Linkage Disequilibrium and Inference of Ancestral
... Before we can assess the likely efficacy of finding genes by genomewide scans for association with a SNP marker, it is essential that the distribution of linkage disequilibrium (LD) across the genome be quantified in more than one target population. Several moderate efforts have been reported that h ...
... Before we can assess the likely efficacy of finding genes by genomewide scans for association with a SNP marker, it is essential that the distribution of linkage disequilibrium (LD) across the genome be quantified in more than one target population. Several moderate efforts have been reported that h ...
Identification of linked regions using high
... crossover intermediates (C events) are distributed along the four-strand sister chromatid bundle based on a Poisson distribution with a rate of 2(m þ 1) C events per Morgan, and every C event will either resolve in a crossover (Cx) or not (Co). When a C event resolves in a Cx, the next m C’s must re ...
... crossover intermediates (C events) are distributed along the four-strand sister chromatid bundle based on a Poisson distribution with a rate of 2(m þ 1) C events per Morgan, and every C event will either resolve in a crossover (Cx) or not (Co). When a C event resolves in a Cx, the next m C’s must re ...
Detection of Large Expansions in SCA8 Using a Fluorescent Repeat
... Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes using the conventional method. We analyzed the DNA of 17 SCA8 patients and 258 controls from our collection of DNA from patients with ataxia. Each sample had known expansions tested by Southern blot analysis. The research protocol was approv ...
... Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes using the conventional method. We analyzed the DNA of 17 SCA8 patients and 258 controls from our collection of DNA from patients with ataxia. Each sample had known expansions tested by Southern blot analysis. The research protocol was approv ...
Introduction and Preliminaries - Department of Computer and
... Unique Probes VS. Non-unique Probes Unique probes Gene-specific probes or signature probes. Difficult to find ...
... Unique Probes VS. Non-unique Probes Unique probes Gene-specific probes or signature probes. Difficult to find ...
Primers BSHG06 - National Genetics Reference Laboratories
... covering the entire coding regions of the two genes. To date the primers have been used to PCR amplify 474 samples for various combinations of fragments with analysis by both CSCE and sequencing. In total approximately 30,000 reactions have been performed (A pictorial ...
... covering the entire coding regions of the two genes. To date the primers have been used to PCR amplify 474 samples for various combinations of fragments with analysis by both CSCE and sequencing. In total approximately 30,000 reactions have been performed (A pictorial ...
SpliceCenter_DataBuild
... The transcripts in GenBank often contain exons not found in RefSeq transcripts. For this reason, the Gene database cannot use RefSeq or exon numbering. After all transcripts are added to a gene object, an exon number process is performed. Alternate promoter, poly(A), acceptor, or donor sites can cre ...
... The transcripts in GenBank often contain exons not found in RefSeq transcripts. For this reason, the Gene database cannot use RefSeq or exon numbering. After all transcripts are added to a gene object, an exon number process is performed. Alternate promoter, poly(A), acceptor, or donor sites can cre ...
Construction and Analysis of 2 Reciprocal Arabidopsis Introgression
... running buffer at 1500 V, 40 mA, and 40 W. Plant Materials and SubIL Development Col-0 was initially obtained from G. Rédei (University of Missouri-Columbia, USA) and C24 from J. P. Hernalsteens (Vrije Universiteit Brussels). As a base population for IL development, we developed 2 sets of reciproca ...
... running buffer at 1500 V, 40 mA, and 40 W. Plant Materials and SubIL Development Col-0 was initially obtained from G. Rédei (University of Missouri-Columbia, USA) and C24 from J. P. Hernalsteens (Vrije Universiteit Brussels). As a base population for IL development, we developed 2 sets of reciproca ...
Molecular Analysis of the Coprinus cinereus Mating Type A Factor
... pathways were selected.Amut haploids express A regulated pathways; however, these mutations are dominant (DAY 1963a; RAPER, BOYDand RAPER 1965; SWAMY,UNO and ISHIKAWA 1984). With an activator model, two different alleles of at least one A subunit would be necessary to activate expression of the A re ...
... pathways were selected.Amut haploids express A regulated pathways; however, these mutations are dominant (DAY 1963a; RAPER, BOYDand RAPER 1965; SWAMY,UNO and ISHIKAWA 1984). With an activator model, two different alleles of at least one A subunit would be necessary to activate expression of the A re ...
CpG Mutation Rates in the Human Genome Are
... shown that DNA melting is the rate-limiting step in cytosine deamination. Here we show, through the analysis of human single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), that the mutation rate produced by 5mC deamination is highly dependent on local GC content. In fact, linear regression analysis showed that th ...
