Vocal Harmonizer and Vocoder
... We designed and built a vocoder and vocal harmonizer. The vocoder allows one sound to be manipulated to sound like another, such as to make white noise sound like speech. The harmonizer detects the frequency of the operator singing into a microphone and creates a set of output waveforms which form a ...
... We designed and built a vocoder and vocal harmonizer. The vocoder allows one sound to be manipulated to sound like another, such as to make white noise sound like speech. The harmonizer detects the frequency of the operator singing into a microphone and creates a set of output waveforms which form a ...
Optimized Resonant Harmonic Filters
... as a2 increases and a1 declines, the lower frequency pole p1 will increase in value and the separation between the poles will decrease. As shown by equation (7), the pole locations of three and four branch RHFs are given by the zeros of cubic and quartic polynomials respectively. Although there are ...
... as a2 increases and a1 declines, the lower frequency pole p1 will increase in value and the separation between the poles will decrease. As shown by equation (7), the pole locations of three and four branch RHFs are given by the zeros of cubic and quartic polynomials respectively. Although there are ...
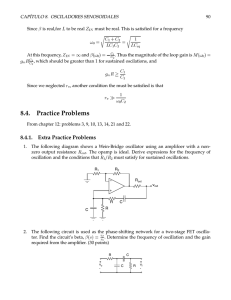
Closed Loop Gain of an Operational Amplifier
... the fact excessively high gains are obtained at low frequencies across a short bandwidth. The desirable effect is generally a smaller gain that is constant over a wide range of frequencies. This is achieved by ‘feeding back’ a fraction of Vout into the inverting input of the Op-Amp, shown in Figure ...
... the fact excessively high gains are obtained at low frequencies across a short bandwidth. The desirable effect is generally a smaller gain that is constant over a wide range of frequencies. This is achieved by ‘feeding back’ a fraction of Vout into the inverting input of the Op-Amp, shown in Figure ...
A SIGE LOW PHASE NOISE PUSH
... This paper describes a monolithically integrated push-push oscillator fabricated in a production-near SiGe:C bipolar technology. The transistors used in this work show a maximum transit frequency f T = 200 GHz and a maximum frequency of oscillation f max = 275 GHz. For the passive circuitry transmis ...
... This paper describes a monolithically integrated push-push oscillator fabricated in a production-near SiGe:C bipolar technology. The transistors used in this work show a maximum transit frequency f T = 200 GHz and a maximum frequency of oscillation f max = 275 GHz. For the passive circuitry transmis ...
Equalization (audio)

Equalization (British: equalisation) is the process of adjusting the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal. The most well known use of equalization is in sound recording and reproduction but there are many other applications in electronics and telecommunications. The circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization is called an equalizer. These devices strengthen (boost) or weaken (cut) the energy of specific frequency bands.In sound recording and reproduction, equalization is the process commonly used to alter the frequency response of an audio system using linear filters. Most hi-fi equipment uses relatively simple filters to make bass and treble adjustments. Graphic and parametric equalizers have much more flexibility in tailoring the frequency content of an audio signal. An equalizer is the circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization. Since equalizers, ""adjust the amplitude of audio signals at particular frequencies,"" they are, ""in other words, frequency-specific volume knobs.""In the field of audio electronics, the term ""equalization"" has come to include the adjustment of frequency responses for practical or aesthetic reasons, often resulting in a net response that is not truly equalized. The term EQ specifically refers to this variant of the term. Stereos typically have adjustable equalizers which boost or cut bass or treble frequencies. Broadcast and recording studios use sophisticated equalizers capable of much more detailed adjustments, such as eliminating unwanted sounds or making certain instruments or voices more prominent.Equalizers are used in recording studios, radio studios and production control rooms, and live sound reinforcement to correct the response of microphones, instrument pick-ups, loudspeakers, and hall acoustics. Equalization may also be used to eliminate unwanted sounds, make certain instruments or voices more prominent, enhance particular aspects of an instrument's tone, or combat feedback (howling) in a public address system. Equalizers are also used in music production to adjust the timbre of individual instruments by adjusting their frequency content and to fit individual instruments within the overall frequency spectrum of the mix.The most common equalizers in music production are parametric, semi-parametric, graphic, peak, and program equalizers. Graphic equalizers are often included in consumer audio equipment and software which plays music on home computers. Parametric equalizers require more expertise than graphic equalizers, and they can provide more specific compensation or alteration around a chosen frequency. This may be used in order to remove (or to create) a resonance, for instance.