COMBINED SERIES-PARALLEL CIRCUIT EXAMPLE
... The combination of parallel resistors resulted in equivalent resistances less than any single resistor in the combination, as expected. The voltage across R5 was less than the voltage supplied by the battery, as expected. ...
... The combination of parallel resistors resulted in equivalent resistances less than any single resistor in the combination, as expected. The voltage across R5 was less than the voltage supplied by the battery, as expected. ...
Exercise 3
... 1. Measure and record the voltage supplied to the circuit:___________________. 2. Measure and record the voltage drop across each resistor: R1:____________________ R2:____________________ R3:____________________ 3. Is it true that the sum of the voltage drops across the circuit is equal the voltage ...
... 1. Measure and record the voltage supplied to the circuit:___________________. 2. Measure and record the voltage drop across each resistor: R1:____________________ R2:____________________ R3:____________________ 3. Is it true that the sum of the voltage drops across the circuit is equal the voltage ...
smith_wangaDAC2
... by 400mV over -40C to 85C (3.2 mV/˚C) • 1.1V reference varies by 150mV over -40C to 85C (1.2 mV/˚C) ...
... by 400mV over -40C to 85C (3.2 mV/˚C) • 1.1V reference varies by 150mV over -40C to 85C (1.2 mV/˚C) ...
R09 SET-1 Code No: R09221902
... Answer any five questions All questions carry equal marks --1.a) What are the Four Differential Amplifier Configurations? Compare and Contrast these configurations with Circuit Diagrams. b) For an Op-Amp, PSRR=70dB, CMRR=105, differential mode gain Ad=105. The output voltage changes by 20V in 4μsec. ...
... Answer any five questions All questions carry equal marks --1.a) What are the Four Differential Amplifier Configurations? Compare and Contrast these configurations with Circuit Diagrams. b) For an Op-Amp, PSRR=70dB, CMRR=105, differential mode gain Ad=105. The output voltage changes by 20V in 4μsec. ...
Portable Appliance Testing Course Pre-Study Revision
... i.e.… voltage (V) measured in volts (V), current (I) measured in Amperes (or amps for short) (A), resistance (R) measured in ohm’s (), power (P) measured in watts (W) The candidate will need to understand basic numeric prefixes used with electrical symbols and measurement units i.e.… milli (m) a ...
... i.e.… voltage (V) measured in volts (V), current (I) measured in Amperes (or amps for short) (A), resistance (R) measured in ohm’s (), power (P) measured in watts (W) The candidate will need to understand basic numeric prefixes used with electrical symbols and measurement units i.e.… milli (m) a ...
(ADC) and Digital to analog converter (DAC)
... What input is needed to get a 6.5 volt output? 2. A bipolar DAC hat 10 bits and a reference of 5v.what outputs will result from input of 04FH and 2A4H.What digital input gives a zero output voltage? 3. Determine how many bits a D/A converter must have to provide output increments of 0.04 volts or le ...
... What input is needed to get a 6.5 volt output? 2. A bipolar DAC hat 10 bits and a reference of 5v.what outputs will result from input of 04FH and 2A4H.What digital input gives a zero output voltage? 3. Determine how many bits a D/A converter must have to provide output increments of 0.04 volts or le ...
EO323_04-05 - University of Brighton
... manner. A differential amplifier using operational amplifier A1, a voltage inverter, INV and an integrator using operational amplifier A2. The circuit is initially in a stable state with the input voltage Vin equal to zero and no voltage across the capacitor Vc. However whenever an input voltage is ...
... manner. A differential amplifier using operational amplifier A1, a voltage inverter, INV and an integrator using operational amplifier A2. The circuit is initially in a stable state with the input voltage Vin equal to zero and no voltage across the capacitor Vc. However whenever an input voltage is ...
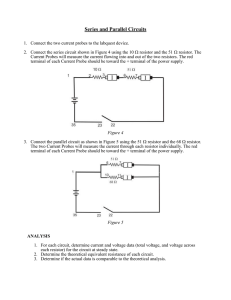
Series and Parallel Circuits
... 1. Connect the two current probes to the labquest device. 2. Connect the series circuit shown in Figure 4 using the 10 resistor and the 51 resistor. The Current Probes will measure the current flowing into and out of the two resistors. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the ...
... 1. Connect the two current probes to the labquest device. 2. Connect the series circuit shown in Figure 4 using the 10 resistor and the 51 resistor. The Current Probes will measure the current flowing into and out of the two resistors. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the ...
14.1 Series Circuits
... •I=V/R • You can calculate current (I) if you know voltage and resistance ...
... •I=V/R • You can calculate current (I) if you know voltage and resistance ...
Chapter 3 Special-Purpose Diodes
... There are other input parameters to be considered for opamp operation. The input bias current is the dc current required to properly operate the first stage within the opamp. The input impedance is another. Also, the input offset current which can become a problem if both dc input currents are not t ...
... There are other input parameters to be considered for opamp operation. The input bias current is the dc current required to properly operate the first stage within the opamp. The input impedance is another. Also, the input offset current which can become a problem if both dc input currents are not t ...
Introduction - facstaff.bucknell.edu
... voltage of an LM 35 from a 10 mV/°C scale to a 10 mV/°F scale. Use power supply voltages of ±10 V for the entire circuit. You will have to determine appropriate values for resistors R1 and R2 and the voltage reference Vref. Initially use a short in place of Rx. (That is, set Rx = 0.) Note that many ...
... voltage of an LM 35 from a 10 mV/°C scale to a 10 mV/°F scale. Use power supply voltages of ±10 V for the entire circuit. You will have to determine appropriate values for resistors R1 and R2 and the voltage reference Vref. Initially use a short in place of Rx. (That is, set Rx = 0.) Note that many ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).