The Biology of Trauma - BC Association of Social Workers
... Lack interpersonal connections Often insist don’t recall childhood Incoherent ...
... Lack interpersonal connections Often insist don’t recall childhood Incoherent ...
Respiratory System
... Your hairs in your nose help clean the air and warm it as well. The surface area of your lungs is approximately the same size of a tennis court. Some people can hold their breath for more than 20 minutes, such as free divers. Asthma was once treated with psychotherapy during the 1930s-1950s. ...
... Your hairs in your nose help clean the air and warm it as well. The surface area of your lungs is approximately the same size of a tennis court. Some people can hold their breath for more than 20 minutes, such as free divers. Asthma was once treated with psychotherapy during the 1930s-1950s. ...
Introduction
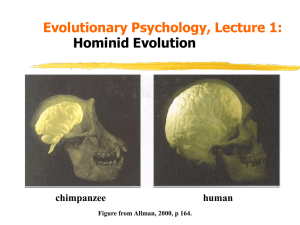
... Hominid Brain Evolution. As Allman (2000) points out, if large brains enable animals to deal better with changing and unpredictable environments then why don't all species have large and complex brains? In fact animals with large brains are rare, probably due to the costs involved: A large brai ...
... Hominid Brain Evolution. As Allman (2000) points out, if large brains enable animals to deal better with changing and unpredictable environments then why don't all species have large and complex brains? In fact animals with large brains are rare, probably due to the costs involved: A large brai ...
Nervous
... stimuli. • There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves which branch from the spinal cord to control such processes as breathing, arm movement, and leg movement. ...
... stimuli. • There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves which branch from the spinal cord to control such processes as breathing, arm movement, and leg movement. ...
Andrew Rosen - Chapter 3: The Brain and Nervous System Intro
... Neurons – Individual cells that act as the main information processors of the nervous system (100 billion) Glia cells – Another brain cell outnumbering neurons 10:1 Nerve impulse – Means through which individual neurons communicate with one another ...
... Neurons – Individual cells that act as the main information processors of the nervous system (100 billion) Glia cells – Another brain cell outnumbering neurons 10:1 Nerve impulse – Means through which individual neurons communicate with one another ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
VCE Psychology Trail - Unit 1
... Phrenology head 4. The phrenology head is an example of another pseudoscience. Look at the names given by phrenology to the regions of the head and write six in the spaces below: a ...
... Phrenology head 4. The phrenology head is an example of another pseudoscience. Look at the names given by phrenology to the regions of the head and write six in the spaces below: a ...
Nonlinear Behavior of Neocortical Networks
... sophistication of neural nets and increase their power (Spruston and Kath 2004). Examination of nonlinear components of network activity may provide a powerful link between the understanding of single neuron behavior and the power of the brain as a whole. Determining how the brain establishes and ma ...
... sophistication of neural nets and increase their power (Spruston and Kath 2004). Examination of nonlinear components of network activity may provide a powerful link between the understanding of single neuron behavior and the power of the brain as a whole. Determining how the brain establishes and ma ...
Answers
... 1. A neuron is a ___NERVE___ cell. The brain is made up of about _100__billion neurons. 2. Neurons are similar to other cells in the body in some ways such as: a. Neurons are surrounded by a ________MEMBRANE_______________________. b. Neurons have a ______NUCLEUS____________ that contains __GENES___ ...
... 1. A neuron is a ___NERVE___ cell. The brain is made up of about _100__billion neurons. 2. Neurons are similar to other cells in the body in some ways such as: a. Neurons are surrounded by a ________MEMBRANE_______________________. b. Neurons have a ______NUCLEUS____________ that contains __GENES___ ...
Samantha Zarati - A critical review of computational neurological models
... and the novel creation Neurogrid. Though other techniques exist, these two general types of approaches encompass the diversity of models used to simulate neural networks; specific examples within each approach are either revolutionary or extremely widely used, and so are significant in different way ...
... and the novel creation Neurogrid. Though other techniques exist, these two general types of approaches encompass the diversity of models used to simulate neural networks; specific examples within each approach are either revolutionary or extremely widely used, and so are significant in different way ...
What happens in a neuron
... broad spectrum of signs and symptoms. Disease onset usually occurs in young adults, and it is more common in women. MS affects the ability of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord to communicate with each other effectively. Nerve cells communicate by sending electrical signals called action poten ...
