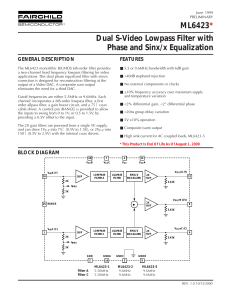
ML6423 Dual S-Video Lowpass Filter with Phase and Sinx/x
... Figure 6 shows the problem in the frequency domain. Curve A shows the amplitude response of the ML6423 filter, while curve B shows the signal spectrum as it is distorted by the sampling process. Curve C shows the composite of the two curves which is the result of passing the sampled waveform through ...
... Figure 6 shows the problem in the frequency domain. Curve A shows the amplitude response of the ML6423 filter, while curve B shows the signal spectrum as it is distorted by the sampling process. Curve C shows the composite of the two curves which is the result of passing the sampled waveform through ...
lce: reactive components
... frequency called the resonant frequency the ratio of the output and input amplitude is zero or roughly zero . This shows that no current is flowing at that resonant frequency . This is mainly due to the C-R circuit which is a high pass filter ie current can only pass through the capacitor in a high ...
... frequency called the resonant frequency the ratio of the output and input amplitude is zero or roughly zero . This shows that no current is flowing at that resonant frequency . This is mainly due to the C-R circuit which is a high pass filter ie current can only pass through the capacitor in a high ...
Chapter 4 : Resonance Circuit
... Lower value of Q larger the bandwidth. (Lower the selectivity) ...
... Lower value of Q larger the bandwidth. (Lower the selectivity) ...
Image 414 mk2
... consisting of inductors, resistors, and in a tuneful and agile fashion, and a capacitors that controls the distribu- subwoofer would be left with little to tion of frequencies to the tweeters and do but fill in the very bottom end for woofers. You can’t just feed a full-range the sake of atmospheric ...
... consisting of inductors, resistors, and in a tuneful and agile fashion, and a capacitors that controls the distribu- subwoofer would be left with little to tion of frequencies to the tweeters and do but fill in the very bottom end for woofers. You can’t just feed a full-range the sake of atmospheric ...
High Pass Filter
... Zc=impedance of capacitor * In the high pass filter circuit, the resistor pair and the capacitor act like a voltage divider.i.e. Vout=Zr/(Zc+Zr). When Zc decreases, the Vout approaches Vs. The voltage gain (which is Vout/Vs) approaches 1 with increasing frequency. This is because as frequency increa ...
... Zc=impedance of capacitor * In the high pass filter circuit, the resistor pair and the capacitor act like a voltage divider.i.e. Vout=Zr/(Zc+Zr). When Zc decreases, the Vout approaches Vs. The voltage gain (which is Vout/Vs) approaches 1 with increasing frequency. This is because as frequency increa ...
Angle Modulation Part 2
... To detect an FM signal, it is necessary to have a circuit whose output voltage varies linearly with the frequency of the input signal. The most commonly used demodulator is the PLL demodulator. Can be use to detect either NBFM or WBFM. ...
... To detect an FM signal, it is necessary to have a circuit whose output voltage varies linearly with the frequency of the input signal. The most commonly used demodulator is the PLL demodulator. Can be use to detect either NBFM or WBFM. ...
The practical physics of hearing aids
... metres, so high pitched sounds are reflected many more times than those of low pitch. The fading reflections (reverberations) of any sound therefore have many more high frequency components than low. Processed by a hearing aid, this often produces an unpleasant shrillness. Sharp sounds, such as cutl ...
... metres, so high pitched sounds are reflected many more times than those of low pitch. The fading reflections (reverberations) of any sound therefore have many more high frequency components than low. Processed by a hearing aid, this often produces an unpleasant shrillness. Sharp sounds, such as cutl ...
Homework Problem Set 8 Solutions How is an LRC circuit similar to
... 1) How is an LRC circuit similar to a mechanical harmonic oscillator? Which component of the circuit acts like a “mass”? Which component of the circuit acts like “friction”? An LRC circuit is similar to a mechanical oscillator because they alternate between potential and kinetic energy. The componen ...
... 1) How is an LRC circuit similar to a mechanical harmonic oscillator? Which component of the circuit acts like a “mass”? Which component of the circuit acts like “friction”? An LRC circuit is similar to a mechanical oscillator because they alternate between potential and kinetic energy. The componen ...
