Peripheral Nervous System
... from the senses, controls the skeletal muscles, and carries out processes like judging, remembering, and learning. The cerebrum is divided into the right and left cerebrum. Each half has its own functions. The right cerebrum receives impulses from the skeletal muscles on the left side of the body an ...
... from the senses, controls the skeletal muscles, and carries out processes like judging, remembering, and learning. The cerebrum is divided into the right and left cerebrum. Each half has its own functions. The right cerebrum receives impulses from the skeletal muscles on the left side of the body an ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functions sensory, integrative and ...
... of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functions sensory, integrative and ...
Which structures of the eye are responsible for refraction of light
... What is strabismus and which structures can be responsible? Which areas of the brain receive synapses from axons of retinal ganglion cells? What is the function of each of the following structures: LGN, suprachiasmatic nucleus, pretectum and superior colliculus. What sorts of deficits would be expec ...
... What is strabismus and which structures can be responsible? Which areas of the brain receive synapses from axons of retinal ganglion cells? What is the function of each of the following structures: LGN, suprachiasmatic nucleus, pretectum and superior colliculus. What sorts of deficits would be expec ...
Early Care and Education: Our Social Experiment
... pliancy of living silly putty. Diamond goes on to say that “more than any other organ, the brain can be shaped by stimulation and use, by disease, and trauma, by dull routine and disuse into a center of thought, sensation, and regulation most appropriate for a given individual's life” (p. 58). Healt ...
... pliancy of living silly putty. Diamond goes on to say that “more than any other organ, the brain can be shaped by stimulation and use, by disease, and trauma, by dull routine and disuse into a center of thought, sensation, and regulation most appropriate for a given individual's life” (p. 58). Healt ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functions sensory, integrative and ...
... of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functions sensory, integrative and ...
Annotated Bibliography Ferdinando A. Mussa
... signals obtained represent only a field of potential rather than specific cellular activity. Noninvasive methods, however, limit the rate at which information, and thus the patient’s intent, is extractable from the EEG signals. This delay may be sufficient for tasks such as moving a cursor; however, ...
... signals obtained represent only a field of potential rather than specific cellular activity. Noninvasive methods, however, limit the rate at which information, and thus the patient’s intent, is extractable from the EEG signals. This delay may be sufficient for tasks such as moving a cursor; however, ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... • MNS: observing action elicits similar motor activations as if it had been performed by oneself; visuo-motor neurons. • This helps to understand actions of others, modeling behavior via embodied simulation of their actions, intentions, and emotions. • MNS theory of autism (Williams et al, 2001): di ...
... • MNS: observing action elicits similar motor activations as if it had been performed by oneself; visuo-motor neurons. • This helps to understand actions of others, modeling behavior via embodied simulation of their actions, intentions, and emotions. • MNS theory of autism (Williams et al, 2001): di ...
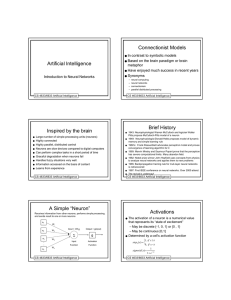
Artificial Intelligence Connectionist Models Inspired by the brain
... 1987: First IEEE conference on neural networks. Over 2000 attend. The revival is underway! ...
... 1987: First IEEE conference on neural networks. Over 2000 attend. The revival is underway! ...
Introduction of the Nervous System
... We must not confuse these with "reactions", which are different from reflexes in that they are voluntary responses to a stimulus from the environment. ...
... We must not confuse these with "reactions", which are different from reflexes in that they are voluntary responses to a stimulus from the environment. ...
Central nervous system practical block
... demyelinated area. The lesion is centered around a small vein (arrow) which is surrounded by inflammatory cells . ...
... demyelinated area. The lesion is centered around a small vein (arrow) which is surrounded by inflammatory cells . ...
Nervous System I
... of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functions sensory, integrative and ...
