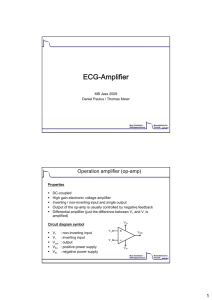
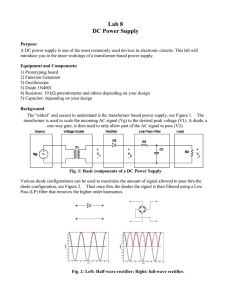
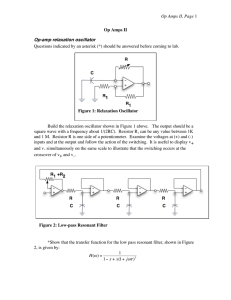
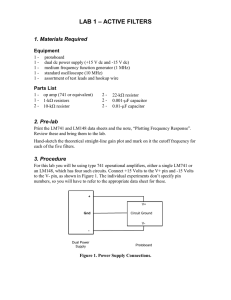
design_review - ECE Senior Design
... Aliasing is a phenomenon of sampled data filters which causes two signals to become indistinguishable from one another due to overlapping It can occur when a signal is sampled insufficiently Anti-Aliasing is a common practice using an anti-aliasing filter to limit, or restrict the bandwidth to that ...
... Aliasing is a phenomenon of sampled data filters which causes two signals to become indistinguishable from one another due to overlapping It can occur when a signal is sampled insufficiently Anti-Aliasing is a common practice using an anti-aliasing filter to limit, or restrict the bandwidth to that ...
Active filters
... harmonic filtering, active harmonic filters are used for damping, isolation, termination, powerfactor correction, voltage regulation, load balancing, and voltage-flicker reduction. Compared to passive filters, active harmonic filters provide superior filtering performance and more flexible operation ...
... harmonic filtering, active harmonic filters are used for damping, isolation, termination, powerfactor correction, voltage regulation, load balancing, and voltage-flicker reduction. Compared to passive filters, active harmonic filters provide superior filtering performance and more flexible operation ...
Sélectivité et anisotropie des Filtres Spatiaux :
... applied to a voltage source inverter operating as an active filter. This active filter compensates harmonic current and reactive power of nonlinear loads simultaneously. The proposed scheme uses a pulse width modulation (PWM) technique to generate the switching signals to the active filter, p-q theo ...
... applied to a voltage source inverter operating as an active filter. This active filter compensates harmonic current and reactive power of nonlinear loads simultaneously. The proposed scheme uses a pulse width modulation (PWM) technique to generate the switching signals to the active filter, p-q theo ...
Coulomb`s Law
... – Ease of handling large quantities that can vary over many orders of magnitude. • However, keep this compression firmly in mind! For example, the Richter scale for earthquake intensity is logarithmic -- a 7 on the Richter scale actually has an amplitude 10 times more powerful than a 6, correspondin ...
... – Ease of handling large quantities that can vary over many orders of magnitude. • However, keep this compression firmly in mind! For example, the Richter scale for earthquake intensity is logarithmic -- a 7 on the Richter scale actually has an amplitude 10 times more powerful than a 6, correspondin ...
COMPARISON OF CONTROL ALGORITHMS FOR SHUNT ACTIVE
... that cancel harmonic content from non – linear loads. One of the cornerstones of the active filter is its control strategy that is implemented in the active filter controller. The performance of an active filter depends mainly on the selected reference generation scheme. Shunt Active Filter generate ...
... that cancel harmonic content from non – linear loads. One of the cornerstones of the active filter is its control strategy that is implemented in the active filter controller. The performance of an active filter depends mainly on the selected reference generation scheme. Shunt Active Filter generate ...
In this project, you are going to design an active Low
... A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a certain cut-off frequency and preventing the passage of signals with frequencies higher than the cut-off frequency [1]. The most important feature of a low pass filter is that the cut-off frequency and gain of the filter ...
... A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a certain cut-off frequency and preventing the passage of signals with frequencies higher than the cut-off frequency [1]. The most important feature of a low pass filter is that the cut-off frequency and gain of the filter ...
EMC Components and Filters
... Z0 should be as low as possible (a few Ω) Difficult with spaced round conductors ...
... Z0 should be as low as possible (a few Ω) Difficult with spaced round conductors ...
Filters
... • As the name would indicate, a band-pass filter (BPF) will allow signals of a desired frequency to ‘pass’ into the circuit, but at the same time it rejects all other unwanted frequencies. • The last lesson showed us that a series resonant circuit has a frequency response characteristic similar to t ...
... • As the name would indicate, a band-pass filter (BPF) will allow signals of a desired frequency to ‘pass’ into the circuit, but at the same time it rejects all other unwanted frequencies. • The last lesson showed us that a series resonant circuit has a frequency response characteristic similar to t ...
Active Filters - UniMAP Portal
... synthesize the desired filter characteristics. •have high input impedance, low output impedance, and virtually any arbitrary gain. •They are also usually easier to design than passive filters. •They lack inductors. ...
... synthesize the desired filter characteristics. •have high input impedance, low output impedance, and virtually any arbitrary gain. •They are also usually easier to design than passive filters. •They lack inductors. ...
High-pass.filter
... Such a filter could be used to direct high frequencies to a tweeter speaker while blocking bass signals which could interfere with or damage the speaker. A low-pass filter, using a coil instead of a capacitor, could simultaneously be used to direct low frequencies to the woofer. See audio ...
... Such a filter could be used to direct high frequencies to a tweeter speaker while blocking bass signals which could interfere with or damage the speaker. A low-pass filter, using a coil instead of a capacitor, could simultaneously be used to direct low frequencies to the woofer. See audio ...
Capacitor Self
... In radio receivers (FM, TV, wireless telephones, ...), it is very typical to result in an effective 10-pole (or higher) bandpass filter having a narrow bandwidth and an elliptic roll-off curve of 100+ dB/Octave. Tradeoffs: Filter design is always full of tradeoffs, as are most engineering problems. ...
... In radio receivers (FM, TV, wireless telephones, ...), it is very typical to result in an effective 10-pole (or higher) bandpass filter having a narrow bandwidth and an elliptic roll-off curve of 100+ dB/Octave. Tradeoffs: Filter design is always full of tradeoffs, as are most engineering problems. ...