TIA Contribution Ref Codec, Loudness Ratings, Handsfree
... Contribution: Calculation of Loudness Ratings NOTE to Editor: It may be clearer to add these equations to the document as well as referring to P.79 (Maybe as an appendix). The equations are specific to this document. ...
... Contribution: Calculation of Loudness Ratings NOTE to Editor: It may be clearer to add these equations to the document as well as referring to P.79 (Maybe as an appendix). The equations are specific to this document. ...
Measurement of internal work during running
... If skin resistance is 2 Mw and input resistance is 10 Mw then voltage at amplifier will be [10/(10 + 2) = 0.833] 83.3% of its true value. By reducing skin resistance to 100 kw this can be improved to 99%. By also using a 100 Mw resistance amplifier the signal will be 99.9%. ...
... If skin resistance is 2 Mw and input resistance is 10 Mw then voltage at amplifier will be [10/(10 + 2) = 0.833] 83.3% of its true value. By reducing skin resistance to 100 kw this can be improved to 99%. By also using a 100 Mw resistance amplifier the signal will be 99.9%. ...
Experiment #9 Report (and pre-lab)
... 7. Use the above equations to find the frequencies, at which the output voltage is approximately 0.707 times the maximum possible output voltage (i.e., the half-power points). Record these values below. Then use the oscilloscope to determine such cutoff frequencies experimentally by observing the f ...
... 7. Use the above equations to find the frequencies, at which the output voltage is approximately 0.707 times the maximum possible output voltage (i.e., the half-power points). Record these values below. Then use the oscilloscope to determine such cutoff frequencies experimentally by observing the f ...
Resonant Circuit
... • R=Rsh(L/W) – Rsh is the sheet resistance – Rsh is 22 mOhms per square for W=6um. – If the outer diameter is 135 um, the length is approximately 135um x4=540 um. – R=22 mOhms x (540/6)=1.98 Ohms ...
... • R=Rsh(L/W) – Rsh is the sheet resistance – Rsh is 22 mOhms per square for W=6um. – If the outer diameter is 135 um, the length is approximately 135um x4=540 um. – R=22 mOhms x (540/6)=1.98 Ohms ...
Equalization (audio)

Equalization (British: equalisation) is the process of adjusting the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal. The most well known use of equalization is in sound recording and reproduction but there are many other applications in electronics and telecommunications. The circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization is called an equalizer. These devices strengthen (boost) or weaken (cut) the energy of specific frequency bands.In sound recording and reproduction, equalization is the process commonly used to alter the frequency response of an audio system using linear filters. Most hi-fi equipment uses relatively simple filters to make bass and treble adjustments. Graphic and parametric equalizers have much more flexibility in tailoring the frequency content of an audio signal. An equalizer is the circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization. Since equalizers, ""adjust the amplitude of audio signals at particular frequencies,"" they are, ""in other words, frequency-specific volume knobs.""In the field of audio electronics, the term ""equalization"" has come to include the adjustment of frequency responses for practical or aesthetic reasons, often resulting in a net response that is not truly equalized. The term EQ specifically refers to this variant of the term. Stereos typically have adjustable equalizers which boost or cut bass or treble frequencies. Broadcast and recording studios use sophisticated equalizers capable of much more detailed adjustments, such as eliminating unwanted sounds or making certain instruments or voices more prominent.Equalizers are used in recording studios, radio studios and production control rooms, and live sound reinforcement to correct the response of microphones, instrument pick-ups, loudspeakers, and hall acoustics. Equalization may also be used to eliminate unwanted sounds, make certain instruments or voices more prominent, enhance particular aspects of an instrument's tone, or combat feedback (howling) in a public address system. Equalizers are also used in music production to adjust the timbre of individual instruments by adjusting their frequency content and to fit individual instruments within the overall frequency spectrum of the mix.The most common equalizers in music production are parametric, semi-parametric, graphic, peak, and program equalizers. Graphic equalizers are often included in consumer audio equipment and software which plays music on home computers. Parametric equalizers require more expertise than graphic equalizers, and they can provide more specific compensation or alteration around a chosen frequency. This may be used in order to remove (or to create) a resonance, for instance.