Document
... Meth & the Brain: •Prolonged use destroys dopamine receptors (which create the feeling of pleasure in the brain) •Can also lead to psychotic behaviors, including paranoia, insomnia, delusions, hallucinations, and even death Meth & the Body: •Destroys tissues and blood vessels, leaving the body inca ...
... Meth & the Brain: •Prolonged use destroys dopamine receptors (which create the feeling of pleasure in the brain) •Can also lead to psychotic behaviors, including paranoia, insomnia, delusions, hallucinations, and even death Meth & the Body: •Destroys tissues and blood vessels, leaving the body inca ...
weiten6_PPT07
... storage, and retrieval. Some theorists have drawn an analogy between these processes and elements of information processing by computers, as depicted here. The analogies for encoding and retrieval work pretty well, but the storage analogy is somewhat misleading. When information is stored on a hard ...
... storage, and retrieval. Some theorists have drawn an analogy between these processes and elements of information processing by computers, as depicted here. The analogies for encoding and retrieval work pretty well, but the storage analogy is somewhat misleading. When information is stored on a hard ...
Lab07 Brain - Tacoma Community College
... 1. Coverings of the Brain: The brain and spinal cord are protected by multiple layers of tissue. Most external is the skin, followed by the skull. Underneath the skull are three layers of c ...
... 1. Coverings of the Brain: The brain and spinal cord are protected by multiple layers of tissue. Most external is the skin, followed by the skull. Underneath the skull are three layers of c ...
Unit 7A Study Guide
... D) was not restricted to specific regions of the cortex. E) was not restricted to the association areas. 18. Research by Kandel and Schwartz on sea slugs indicates that memory formation is associated with the A) structure of DNA molecules. B) release of certain neurotransmitters. C) activity level o ...
... D) was not restricted to specific regions of the cortex. E) was not restricted to the association areas. 18. Research by Kandel and Schwartz on sea slugs indicates that memory formation is associated with the A) structure of DNA molecules. B) release of certain neurotransmitters. C) activity level o ...
background information - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... Cigarettes create dangerous health risks to the human body. For example, the chemicals in cigarettes can cause cancer in different organs throughout the body. In the circulatory system cigarette smoke can narrow the blood vessels and decrease the amount of blood flow. The small particles, particulat ...
... Cigarettes create dangerous health risks to the human body. For example, the chemicals in cigarettes can cause cancer in different organs throughout the body. In the circulatory system cigarette smoke can narrow the blood vessels and decrease the amount of blood flow. The small particles, particulat ...
Memory - AISG SP Moodle
... Episodic memory (also called autobiographical memory) – memory for personal events and people, i.e. the episodes of your life. Episodic memory is reconstructed as an evolving process of a person’s history. A person’s episodic memory may not be reliable because of memory distortions. ...
... Episodic memory (also called autobiographical memory) – memory for personal events and people, i.e. the episodes of your life. Episodic memory is reconstructed as an evolving process of a person’s history. A person’s episodic memory may not be reliable because of memory distortions. ...
lectures19-20-LTM
... • Immediate or delayed recall: people will remember “Sleep”, even though it was not on the list • Even with source warning, people make ...
... • Immediate or delayed recall: people will remember “Sleep”, even though it was not on the list • Even with source warning, people make ...
File
... There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves…… If you can memorize all 31 in 2 minutes, then you get an ec slip….BUT If you don’t get them all, then you have to lose 5 participation points from your grade. ...
... There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves…… If you can memorize all 31 in 2 minutes, then you get an ec slip….BUT If you don’t get them all, then you have to lose 5 participation points from your grade. ...
Biology 3.5 Responding to Stimuli
... synaptic cleft will be broken down by an enzyme – this is called inactivation • The remaining chemicals are reabsorbed into the presynaptic neuron and used again to make new neurotransmitters. ...
... synaptic cleft will be broken down by an enzyme – this is called inactivation • The remaining chemicals are reabsorbed into the presynaptic neuron and used again to make new neurotransmitters. ...
11-5_TheMulti-CenterAspectOfMotorControl. _NagyD
... The multi-center aspect of motor control All of the body's voluntary movements are controlled by the brain. One of the brain areas most involved in controlling these voluntary movements is the motor cortex. The motor cortex is located in the rear portion of the frontal lobe, just before the central ...
... The multi-center aspect of motor control All of the body's voluntary movements are controlled by the brain. One of the brain areas most involved in controlling these voluntary movements is the motor cortex. The motor cortex is located in the rear portion of the frontal lobe, just before the central ...
