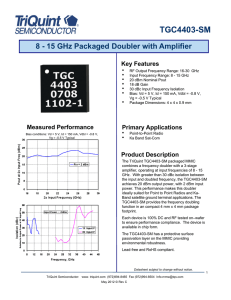
General Description Features
... enables optimal use of MOSFETs with optimal charge and on-resistance characteristics. This results in the minimized need for external heatsinking even when delivering up to 30A of LED current. True differential sensing enables accurate control of the LED current. A wide dimming range is easily imple ...
... enables optimal use of MOSFETs with optimal charge and on-resistance characteristics. This results in the minimized need for external heatsinking even when delivering up to 30A of LED current. True differential sensing enables accurate control of the LED current. A wide dimming range is easily imple ...
FMS6646 Six Channel, SD/HD 1080p Video Filter Driver Description
... FMS6646 without an AC coupling capacitor. The worstcase sync tip compression due to the clamp does not exceed 7mV. The input level set by the clamp, combined with the internal DC offset, keeps the output within its acceptable range. When the input is ACcoupled, the diode clamp sets the sync tip (or ...
... FMS6646 without an AC coupling capacitor. The worstcase sync tip compression due to the clamp does not exceed 7mV. The input level set by the clamp, combined with the internal DC offset, keeps the output within its acceptable range. When the input is ACcoupled, the diode clamp sets the sync tip (or ...
UNIT 12
... capacitance effects (see section 12.5) that can be neglected at audio frequencies. High power r.f. amplifiers which produce up to hundreds of kilowatts of power use thermionic valves since present-day transistors cannot cope with the heat that has to be dissipated for such powers. They are employed ...
... capacitance effects (see section 12.5) that can be neglected at audio frequencies. High power r.f. amplifiers which produce up to hundreds of kilowatts of power use thermionic valves since present-day transistors cannot cope with the heat that has to be dissipated for such powers. They are employed ...
AN1316 Frequency Output Conversion for MPX2000 Series
... Many different “instrumentation-type” amplifier circuits can satisfy the signal conditioning needs of these devices. Depending on the precision and temperature performance demanded by a given application, one can design an amplifier circuit using a wide variety of operational amplifier (op amp) IC p ...
... Many different “instrumentation-type” amplifier circuits can satisfy the signal conditioning needs of these devices. Depending on the precision and temperature performance demanded by a given application, one can design an amplifier circuit using a wide variety of operational amplifier (op amp) IC p ...
REF200 Dual Current Source and Current Sink (Rev. B)
... Applications for the REF200 are limitless. Application Bulletin AB-165 (SBOA046) shows additional REF200 circuits as well as other related current source techniques. In this section, a collection of circuits are shown to illustrate some techniques. If the current sources are subjected to reverse vol ...
... Applications for the REF200 are limitless. Application Bulletin AB-165 (SBOA046) shows additional REF200 circuits as well as other related current source techniques. In this section, a collection of circuits are shown to illustrate some techniques. If the current sources are subjected to reverse vol ...
Alternating Current Circuits
... where V is the voltage amplitude. If V , R, C, and L are fixed and the frequency of the AC generator is variable, we can change the reactances of the inductor and capacitor by changing the frequency of the generator. As the frequency of the generator changes, so does the impedance Z of the circuit a ...
... where V is the voltage amplitude. If V , R, C, and L are fixed and the frequency of the AC generator is variable, we can change the reactances of the inductor and capacitor by changing the frequency of the generator. As the frequency of the generator changes, so does the impedance Z of the circuit a ...
SET 2 - contentcarry
... brief flash of light each time they are struck by an alpha or beta or gamma particles. The production of a flash of light by striking the crystals mentioned above, with alpha, beta or gamma rays, is called scintillation. 9:- (c) Stack works on the principle of LIFO. 10:- (b) the cost of an induction ...
... brief flash of light each time they are struck by an alpha or beta or gamma particles. The production of a flash of light by striking the crystals mentioned above, with alpha, beta or gamma rays, is called scintillation. 9:- (c) Stack works on the principle of LIFO. 10:- (b) the cost of an induction ...
Features
... This device consists of eight Function Blocks inter-connected by a low power Advanced Interconnect Matrix (AIM). The AIM feeds 40 true and complement inputs to each Function Block. The Function Blocks consist of a 40 by 56 P-term PLA and 16 macrocells which contain numerous configuration bits that a ...
... This device consists of eight Function Blocks inter-connected by a low power Advanced Interconnect Matrix (AIM). The AIM feeds 40 true and complement inputs to each Function Block. The Function Blocks consist of a 40 by 56 P-term PLA and 16 macrocells which contain numerous configuration bits that a ...
measuring current - mrhsluniewskiscience
... the resistance of the wire depends upon the range of the ammeter As shunt resistance is small the combined resistance of the galvanometer & the shunt is very low hence the ammeter has much lower resistance than galvanometer An ideal ammeter has zero resistance ...
... the resistance of the wire depends upon the range of the ammeter As shunt resistance is small the combined resistance of the galvanometer & the shunt is very low hence the ammeter has much lower resistance than galvanometer An ideal ammeter has zero resistance ...
Using equivalence resistance to calculate current
... give the greatest brightness in the lamp bulb. Which connection should be made? A across AB B across BC C across CD D across AD E across BD ...
... give the greatest brightness in the lamp bulb. Which connection should be made? A across AB B across BC C across CD D across AD E across BD ...
SiGe BiCMOS Precision Voltage References for
... characteristics of the current gain of the SiGe HBT for curvature compensation. To enable meaningful circuit design, the calibrated VBIC models within the design kit were first modified and fit to low temperature transistor data. The schematic of the BGR circuit is shown in Fig. 4. Each of the bipol ...
... characteristics of the current gain of the SiGe HBT for curvature compensation. To enable meaningful circuit design, the calibrated VBIC models within the design kit were first modified and fit to low temperature transistor data. The schematic of the BGR circuit is shown in Fig. 4. Each of the bipol ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).