The Skin Senses
... • Which sense “dominates?”: It depends • When would you trust touch over vision? ...
... • Which sense “dominates?”: It depends • When would you trust touch over vision? ...
A five minute back examination with neurological assessment
... knee towards ninety degrees (Figure 3). Burning discomfort in the groin or anterior thigh will occur if there is femoral nerve involvement. ▪▪ Palpate the spine for tenderness and for muscle spasm Figure 3: Femoral nerve stretch test ...
... knee towards ninety degrees (Figure 3). Burning discomfort in the groin or anterior thigh will occur if there is femoral nerve involvement. ▪▪ Palpate the spine for tenderness and for muscle spasm Figure 3: Femoral nerve stretch test ...
File
... Are specialised to carry information as electrical impulses from 1 place to another Neurons not only vary in type but differ in size – in the brain they are tiny but the spine and feet can be up to 1m long There are 3 main types: ...
... Are specialised to carry information as electrical impulses from 1 place to another Neurons not only vary in type but differ in size – in the brain they are tiny but the spine and feet can be up to 1m long There are 3 main types: ...
Exploring the Human Nervous System
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
m5zn_e06294c55d2e0eb
... plexuses . The cervical and brachial plexuses are found at the root of the upper limbs, The lumbar and sacral plexuses are found at the root of the lower limbs. ...
... plexuses . The cervical and brachial plexuses are found at the root of the upper limbs, The lumbar and sacral plexuses are found at the root of the lower limbs. ...
BOX 28.5 NEURAL CONTROL OF HUMAN WALKING Human
... Furthermore, clinically complete injuries are not always anatomically complete. As a result, the evidence for existence of a CPG in humans remains indirect. Noninvasive electrophysiological techniques have provided information about how certain brain structures contribute to human walking. For examp ...
... Furthermore, clinically complete injuries are not always anatomically complete. As a result, the evidence for existence of a CPG in humans remains indirect. Noninvasive electrophysiological techniques have provided information about how certain brain structures contribute to human walking. For examp ...
Physiolgy of the nervous system
... 2) Peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes, cerebral nerves (12 pairs) and spinal nerves (31 pairs). Functional classification This classification is concerned only with PNS or peripheral nervous system, which subdivided into: 1) Somatic (voluntary) nervous system, which controls the skeleta ...
... 2) Peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes, cerebral nerves (12 pairs) and spinal nerves (31 pairs). Functional classification This classification is concerned only with PNS or peripheral nervous system, which subdivided into: 1) Somatic (voluntary) nervous system, which controls the skeleta ...
The Nervous System
... Some of the major types of disorders include: neurogenetic diseases (such as Huntington’s disease and muscular dystrophy), developmental disorders (such as cerebral palsy), degenerative diseases of adult life (such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease), metabolic diseases (such as Gaucher’ ...
... Some of the major types of disorders include: neurogenetic diseases (such as Huntington’s disease and muscular dystrophy), developmental disorders (such as cerebral palsy), degenerative diseases of adult life (such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease), metabolic diseases (such as Gaucher’ ...
The Nervous System
... which make up the white matter in the nervous system; while axons that have no myelin sheath are called unmyelinated axons which make up the gray matter in the nervous system. ...
... which make up the white matter in the nervous system; while axons that have no myelin sheath are called unmyelinated axons which make up the gray matter in the nervous system. ...
Bio 103 Nervous System
... - groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other - interneurons work together to perform a common function - each pool receives input from other neurons - each pool generates output to other neurons ...
... - groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other - interneurons work together to perform a common function - each pool receives input from other neurons - each pool generates output to other neurons ...
MS Word doc here
... receptors respond to minute punctures of the epithelium, with a response magnitude that depends on the degree of tissue deformation. They also respond to temperatures in the range of 40-60oC and change their response rates as a linear function of warming (in contrast with the saturating responses di ...
... receptors respond to minute punctures of the epithelium, with a response magnitude that depends on the degree of tissue deformation. They also respond to temperatures in the range of 40-60oC and change their response rates as a linear function of warming (in contrast with the saturating responses di ...
Peripheral Nerve Diseases
... Axonal change: Reduced amplitude or absence of response to stimulation with mild slowing of conduction velocity Localized compression of nerve: Slowing conduction in region of block e.g. Over the elbow when ulnar nerve is compressed there. ...
