Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
... Single RNA molecules labeled with a FRET donor dye and acceptor dye in exon sequences on either side of an intron. The splicing reaction that removes the intron sequence requires magnesium and the protein cofactor CBP2. When donor and acceptor dyes are relatively distant, as when the intron is unfol ...
... Single RNA molecules labeled with a FRET donor dye and acceptor dye in exon sequences on either side of an intron. The splicing reaction that removes the intron sequence requires magnesium and the protein cofactor CBP2. When donor and acceptor dyes are relatively distant, as when the intron is unfol ...
Write-up - UBC Blogs
... What general biological, chemical, and/or physical principles and concepts is this technique based on? ● A molecule acts a ‘donor chromophore,’ in which an electron is excited to a higher state by incident energy. When the electron relaxes back to ground state, it emits a photon which is observed as ...
... What general biological, chemical, and/or physical principles and concepts is this technique based on? ● A molecule acts a ‘donor chromophore,’ in which an electron is excited to a higher state by incident energy. When the electron relaxes back to ground state, it emits a photon which is observed as ...
gfp_exercise_ver5
... Ribbons box. Alternatively, you can click on All Ribbons within the Show Ribbons box to view all structures at the same time. Answer ...
... Ribbons box. Alternatively, you can click on All Ribbons within the Show Ribbons box to view all structures at the same time. Answer ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Modeling the Organism: The Cell in
... of generations, meiosis, conjugation and spore formation. •Review the compartments and cytoskeleton of the eukaryotic cell, comparing and contrasting what you learned in the first semester with this model yeast. •Compare and contrast (in a simple way) mammalian and fungal cell cycles. •Describe the ...
... of generations, meiosis, conjugation and spore formation. •Review the compartments and cytoskeleton of the eukaryotic cell, comparing and contrasting what you learned in the first semester with this model yeast. •Compare and contrast (in a simple way) mammalian and fungal cell cycles. •Describe the ...
Background on Protein and Interactions
... protein are found. • This amino acid is cut out of the genome using enzymes and replaced with the portion of the gene that expresses GFP (or YFP). • The cells are then left to reproduce with this new coding. ...
... protein are found. • This amino acid is cut out of the genome using enzymes and replaced with the portion of the gene that expresses GFP (or YFP). • The cells are then left to reproduce with this new coding. ...
MS Word - VCU Secrets of the Sequence
... student copy master. Micropipettes and a long-wave UV light are required and available separately. Ordering Information: Kit number. 88W8233, Note: Includes perishable materials. Please specify delivery date. http://www.wardsci.com B) In this activity, students use the Biotechnology Explorer program ...
... student copy master. Micropipettes and a long-wave UV light are required and available separately. Ordering Information: Kit number. 88W8233, Note: Includes perishable materials. Please specify delivery date. http://www.wardsci.com B) In this activity, students use the Biotechnology Explorer program ...
Protein Engineering
... cells of E. Coli and C. elegans by the lab of Martin Chalfie : publication in Science. • Although this wt-GFP was fluorescent, it had several drawbacks, including dual peaked excitation spectra, poor photo-stability, and poor folding at 37°C. ...
... cells of E. Coli and C. elegans by the lab of Martin Chalfie : publication in Science. • Although this wt-GFP was fluorescent, it had several drawbacks, including dual peaked excitation spectra, poor photo-stability, and poor folding at 37°C. ...
NbCMT3
... stability. DNA methyltransferases are key enzymes catalyzing DNA methylation. Chromomethylase (CMT) genes are specific to the plant kingdom and encode chromodomain-containing methyltransferases. However, the function of CMT genes in plants remains elusive. In this study, we isolated and characterize ...
... stability. DNA methyltransferases are key enzymes catalyzing DNA methylation. Chromomethylase (CMT) genes are specific to the plant kingdom and encode chromodomain-containing methyltransferases. However, the function of CMT genes in plants remains elusive. In this study, we isolated and characterize ...
Identifying proteins required for chromatin organization using a GFP
... proteins. The gene associated with CA06844 was identified as CG11138 (Kelso et al. 2006), which has an amino acid sequence with homology to the Interferon Regulatory Factor 2 Binding Protein 1 (Childs and Goodbourn 2003), which affects transcription within humans. This gene is uncharacterized, and c ...
... proteins. The gene associated with CA06844 was identified as CG11138 (Kelso et al. 2006), which has an amino acid sequence with homology to the Interferon Regulatory Factor 2 Binding Protein 1 (Childs and Goodbourn 2003), which affects transcription within humans. This gene is uncharacterized, and c ...
DOC
... deGradFP harnesses the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to achieve direct depletion of GFP-tagged proteins. deGradFP is in essence a universal method because it relies on an evolutionarily conserved machinery for protein catabolism in eukaryotic cells; see refs. 5, 6 for review. deGradFP is particularly ...
... deGradFP harnesses the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to achieve direct depletion of GFP-tagged proteins. deGradFP is in essence a universal method because it relies on an evolutionarily conserved machinery for protein catabolism in eukaryotic cells; see refs. 5, 6 for review. deGradFP is particularly ...