... shown that DNA melting is the rate-limiting step in cytosine deamination. Here we show, through the analysis of human single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), that the mutation rate produced by 5mC deamination is highly dependent on local GC content. In fact, linear regression analysis showed that th ...
Site specific insertion of a type I rDNA dement into a unique
... 2; EcoRI and Bglll, track 3; EcoRI and BaraHI, track 4. The gel was blotted onto nitrocellulose and probed with p225, segments C2 and C4 of DmlO3 (Figure 1.) cloned together in pBR322 (right panel); or CR.H6/11, a Hindlll fragment from a recombinant phage carrying a segment of Drosophila DNA carryin ...
... 2; EcoRI and Bglll, track 3; EcoRI and BaraHI, track 4. The gel was blotted onto nitrocellulose and probed with p225, segments C2 and C4 of DmlO3 (Figure 1.) cloned together in pBR322 (right panel); or CR.H6/11, a Hindlll fragment from a recombinant phage carrying a segment of Drosophila DNA carryin ...
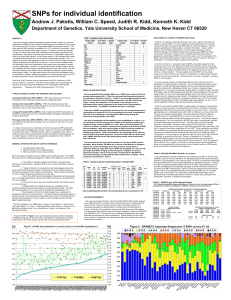
SNPs for individual identification
... concerns over identifying high likelihood of an individual developing a cancer, Alzheimer disease, or Huntington disease does preclude using SNPs that would convey such information. However, from a scientific perspective that does not generalize to precluding all SNPs from even those genes, much les ...
... concerns over identifying high likelihood of an individual developing a cancer, Alzheimer disease, or Huntington disease does preclude using SNPs that would convey such information. However, from a scientific perspective that does not generalize to precluding all SNPs from even those genes, much les ...
Functional SNPs in the SCGB3A2 promoter are
... show an absolute correlation with disease predisposition and the exact genetic requirements for the development of GD are still unknown. A previous genome-wide study of 54 Chinese Han GD pedigrees provided the strongest evidence for linkage at D5s436 on chromosome 5q31. When four additional markers ...
... show an absolute correlation with disease predisposition and the exact genetic requirements for the development of GD are still unknown. A previous genome-wide study of 54 Chinese Han GD pedigrees provided the strongest evidence for linkage at D5s436 on chromosome 5q31. When four additional markers ...
The Development of a Genetic Marker for Resistance to Fescue
... Ipswich, MA). The enzyme cuts the DNA sequence at the specific polymorphism if it contains an A; if the sequence contains a G it would not be cut. A gel was then run to allow the DNA fragments to separate so that the genotype of the animals could be determined. The genotypes were then compared with ...
... Ipswich, MA). The enzyme cuts the DNA sequence at the specific polymorphism if it contains an A; if the sequence contains a G it would not be cut. A gel was then run to allow the DNA fragments to separate so that the genotype of the animals could be determined. The genotypes were then compared with ...
in a patient with Ambras syndrome
... slightly more distal than is revealed by G-banding alone. We took advantage of the fact that the entire sequence of the split clone KB1153C10 (Acc# AP001331) was known, and utilized this to design probes for Southern analysis. In order to map the breakpoint region on the BAC KB1153C10, we chose rest ...
... slightly more distal than is revealed by G-banding alone. We took advantage of the fact that the entire sequence of the split clone KB1153C10 (Acc# AP001331) was known, and utilized this to design probes for Southern analysis. In order to map the breakpoint region on the BAC KB1153C10, we chose rest ...
Chromosomes Carrying Meiotic Avoidance Loci
... To establish the location of contigs A and B within the repetitive region and concurrently gain an insight into the size of the intervening sequences (gap) between contigs A and B, we developed specific FISH probes for each contig. Potentially unique LOA-linked sequences derived from the 454 sequenc ...
... To establish the location of contigs A and B within the repetitive region and concurrently gain an insight into the size of the intervening sequences (gap) between contigs A and B, we developed specific FISH probes for each contig. Potentially unique LOA-linked sequences derived from the 454 sequenc ...
Non contiguous-finished genome sequence and description of
... Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of Bacillus jeddahensis strain JCET relative to other type strains within the Bacillus genus. GenBank accession numbers are indicated in parentheses. Sequences were aligned using MUSCLE, and phylogenetic inferences obtained using the maximum-likelihood met ...
... Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of Bacillus jeddahensis strain JCET relative to other type strains within the Bacillus genus. GenBank accession numbers are indicated in parentheses. Sequences were aligned using MUSCLE, and phylogenetic inferences obtained using the maximum-likelihood met ...
