Extremely Low Frequency Plasmons in Metallic Microstructures
... twice the lattice spacing. Therefore Bragg diffraction effects would interfere with our simple plasmon picture. Choosing a small radius ensures that diffraction occurs only at much higher frequencies. ...
... twice the lattice spacing. Therefore Bragg diffraction effects would interfere with our simple plasmon picture. Choosing a small radius ensures that diffraction occurs only at much higher frequencies. ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... • High-pitched sounds used in music are most often less than 4000 Hz, but the average human ear can hear sounds with frequencies up to 18,000 Hz. – Some people and most dogs can hear tones of higher pitch than this. – The upper limit of hearing in people gets lower as they grow older. – A high-pitch ...
... • High-pitched sounds used in music are most often less than 4000 Hz, but the average human ear can hear sounds with frequencies up to 18,000 Hz. – Some people and most dogs can hear tones of higher pitch than this. – The upper limit of hearing in people gets lower as they grow older. – A high-pitch ...
The text of the original article (Word 2000 format)
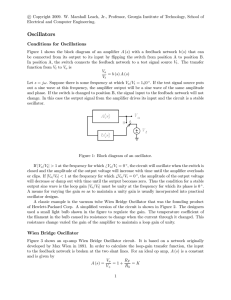
... antenna only produces a few millivolts peak of 50Hz hum in the test circuit, which does not upset calculations. However, in locations near overhead high voltage lines, hum pickup may possibly become a problem, and can be dealt with either by placing an RF choke directly across the instrument termina ...
... antenna only produces a few millivolts peak of 50Hz hum in the test circuit, which does not upset calculations. However, in locations near overhead high voltage lines, hum pickup may possibly become a problem, and can be dealt with either by placing an RF choke directly across the instrument termina ...
ppt - EC - Unit 6 - sine wave -1
... • A VCO is an oscillator circuit in which the frequency can be varied by an applied voltage • This is achieved by “varicap”, whose capacitance varies with applied voltage. • Varicap is used in tank circuit, which determines frequency ...
... • A VCO is an oscillator circuit in which the frequency can be varied by an applied voltage • This is achieved by “varicap”, whose capacitance varies with applied voltage. • Varicap is used in tank circuit, which determines frequency ...
Equalization (audio)

Equalization (British: equalisation) is the process of adjusting the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal. The most well known use of equalization is in sound recording and reproduction but there are many other applications in electronics and telecommunications. The circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization is called an equalizer. These devices strengthen (boost) or weaken (cut) the energy of specific frequency bands.In sound recording and reproduction, equalization is the process commonly used to alter the frequency response of an audio system using linear filters. Most hi-fi equipment uses relatively simple filters to make bass and treble adjustments. Graphic and parametric equalizers have much more flexibility in tailoring the frequency content of an audio signal. An equalizer is the circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization. Since equalizers, ""adjust the amplitude of audio signals at particular frequencies,"" they are, ""in other words, frequency-specific volume knobs.""In the field of audio electronics, the term ""equalization"" has come to include the adjustment of frequency responses for practical or aesthetic reasons, often resulting in a net response that is not truly equalized. The term EQ specifically refers to this variant of the term. Stereos typically have adjustable equalizers which boost or cut bass or treble frequencies. Broadcast and recording studios use sophisticated equalizers capable of much more detailed adjustments, such as eliminating unwanted sounds or making certain instruments or voices more prominent.Equalizers are used in recording studios, radio studios and production control rooms, and live sound reinforcement to correct the response of microphones, instrument pick-ups, loudspeakers, and hall acoustics. Equalization may also be used to eliminate unwanted sounds, make certain instruments or voices more prominent, enhance particular aspects of an instrument's tone, or combat feedback (howling) in a public address system. Equalizers are also used in music production to adjust the timbre of individual instruments by adjusting their frequency content and to fit individual instruments within the overall frequency spectrum of the mix.The most common equalizers in music production are parametric, semi-parametric, graphic, peak, and program equalizers. Graphic equalizers are often included in consumer audio equipment and software which plays music on home computers. Parametric equalizers require more expertise than graphic equalizers, and they can provide more specific compensation or alteration around a chosen frequency. This may be used in order to remove (or to create) a resonance, for instance.