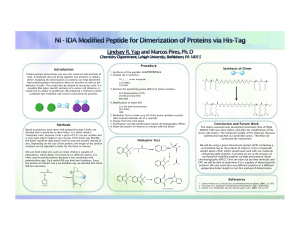
Introduction Methods Procedure Conclusion and Future Work
... cells. A molecule that can bring together two proteins is called a dimer. Studying the dimerization or proteins can help determine how protein-protein interactions alters its function as well as the behavior of cells. This could also be related to cancerous cells. It is possible that when specific p ...
... cells. A molecule that can bring together two proteins is called a dimer. Studying the dimerization or proteins can help determine how protein-protein interactions alters its function as well as the behavior of cells. This could also be related to cancerous cells. It is possible that when specific p ...
Normal human CD34+ haematopoietic progenitor cells
... Supplementary Figure S2. Validation of functional MYCT1 expression. Normal human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells were purified from human cord blood and transduced with the retroviral expression vectors detailed in Supplementary Figure S1. (A) Verification of transduction efficiency was determi ...
... Supplementary Figure S2. Validation of functional MYCT1 expression. Normal human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells were purified from human cord blood and transduced with the retroviral expression vectors detailed in Supplementary Figure S1. (A) Verification of transduction efficiency was determi ...
Analyses for Molecular Interactions in Living Cells
... and is buried almost perfectly in the center of the cylinder, which has been called a b-can Ser65, Tyr66, and Gly67 are key residues to form chromophore ...
... and is buried almost perfectly in the center of the cylinder, which has been called a b-can Ser65, Tyr66, and Gly67 are key residues to form chromophore ...
Protein interactions are essential for many biological functions to occur. ... Erika Lacy: Cell Biology & Neuroscience
... Protein interactions are essential for many biological functions to occur. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) assay is a complementation-based technique used to study protein interactions. One benefit of this approach is that protein interactions as well as the location of that interact ...
... Protein interactions are essential for many biological functions to occur. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) assay is a complementation-based technique used to study protein interactions. One benefit of this approach is that protein interactions as well as the location of that interact ...
Endocytosis of GFP tagged potassium channel KAT1 against high
... mean diameter of around 300 nm. In parallel with the changes in membrane area also the number of potassium channels is adjusted with the result that the K+-channel concentration is kept nearly constant during excursions of the surface area. Collectively this suggests that these K+-channel proteins a ...
... mean diameter of around 300 nm. In parallel with the changes in membrane area also the number of potassium channels is adjusted with the result that the K+-channel concentration is kept nearly constant during excursions of the surface area. Collectively this suggests that these K+-channel proteins a ...
pGLO MUTAGENESIS To be able to study any trait in any organism
... To be able to study any trait in any organism, one needs to compare the wild type (the most common type) to the altered types (mutants). Mutations occur naturally in every gene but at a very low rate and over a long period of time. If the mutation is advantageous to the organism, it will get incorpo ...
... To be able to study any trait in any organism, one needs to compare the wild type (the most common type) to the altered types (mutants). Mutations occur naturally in every gene but at a very low rate and over a long period of time. If the mutation is advantageous to the organism, it will get incorpo ...
Document
... paper to collection tube where column seats to insure column flow • Rest pipet tip on side of column to avoid column bed disturbance ...
... paper to collection tube where column seats to insure column flow • Rest pipet tip on side of column to avoid column bed disturbance ...
Slide 1
... A donor molecule is excited and can emit (green). Energy can be transmitted to the acceptor if they are close. The acceptor emits at a longer wavelength (red) Measure both green and red emissions. High red signal means donor and acceptor are close. High green signal means they are far apart. Possibl ...
... A donor molecule is excited and can emit (green). Energy can be transmitted to the acceptor if they are close. The acceptor emits at a longer wavelength (red) Measure both green and red emissions. High red signal means donor and acceptor are close. High green signal means they are far apart. Possibl ...
Green fluorescent protein

The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein composed of 238 amino acid residues (26.9 kDa) that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. Although many other marine organisms have similar green fluorescent proteins, GFP traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria. The GFP from A. victoria has a major excitation peak at a wavelength of 395 nm and a minor one at 475 nm. Its emission peak is at 509 nm, which is in the lower green portion of the visible spectrum. The fluorescence quantum yield (QY) of GFP is 0.79. The GFP from the sea pansy (Renilla reniformis) has a single major excitation peak at 498 nm.In cell and molecular biology, the GFP gene is frequently used as a reporter of expression. In modified forms it has been used to make biosensors, and many animals have been created that express GFP as a proof-of-concept that a gene can be expressed throughout a given organism. The GFP gene can be introduced into organisms and maintained in their genome through breeding, injection with a viral vector, or cell transformation. To date, the GFP gene has been introduced and expressed in many Bacteria, Yeast and other Fungi, fish (such as zebrafish), plant, fly, and mammalian cells, including human. Martin Chalfie, Osamu Shimomura, and Roger Y. Tsien were awarded the 2008 Nobel Prize in Chemistry on 10 October 2008 for their discovery and development of the green fluorescent protein.