Addictive Drug Use - Dayton Independent Schools
... Monitor both external and internal environments. Integration: Process the information and often integrate it with stored information. Motor output: If necessary, signal effector organs to make an appropriate response. ...
... Monitor both external and internal environments. Integration: Process the information and often integrate it with stored information. Motor output: If necessary, signal effector organs to make an appropriate response. ...
Document
... Telencephalon (endbrain) is located at the front of the forebrain. – called cerebrum in mammals mammals have brains particularly large relative to their body mass largely reflects enlargement of cerebrum center for correlation, association, and learning in mammals ...
... Telencephalon (endbrain) is located at the front of the forebrain. – called cerebrum in mammals mammals have brains particularly large relative to their body mass largely reflects enlargement of cerebrum center for correlation, association, and learning in mammals ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... 1. Mammal forebrains are larger than other vertebrates because the forebrain includes a neocortex. ...
... 1. Mammal forebrains are larger than other vertebrates because the forebrain includes a neocortex. ...
Name: Date: Grade / Section: _____ Neurons Questions Notes 1
... ● A nerve impulse (message) travels in the form of an ________________ or _____________ signal ● Nerve impulses can travel as fast as ________! ● There is a tiny ________ between each axon tip and the next structure (dendrite of another neuron, muscle cell, sweat gland, etc.). This space is called a ...
... ● A nerve impulse (message) travels in the form of an ________________ or _____________ signal ● Nerve impulses can travel as fast as ________! ● There is a tiny ________ between each axon tip and the next structure (dendrite of another neuron, muscle cell, sweat gland, etc.). This space is called a ...
Sensation2011
... Specialized neurons that are activated by stimulation and transduce (convert) it into a nerve impulse Sensory pathway – Bundles of neurons that carry information from the sense organs to the brain ...
... Specialized neurons that are activated by stimulation and transduce (convert) it into a nerve impulse Sensory pathway – Bundles of neurons that carry information from the sense organs to the brain ...
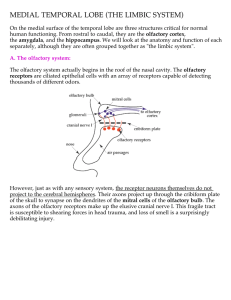
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
... The second type is what we most commonly associate with "memory". This is long-term or declarative memory, and is composed of all the facts, figures, and names you have ever learned. All of your experiences and conscious memory fall into this category. It is analogous to the hard drive of a computer ...
... The second type is what we most commonly associate with "memory". This is long-term or declarative memory, and is composed of all the facts, figures, and names you have ever learned. All of your experiences and conscious memory fall into this category. It is analogous to the hard drive of a computer ...
chapter38
... from the presynaptic neuron by exocytosis that can stimulate the postsynaptic neuron. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters. ...
... from the presynaptic neuron by exocytosis that can stimulate the postsynaptic neuron. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters. ...
Cognitive Psychology
... Sensory stores, a short term store and a long term store. • In the sensory stores, information and knowledge that comes to us from the senses is stored momentarily. After processing, some of this information is sent on to the short term store. • Some of the information in the short term store is the ...
... Sensory stores, a short term store and a long term store. • In the sensory stores, information and knowledge that comes to us from the senses is stored momentarily. After processing, some of this information is sent on to the short term store. • Some of the information in the short term store is the ...
structure and function of the neurologic system
... – Neurotransmitter binds the receptor on the postsynaptic neuron • Signals opening of nearby Na+ channels • Membrane potential changes in the postsynaptic neuron • Generation of action potential • Action potential travels through postsynaptic neuron’s dendrite, cell body and axon to axon ending ...
... – Neurotransmitter binds the receptor on the postsynaptic neuron • Signals opening of nearby Na+ channels • Membrane potential changes in the postsynaptic neuron • Generation of action potential • Action potential travels through postsynaptic neuron’s dendrite, cell body and axon to axon ending ...
File
... synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ floods into cell E. Stimulus triggers membrane depolarization ...
... synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ floods into cell E. Stimulus triggers membrane depolarization ...
Key to midterm - UCSD Cognitive Science
... 3. How would you reconcile the following observations: “Alternate states of consciousness (ASCs) are principally due to frontal cortex activity. However, a large body of evidence from lesion, imaging, and electrophysiological studies suggests that the prefrontal cortex is not necessary for basic aw ...
... 3. How would you reconcile the following observations: “Alternate states of consciousness (ASCs) are principally due to frontal cortex activity. However, a large body of evidence from lesion, imaging, and electrophysiological studies suggests that the prefrontal cortex is not necessary for basic aw ...