MAX3040–MAX3045 ±10kV ESD-Protected, Quad 5V RS-485/RS-422 Transmitters General Description
... IEC 1000-4-4 Electrical Fast Transient/Burst (EFT/B) is an immunity test for the evaluation of electrical and electronic systems during operating conditions. The test was adapted for evaluation of integrated circuits with power applied. Repetitive fast transients with severe pulsed EMI were applied ...
... IEC 1000-4-4 Electrical Fast Transient/Burst (EFT/B) is an immunity test for the evaluation of electrical and electronic systems during operating conditions. The test was adapted for evaluation of integrated circuits with power applied. Repetitive fast transients with severe pulsed EMI were applied ...
PDF: 410KB
... DIP-PFC should be used together with its control IC and DIP-IPM. 3. It is necessary to operate DIP-PFC, the control IC, DIP-IPM and MCU on the same GND stage. This GND is usually set to the DIP-PFC N terminal. 4. A large charge current of the electrolytic condenser will flow on the DIP-PFC when appl ...
... DIP-PFC should be used together with its control IC and DIP-IPM. 3. It is necessary to operate DIP-PFC, the control IC, DIP-IPM and MCU on the same GND stage. This GND is usually set to the DIP-PFC N terminal. 4. A large charge current of the electrolytic condenser will flow on the DIP-PFC when appl ...
DIP-PFC APPLICATION NOTE MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION POWER SEMICONDUCTOR
... DIP-PFC should be used together with its control IC and DIP-IPM. 3. It is necessary to operate DIP-PFC, the control IC, DIP-IPM and MCU on the same GND stage. This GND is usually set to the DIP-PFC N terminal. 4. A large charge current of the electrolytic condenser will flow on the DIP-PFC when appl ...
... DIP-PFC should be used together with its control IC and DIP-IPM. 3. It is necessary to operate DIP-PFC, the control IC, DIP-IPM and MCU on the same GND stage. This GND is usually set to the DIP-PFC N terminal. 4. A large charge current of the electrolytic condenser will flow on the DIP-PFC when appl ...
hxlvdsr - Honeywell
... (2) Maximum LVDS Receiver Jitter performance is guaranteed between -5°C and 125°C case temperature, between 3.0 V and 3.6 V; and pre- and post-radiation. a. Receiver input is terminated with 100 Ω ± 1% resistor. b. Receiver differential input signal of 200 mVP-P(differential) amplitude, Common Mode ...
... (2) Maximum LVDS Receiver Jitter performance is guaranteed between -5°C and 125°C case temperature, between 3.0 V and 3.6 V; and pre- and post-radiation. a. Receiver input is terminated with 100 Ω ± 1% resistor. b. Receiver differential input signal of 200 mVP-P(differential) amplitude, Common Mode ...
Charge and Discharge of a Capacitor
... capacitors. In plasma physics short pulses of energy at extremely high voltages and currents are frequently needed. A capacitor can be slowly charged to the necessary voltage and then discharged quickly to provide the energy needed. It is even possible to charge several capacitors to a certain volta ...
... capacitors. In plasma physics short pulses of energy at extremely high voltages and currents are frequently needed. A capacitor can be slowly charged to the necessary voltage and then discharged quickly to provide the energy needed. It is even possible to charge several capacitors to a certain volta ...
Sample Formal Report - Courses
... provides a relationship between the voltage and current associated with a resistor, while KVL and KCL provide constraints on the sum of the voltages around a closed loop and the sum of currents at a circuit node. Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Laws are applied frequently in the analysis and design of ele ...
... provides a relationship between the voltage and current associated with a resistor, while KVL and KCL provide constraints on the sum of the voltages around a closed loop and the sum of currents at a circuit node. Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Laws are applied frequently in the analysis and design of ele ...
MAX8833 Dual, 3A, 2MHz Step-Down Regulator General Description Features
... The MAX8833 high-efficiency, dual step-down regulator is capable of delivering up to 3A at each output. The device operates from a 2.35V to 3.6V supply, and provides output voltages from 0.6V to 0.9 x VIN, making it ideal for on-board point-of-load applications. Total output error is less than ±1% o ...