Sequencing breakthroughs for genomic ecology and
... which are straightforward to detect and to assay (see below). Insertion and/or deletion of sequence (indels), genomic rearrangements (such as segmental duplications, inversions and translocations), copy number polymorphisms caused by local duplication and other structural variations are also common ...
... which are straightforward to detect and to assay (see below). Insertion and/or deletion of sequence (indels), genomic rearrangements (such as segmental duplications, inversions and translocations), copy number polymorphisms caused by local duplication and other structural variations are also common ...
Affymetrix Chips
... reflects the significance of the differences between PM and MM. It assigns each probe pair a rank based on how far the probe pair Discrimination Score is from t P-value or statistical significance of a result is the probability that the observed change in a sample ...
... reflects the significance of the differences between PM and MM. It assigns each probe pair a rank based on how far the probe pair Discrimination Score is from t P-value or statistical significance of a result is the probability that the observed change in a sample ...
SNP Analysis (GAW15 data)
... the MHC region makes the largest single contribution (relative recurrence risk ~1.8 ) to disease susceptibility7 A set of alleles at the DRB1 locus, many of which share a common polymorphic sequence, the “shared epitope”, explain a large portion, but not all, of the genetic risk within the MHC. ...
... the MHC region makes the largest single contribution (relative recurrence risk ~1.8 ) to disease susceptibility7 A set of alleles at the DRB1 locus, many of which share a common polymorphic sequence, the “shared epitope”, explain a large portion, but not all, of the genetic risk within the MHC. ...
Construction of nanA mutants
... each case. The 1500 bp Janus Cassette was amplified with primers Janus KpnF and Janus SacIR. The PCR products generated from the 3 individual reactions were then cleaned and digested with the appropriate enzymes, cleaned again, and then ligated. The ligation mix was used as template for an extended ...
... each case. The 1500 bp Janus Cassette was amplified with primers Janus KpnF and Janus SacIR. The PCR products generated from the 3 individual reactions were then cleaned and digested with the appropriate enzymes, cleaned again, and then ligated. The ligation mix was used as template for an extended ...
A Genetic Linkage Map of Mouse Chromosome 10
... Bcr-related locus in the mouse rather than the structural gene. We mapped the mouse Bcr cDNA probe using multiple restriction enzymes (data not shown), but all polymorphisms segregated to the same locus on chromosome 10. Probes derived from exon 1 of the human BCR structural gene exhibit nohomology ...
... Bcr-related locus in the mouse rather than the structural gene. We mapped the mouse Bcr cDNA probe using multiple restriction enzymes (data not shown), but all polymorphisms segregated to the same locus on chromosome 10. Probes derived from exon 1 of the human BCR structural gene exhibit nohomology ...
Localization of CSNBX (CSNB4) between the retinitis
... X-linked congenital stationary night blindness (CSNBX) is a nonprogressive disease causing night blindness and reduced visual acuity. Distinct genetic loci have been reported for CSNBX at Xp21.1, which is potentially allelic with the RP3 gene, and at Xpll.23, which is potentially allelic with the RP ...
... X-linked congenital stationary night blindness (CSNBX) is a nonprogressive disease causing night blindness and reduced visual acuity. Distinct genetic loci have been reported for CSNBX at Xp21.1, which is potentially allelic with the RP3 gene, and at Xpll.23, which is potentially allelic with the RP ...
Molecular Inversion Probe

Molecular Inversion Probe (MIP) belongs to the class of Capture by Circularization molecular techniques for performing genomic partitioning, a process through which one captures and enriches specific regions of the genome. Probes used in this technique are single stranded DNA molecules and, similar to other genomic partitioning techniques, contain sequences that are complementary to the target in the genome; these probes hybridize to and capture the genomic target. MIP stands unique from other genomic partitioning strategies in that MIP probes share the common design of two genomic target complementary segments separated by a linker region. With this design, when the probe hybridizes to the target, it undergoes an inversion in configuration (as suggested by the name of the technique) and circularizes. Specifically, the two target complementary regions at the 5’ and 3’ ends of the probe become adjacent to one another while the internal linker region forms a free hanging loop. The technology has been used extensively in the HapMap project for large-scale SNP genotyping as well as for studying gene copy alterationsand characteristics of specific genomic loci to identify biomarkers for different diseases such as cancer. Key strengths of the MIP technology include its high specificity to the target and its scalability for high-throughput, multiplexed analyses where tens of thousands of genomic loci are assayed simultaneously.