Design of Low Phase Noise LC VCO for UHF RFID Reader
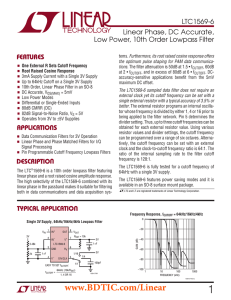
... A. Structure of frequency synthesizer third-order sigma-delta modulator are used in the feedback A frequency synthesizer based on a fractional-N PLL is path of the frequency synthesizer. A 1.8 GHz LO signal is designed as depicted in Fig.1. The synthesizer uses off-chip generated by an integrated VC ...
... A. Structure of frequency synthesizer third-order sigma-delta modulator are used in the feedback A frequency synthesizer based on a fractional-N PLL is path of the frequency synthesizer. A 1.8 GHz LO signal is designed as depicted in Fig.1. The synthesizer uses off-chip generated by an integrated VC ...
Radio Receivers
... The detector removes information from the modulated wave. The AGC used in AM receivers and not used FM receivers because in FM there is no information contained in Amplitude. With FM receivers a constant amplitude IF signal in to demodulator is desirable. FM RX have mush more UIF gain than AM recei ...
... The detector removes information from the modulated wave. The AGC used in AM receivers and not used FM receivers because in FM there is no information contained in Amplitude. With FM receivers a constant amplitude IF signal in to demodulator is desirable. FM RX have mush more UIF gain than AM recei ...
Audiometers, Calibration
... Output values obtained at SLM are compared to standards for each frequency tested (Table 4.1) ...
... Output values obtained at SLM are compared to standards for each frequency tested (Table 4.1) ...
Page 43, Foundation Electronics, Kemp
... For each of the specifications below draw out the Karnaugh map and produce a circuit using NAND gates only to satisfy requirements. 30. The shuttle has a voting system whereby 3 computers vote on what to do. The final decision always goes with the majority so that if one computer goes down the other ...
... For each of the specifications below draw out the Karnaugh map and produce a circuit using NAND gates only to satisfy requirements. 30. The shuttle has a voting system whereby 3 computers vote on what to do. The final decision always goes with the majority so that if one computer goes down the other ...
L. Huang, W. Rieutort-Louis, A. Gualdino, L. Teagno, Y. Hu, J. Mouro, J. Sanz-Robinson, J.C. Sturm, S. Wagner, V. Chu, J. Conde, and N. Verma, "An ASIC for Readout of Post-processed Thin-film MEMS Resonators by Employing Capacitive Interfacing and Active Parasitic Cancellation", VLSI Symp. on Circuits (VLSI) (JUN2014).
... on-chip function generator and applied to the MEMS. This results in two currents: (1) an intended current IM through the motional RMLMCM; and (2) a parasitic current ICP through the parallel feed-through capacitor. The two currents are combined and converted to a voltage through the small resistor R ...
... on-chip function generator and applied to the MEMS. This results in two currents: (1) an intended current IM through the motional RMLMCM; and (2) a parasitic current ICP through the parallel feed-through capacitor. The two currents are combined and converted to a voltage through the small resistor R ...
using the sa605/615 if processor ic
... layout was not “optimum” (PCB was adapted from a 10.7 design) and a better one could help here. Even so the broad bandwidth and shallow rejection of the L/C based filters will make it difficult to get much better than this. This circuit illustrates that the SA605 can be made to work with L/C filters ...
... layout was not “optimum” (PCB was adapted from a 10.7 design) and a better one could help here. Even so the broad bandwidth and shallow rejection of the L/C based filters will make it difficult to get much better than this. This circuit illustrates that the SA605 can be made to work with L/C filters ...
Owners Enjoyment Manual
... Knowing where your frequency response problems exist is half the battle of setting up a good sounding system. The warble-tone signal generator and precision relative sound level meter built into the Richter Scale provide an impartial judge of the peaks, dips and speaker/room interactions. The measur ...
... Knowing where your frequency response problems exist is half the battle of setting up a good sounding system. The warble-tone signal generator and precision relative sound level meter built into the Richter Scale provide an impartial judge of the peaks, dips and speaker/room interactions. The measur ...
Equalization (audio)

Equalization (British: equalisation) is the process of adjusting the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal. The most well known use of equalization is in sound recording and reproduction but there are many other applications in electronics and telecommunications. The circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization is called an equalizer. These devices strengthen (boost) or weaken (cut) the energy of specific frequency bands.In sound recording and reproduction, equalization is the process commonly used to alter the frequency response of an audio system using linear filters. Most hi-fi equipment uses relatively simple filters to make bass and treble adjustments. Graphic and parametric equalizers have much more flexibility in tailoring the frequency content of an audio signal. An equalizer is the circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization. Since equalizers, ""adjust the amplitude of audio signals at particular frequencies,"" they are, ""in other words, frequency-specific volume knobs.""In the field of audio electronics, the term ""equalization"" has come to include the adjustment of frequency responses for practical or aesthetic reasons, often resulting in a net response that is not truly equalized. The term EQ specifically refers to this variant of the term. Stereos typically have adjustable equalizers which boost or cut bass or treble frequencies. Broadcast and recording studios use sophisticated equalizers capable of much more detailed adjustments, such as eliminating unwanted sounds or making certain instruments or voices more prominent.Equalizers are used in recording studios, radio studios and production control rooms, and live sound reinforcement to correct the response of microphones, instrument pick-ups, loudspeakers, and hall acoustics. Equalization may also be used to eliminate unwanted sounds, make certain instruments or voices more prominent, enhance particular aspects of an instrument's tone, or combat feedback (howling) in a public address system. Equalizers are also used in music production to adjust the timbre of individual instruments by adjusting their frequency content and to fit individual instruments within the overall frequency spectrum of the mix.The most common equalizers in music production are parametric, semi-parametric, graphic, peak, and program equalizers. Graphic equalizers are often included in consumer audio equipment and software which plays music on home computers. Parametric equalizers require more expertise than graphic equalizers, and they can provide more specific compensation or alteration around a chosen frequency. This may be used in order to remove (or to create) a resonance, for instance.