an266 vcxo tuning slope (kv), stability, and absolute
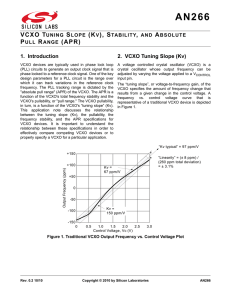
... 3.1%. Note, however, that linearity is not necessarily a good indicator of how well the actual gain at a specific operating point (sometimes referred to as the “incremental gain”) matches the specified Kv typical value. Traditional VCXO devices use a varactor diode to vary the capacitive loading on ...
... 3.1%. Note, however, that linearity is not necessarily a good indicator of how well the actual gain at a specific operating point (sometimes referred to as the “incremental gain”) matches the specified Kv typical value. Traditional VCXO devices use a varactor diode to vary the capacitive loading on ...
70 MHz AND 140 MHz IF TO IF FREQUENCY CONVERTERS
... Relative humidity.............................................. Up to 95% at 40°C Atmospheric pressure ...................................... Up to 40,000 feet Shock and vibration.......................................... Normal handling by commercial carriers ...
... Relative humidity.............................................. Up to 95% at 40°C Atmospheric pressure ...................................... Up to 40,000 feet Shock and vibration.......................................... Normal handling by commercial carriers ...
Experiment 2 - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
... Note about “Low” and “High”: While it may seem that terms like low and high, when applied to something like frequency, are fuzzy, ill-defined terms. That is definitely not the case. Here, we mean something quite specific by the expression low frequency. A frequency is only low when the capacitive im ...
... Note about “Low” and “High”: While it may seem that terms like low and high, when applied to something like frequency, are fuzzy, ill-defined terms. That is definitely not the case. Here, we mean something quite specific by the expression low frequency. A frequency is only low when the capacitive im ...
0.1Hz to 10Hz Noise Filter
... The objective of this circuit is to amplify low frequency noise to a level that can be measured by a typical oscilloscope. This measurement is a common figure of merit given in amplifier data sheets. The standard bandwidth used in these measurements is 0.1Hz to 10Hz. Many precision amplifiers will h ...
... The objective of this circuit is to amplify low frequency noise to a level that can be measured by a typical oscilloscope. This measurement is a common figure of merit given in amplifier data sheets. The standard bandwidth used in these measurements is 0.1Hz to 10Hz. Many precision amplifiers will h ...
Linearization of Monolithic LNAs Using Low- Frequency Low-Impedance Input Termination E. Larson2
... integration. Traditionally, FETs (both GaAs and silicon) were perceived to be more linear devices than BJTs. At the early stages of the wireless revolution, GaAs-based HEMTs were commonly used in low-distortion amplifiers either as discrete devices or in ICs [2]. However, high material cost and rela ...
... integration. Traditionally, FETs (both GaAs and silicon) were perceived to be more linear devices than BJTs. At the early stages of the wireless revolution, GaAs-based HEMTs were commonly used in low-distortion amplifiers either as discrete devices or in ICs [2]. However, high material cost and rela ...
Power Quality improvement using passive shunt filter Assistant
... compensation because they are simple in structure and easy to install Different topologies of passive filters were emerged during stages of research. They are generally classified into series and shunt passive filters. Series passive filters use high series impedance to block harmonics, and shunt fi ...
... compensation because they are simple in structure and easy to install Different topologies of passive filters were emerged during stages of research. They are generally classified into series and shunt passive filters. Series passive filters use high series impedance to block harmonics, and shunt fi ...
Good Dynamics Processing RaneNote 141
... shortened, the distortion increases. For a limiter operating with a release time of perhaps 500 ms, at 500 Hz this distortion easily exceeds several percent THD. It is quite audible. This may be improved by using a second-order release filter as mentioned, but ultimately the best fix is to use the l ...
... shortened, the distortion increases. For a limiter operating with a release time of perhaps 500 ms, at 500 Hz this distortion easily exceeds several percent THD. It is quite audible. This may be improved by using a second-order release filter as mentioned, but ultimately the best fix is to use the l ...
Operating Manual
... Incoming as well as outgoing wires and wires for extra low voltages (ELV) must be separated from dangerous electrical cables (SELV circuits) by using a double resp. increased isolation. All selected wires and isolations must be conform to the provided voltage- and temperatureranges. Further all coun ...
... Incoming as well as outgoing wires and wires for extra low voltages (ELV) must be separated from dangerous electrical cables (SELV circuits) by using a double resp. increased isolation. All selected wires and isolations must be conform to the provided voltage- and temperatureranges. Further all coun ...
Equalization (audio)

Equalization (British: equalisation) is the process of adjusting the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal. The most well known use of equalization is in sound recording and reproduction but there are many other applications in electronics and telecommunications. The circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization is called an equalizer. These devices strengthen (boost) or weaken (cut) the energy of specific frequency bands.In sound recording and reproduction, equalization is the process commonly used to alter the frequency response of an audio system using linear filters. Most hi-fi equipment uses relatively simple filters to make bass and treble adjustments. Graphic and parametric equalizers have much more flexibility in tailoring the frequency content of an audio signal. An equalizer is the circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization. Since equalizers, ""adjust the amplitude of audio signals at particular frequencies,"" they are, ""in other words, frequency-specific volume knobs.""In the field of audio electronics, the term ""equalization"" has come to include the adjustment of frequency responses for practical or aesthetic reasons, often resulting in a net response that is not truly equalized. The term EQ specifically refers to this variant of the term. Stereos typically have adjustable equalizers which boost or cut bass or treble frequencies. Broadcast and recording studios use sophisticated equalizers capable of much more detailed adjustments, such as eliminating unwanted sounds or making certain instruments or voices more prominent.Equalizers are used in recording studios, radio studios and production control rooms, and live sound reinforcement to correct the response of microphones, instrument pick-ups, loudspeakers, and hall acoustics. Equalization may also be used to eliminate unwanted sounds, make certain instruments or voices more prominent, enhance particular aspects of an instrument's tone, or combat feedback (howling) in a public address system. Equalizers are also used in music production to adjust the timbre of individual instruments by adjusting their frequency content and to fit individual instruments within the overall frequency spectrum of the mix.The most common equalizers in music production are parametric, semi-parametric, graphic, peak, and program equalizers. Graphic equalizers are often included in consumer audio equipment and software which plays music on home computers. Parametric equalizers require more expertise than graphic equalizers, and they can provide more specific compensation or alteration around a chosen frequency. This may be used in order to remove (or to create) a resonance, for instance.