... of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functions sensory, integrative and ...
doc nervous system notes
... a horse tail-like of nerves called cauda equina. Two enlargements: cervical enlargement (nerves to arms) and lumbar enlargement (nerves to legs). Encased within a vertebral column composed of vertebrae called by regions (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral), 31 spinal segments where a pair of spinal ...
... a horse tail-like of nerves called cauda equina. Two enlargements: cervical enlargement (nerves to arms) and lumbar enlargement (nerves to legs). Encased within a vertebral column composed of vertebrae called by regions (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral), 31 spinal segments where a pair of spinal ...
Introduction - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Posterior gray horns contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei; anterior gray horns contain somatic motor nuclei. Lateral gray horns contain visceral motor neurons. Gray commissures contain the axons of interneurons that cross from one side of the cord to the other. ...
... Posterior gray horns contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei; anterior gray horns contain somatic motor nuclei. Lateral gray horns contain visceral motor neurons. Gray commissures contain the axons of interneurons that cross from one side of the cord to the other. ...
Modification of brain circuits as a result of experience
... Long-term depression ( LTD) is the opposite of long-term potentiation (LTP). Cells become less sensitive to input. •Occurs when communication across the synapse is silenced or weakened. (stimulation at a low rate over long period) •LTD is important in the cerebellum, in procedural memory, where the ...
... Long-term depression ( LTD) is the opposite of long-term potentiation (LTP). Cells become less sensitive to input. •Occurs when communication across the synapse is silenced or weakened. (stimulation at a low rate over long period) •LTD is important in the cerebellum, in procedural memory, where the ...
Lecture 14 - School of Computing
... NO secreted by a neuron affects all neurons within range – regardless of circuitry. Such influences go beyond excitation or inhibition. NO has the potential to modulate many aspects of the neuron’s behaviour. ...
... NO secreted by a neuron affects all neurons within range – regardless of circuitry. Such influences go beyond excitation or inhibition. NO has the potential to modulate many aspects of the neuron’s behaviour. ...
The nervous system can be divided into several connected systems
... The thalamus receives sensory information and relays this information to the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex also sends information to the thalamus which then transmits this information to other areas of the brain and spinal cord. ...
... The thalamus receives sensory information and relays this information to the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex also sends information to the thalamus which then transmits this information to other areas of the brain and spinal cord. ...
Brain - People
... PSTHs of all area studied show different periods of increased or decreased activity spanning across the whole length of trial ...
... PSTHs of all area studied show different periods of increased or decreased activity spanning across the whole length of trial ...
Power Point
... excitatory and inhibitory transmitters. Inhibitory transmitters decrease the permeability of the affected membrane for ...
... excitatory and inhibitory transmitters. Inhibitory transmitters decrease the permeability of the affected membrane for ...
Nervous System - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... The nervous system receives and then sends out information about your body. It also monitors and responds to changes in your environment. ◊ Name a few important body functions that your nervous system controls on its own without you having to think about it much? ...
... The nervous system receives and then sends out information about your body. It also monitors and responds to changes in your environment. ◊ Name a few important body functions that your nervous system controls on its own without you having to think about it much? ...
module 6 - sandrablake
... a neuron always fires with the same intensity no matter what the stimulation is. It doesn’t matter if there is a strong stimulation or weak stimulation at the cell’s dendrites. As long as there is enough energy to trigger the neuron, it will fire with the same intensity. Read the comparison of a neu ...
... a neuron always fires with the same intensity no matter what the stimulation is. It doesn’t matter if there is a strong stimulation or weak stimulation at the cell’s dendrites. As long as there is enough energy to trigger the neuron, it will fire with the same intensity. Read the comparison of a neu ...
Neuroplasticity - Bakersfield College
... route, interact with guidance molecules Fasciculation – the tendency of developing axons to grow along the paths established by preceding axons ...
... route, interact with guidance molecules Fasciculation – the tendency of developing axons to grow along the paths established by preceding axons ...