades (roughly constant in deuterostomes, decreasing in proterostomes). Rising number of regulatory genetic elements. Rising morphological complexity across clades. ...
... Divergent trends in the number of genes across clades (roughly constant in deuterostomes, decreasing in proterostomes). Rising number of regulatory genetic elements. Rising morphological complexity across clades. ...
Forensic Science: Final Exam Review - Baxley
... o The DNA fragments are placed in an electrophoresis gel and a charge is applied (+ at one end and at the other end). o The different sized fragments migrate towards the + end of the gel. o The smaller pieces move the fastest and farthest. o The different sized fragments produce bands along the gel. ...
... o The DNA fragments are placed in an electrophoresis gel and a charge is applied (+ at one end and at the other end). o The different sized fragments migrate towards the + end of the gel. o The smaller pieces move the fastest and farthest. o The different sized fragments produce bands along the gel. ...
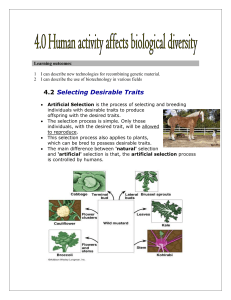
Sc9 - a 4.2 (teacher notes)
... with oral antibiotics but more serious infections usually involve hospitalisation for treatment with intravenous antibiotics. Hormone drugs to stimulate ovulation are used for donor insemination, and may also be used to increase the chance of conception for AI using the male partner's sperm. This so ...
... with oral antibiotics but more serious infections usually involve hospitalisation for treatment with intravenous antibiotics. Hormone drugs to stimulate ovulation are used for donor insemination, and may also be used to increase the chance of conception for AI using the male partner's sperm. This so ...