... broad spectrum of signs and symptoms. Disease onset usually occurs in young adults, and it is more common in women. MS affects the ability of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord to communicate with each other effectively. Nerve cells communicate by sending electrical signals called action poten ...
Document
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of sound? • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive sound information subsequently project the information to the primary auditory cortex. Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary auditory cortex (SII) ...
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of sound? • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive sound information subsequently project the information to the primary auditory cortex. Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary auditory cortex (SII) ...
Cognitive Function
... vitamin A into cells. SERINE – This amino acid is the major component of phosphatidylserine, an integral part of cell membranes in the brain. Phosphatidylserine increases the release of several neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine and epinephrine, thus improving the rate a ...
... vitamin A into cells. SERINE – This amino acid is the major component of phosphatidylserine, an integral part of cell membranes in the brain. Phosphatidylserine increases the release of several neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine and epinephrine, thus improving the rate a ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
lab 8: central nervous system
... Identify the 3 meninges in the split brain model and the model of the spinal cord cross section when you have the opportunity to view these models NOTE: at 4 locations, the cranial dura mater extends deep into the cranial cavity providing support to the brain. Identify the following on the cranial m ...
... Identify the 3 meninges in the split brain model and the model of the spinal cord cross section when you have the opportunity to view these models NOTE: at 4 locations, the cranial dura mater extends deep into the cranial cavity providing support to the brain. Identify the following on the cranial m ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
Neurons - Seung Lab
... Dendrites and axons are types of neurites • They can be distinguished in some types of neurons. • Dendrites receive synaptic inputs. • Axons make synapses on other neurons. ...
... Dendrites and axons are types of neurites • They can be distinguished in some types of neurons. • Dendrites receive synaptic inputs. • Axons make synapses on other neurons. ...
Flyer
... College of Information Science and Technology will be the proud host to BIH ’16 and WI’16. This series provides a premier forum that will bring together researchers and practitioners, high-quality, original research papers and real-world applications in all theoretical and technology areas. Under ou ...
... College of Information Science and Technology will be the proud host to BIH ’16 and WI’16. This series provides a premier forum that will bring together researchers and practitioners, high-quality, original research papers and real-world applications in all theoretical and technology areas. Under ou ...
What Are They Thinking? Understanding Your Child’s Brain
... able to hear external sounds and see light. He feels when his mother rubs her expanded belly. ...
... able to hear external sounds and see light. He feels when his mother rubs her expanded belly. ...
CHAPTER 3 THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... or folded. The folds are called sulci (singular = sulcus) or fissures, and the protruding parts are called gyri (singular = gyrus). On the views of both brains, the cranial nerves have been cut, but the stumps are visible where they exit the brain (indicated by Roman numerals on the cat brain). ...
... or folded. The folds are called sulci (singular = sulcus) or fissures, and the protruding parts are called gyri (singular = gyrus). On the views of both brains, the cranial nerves have been cut, but the stumps are visible where they exit the brain (indicated by Roman numerals on the cat brain). ...
History of Psychology
... 2. Wave 1 – Introspection a. 1879 – beginning of psychology b. Key people i. Wilhelm Wundt – first psych lab @ Leipzig, Germany. 1. Introspection was big to him 2. Structuralism – mind operated by combining subjective emotions and objective sensations ii. William James – The Principles of Psychology ...
... 2. Wave 1 – Introspection a. 1879 – beginning of psychology b. Key people i. Wilhelm Wundt – first psych lab @ Leipzig, Germany. 1. Introspection was big to him 2. Structuralism – mind operated by combining subjective emotions and objective sensations ii. William James – The Principles of Psychology ...
nervous tissue organization neurons neuroglia action potentials
... working = stored in brain & can be recalled by new input, facilitated synapses which are quiet and can be reactivated post tetanic potentiation = easily excited due to recent use long term = info that you retain for a lifetime declarative = memory of events you can describe with words procedural = m ...
... working = stored in brain & can be recalled by new input, facilitated synapses which are quiet and can be reactivated post tetanic potentiation = easily excited due to recent use long term = info that you retain for a lifetime declarative = memory of events you can describe with words procedural = m ...
slides
... parietal cortex: a rather abstract frame of reference – the space defined by the route (i.e., the space defined by sequence of behavior changes and the spaces separating them) ...
... parietal cortex: a rather abstract frame of reference – the space defined by the route (i.e., the space defined by sequence of behavior changes and the spaces separating them) ...