... The MAX8833 high-efficiency, dual step-down regulator is capable of delivering up to 3A at each output. The device operates from a 2.35V to 3.6V supply, and provides output voltages from 0.6V to 0.9 x VIN, making it ideal for on-board point-of-load applications. Total output error is less than ±1% o ...
a 14-Bit, 125 MSPS TxDAC D/A Converter
... Power Dissipation6 (5 V, IOUTFS = 20 mA) Power Dissipation7 (5 V, IOUTFS = 20 mA) Power Dissipation7 (3 V, IOUTFS = 2 mA) Power Supply Rejection Ratio8—AVDD Power Supply Rejection Ratio8—DVDD ...
... Power Dissipation6 (5 V, IOUTFS = 20 mA) Power Dissipation7 (5 V, IOUTFS = 20 mA) Power Dissipation7 (3 V, IOUTFS = 2 mA) Power Supply Rejection Ratio8—AVDD Power Supply Rejection Ratio8—DVDD ...
Experimental Verification of Kirchhoff`s Voltage Law and
... provides a relationship between the voltage and current associated with a resistor, while KVL and KCL provide constraints on the sum of the voltages around a closed loop and the sum of currents at a circuit node. Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Laws are applied frequently in the analysis and design of ele ...
... provides a relationship between the voltage and current associated with a resistor, while KVL and KCL provide constraints on the sum of the voltages around a closed loop and the sum of currents at a circuit node. Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Laws are applied frequently in the analysis and design of ele ...
LTC5582 - 40MHz to 10GHz RMS Power Detector with 57dB Dynamic Range.
... one can be driven with a single-ended signal while the other is AC-coupled to ground. These pins can also be driven with a differential signal. The pins are internally biased to 1.585V and should be DC blocked externally. The differential impedance is typically 400Ω. The impedance of each pin to the ...
... one can be driven with a single-ended signal while the other is AC-coupled to ground. These pins can also be driven with a differential signal. The pins are internally biased to 1.585V and should be DC blocked externally. The differential impedance is typically 400Ω. The impedance of each pin to the ...
Total House Power Monitoring System
... V digital signal from the A/D to a –10-10 V signal required for the serial port. One output from the RS 232 driver chip is sent to the computer via a 9-pin serial port cable. The second output is sent to the computer via a 25-pin serial port cable. The pin assignments for the RS232 driver chip are s ...
... V digital signal from the A/D to a –10-10 V signal required for the serial port. One output from the RS 232 driver chip is sent to the computer via a 9-pin serial port cable. The second output is sent to the computer via a 25-pin serial port cable. The pin assignments for the RS232 driver chip are s ...
TL4242 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The TL4242 is an integrated adjustable constant-current source, driving loads up to 500 mA. The output current level can be adjusted via an external resistor. The device is designed to supply high-power LEDs (for example, OSRAM Dragon LA W57B) under the severe conditions of automotive applications, ...
... The TL4242 is an integrated adjustable constant-current source, driving loads up to 500 mA. The output current level can be adjusted via an external resistor. The device is designed to supply high-power LEDs (for example, OSRAM Dragon LA W57B) under the severe conditions of automotive applications, ...
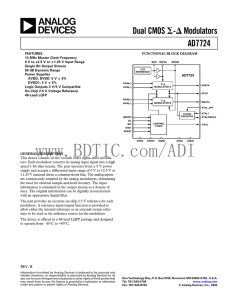
a Dual CMOS AD7724 -
... www.BDTIC.com/ADI Figure 1. Digital Filter (Consists of Two FIR Filters). This Filter is Implemented on the AD7722. ...
... www.BDTIC.com/ADI Figure 1. Digital Filter (Consists of Two FIR Filters). This Filter is Implemented on the AD7722. ...
Electronic Voltmeters and Ammeters
... Alessandro Ferrero was born in Milano (Milan), Italy, in 1954. He received his M.S. degree in Electrical Engineering from the Politecnico di Milano in 1978. In 1983 he joined the Dipartimento di Elettrotecnica of the Politecnico di Milano as an Assistant Professor on Electrical Measurements. From 19 ...
... Alessandro Ferrero was born in Milano (Milan), Italy, in 1954. He received his M.S. degree in Electrical Engineering from the Politecnico di Milano in 1978. In 1983 he joined the Dipartimento di Elettrotecnica of the Politecnico di Milano as an Assistant Professor on Electrical Measurements. From 19 ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).