... Axonal change: Reduced amplitude or absence of response to stimulation with mild slowing of conduction velocity Localized compression of nerve: Slowing conduction in region of block e.g. Over the elbow when ulnar nerve is compressed there. ...
Document
... norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
... norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
Nervous system - Effingham County Schools
... • Unmyelinated fibers conduct impulses slower. • Myelinated fibers conduct impulses faster – Nodes of Ranvier (short region of exposed axon between Schwann cells on neurons) – The more myelin the faster the impulse ...
... • Unmyelinated fibers conduct impulses slower. • Myelinated fibers conduct impulses faster – Nodes of Ranvier (short region of exposed axon between Schwann cells on neurons) – The more myelin the faster the impulse ...
Ch_09_Nervous_System_A_
... norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
... norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
File
... • ___________________ (both sensory and motor) nerves • Contain both sensory nerve fibers and motor nerve fibers • Most nerves are mixed nerves • ALL spinal nerves are mixed nerves (except the first pair) Nerve Fiber Classification • ___________________________________________ (GSE) fibers • Carry m ...
... • ___________________ (both sensory and motor) nerves • Contain both sensory nerve fibers and motor nerve fibers • Most nerves are mixed nerves • ALL spinal nerves are mixed nerves (except the first pair) Nerve Fiber Classification • ___________________________________________ (GSE) fibers • Carry m ...
Lecture 6 Locomotion • Early 20th century experiments showed that
... • In spinal cats treated with L-‐DOPA, brief stimulation of high threshold (muscle and cutaneous) flexor reflex afferents (FRA) triggered sustained bursts of activity in either flexor or extensor MNs depending ...
... • In spinal cats treated with L-‐DOPA, brief stimulation of high threshold (muscle and cutaneous) flexor reflex afferents (FRA) triggered sustained bursts of activity in either flexor or extensor MNs depending ...
File
... Myasthenia Gravis • Chronic disease characterized by weakness primarily in muscles innervated by cranial nerves, as well as in skeletal and respiratory muscles • Thymoma—encapsulated thymus gland tumor • Progressive paresis of affected muscle groups that is partially resolved by resting • Most comm ...
... Myasthenia Gravis • Chronic disease characterized by weakness primarily in muscles innervated by cranial nerves, as well as in skeletal and respiratory muscles • Thymoma—encapsulated thymus gland tumor • Progressive paresis of affected muscle groups that is partially resolved by resting • Most comm ...
nervous quiz RG
... Why did the rat press the level the first time? Which rats were given an addictive stimulus or electrical impulse to stimulate the pleasure centers of the brain? How does cocaine effect nerve cells? Endocrine system ...
... Why did the rat press the level the first time? Which rats were given an addictive stimulus or electrical impulse to stimulate the pleasure centers of the brain? How does cocaine effect nerve cells? Endocrine system ...
ssep anatomy handout
... Peripheral nerves- bundles of nerve fibers in the PNS Peripheral nerves are classified into groups A, B and C. Group A has 4 sizes of nerve fibers Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta. They are all heavily myelinated and range in size from 2 - 20 microns (micrometer) and are as fast as 12 – 120 meters per ...
... Peripheral nerves- bundles of nerve fibers in the PNS Peripheral nerves are classified into groups A, B and C. Group A has 4 sizes of nerve fibers Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta. They are all heavily myelinated and range in size from 2 - 20 microns (micrometer) and are as fast as 12 – 120 meters per ...
Message Transmission
... – This is the junction between any two communicating neurons – It really is a gap (the synaptic cleft), the cells don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic neuron • Crossing the cleft is called synaptic transmission – One-w ...
... – This is the junction between any two communicating neurons – It really is a gap (the synaptic cleft), the cells don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic neuron • Crossing the cleft is called synaptic transmission – One-w ...
Your Name Here______________________________
... Biology 11 Examination #4a - Introduction to the Nervous System Multiple Choice: use your scantron and darken the space corresponding to the letter of the best answer. ...
... Biology 11 Examination #4a - Introduction to the Nervous System Multiple Choice: use your scantron and darken the space corresponding to the letter of the best answer. ...
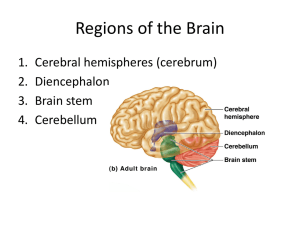
Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum
... • Commonly called a stroke • The result of a ruptured blood vessel supplying a region of the brain • Brain tissue supplied with oxygen from that blood source dies • Loss of some functions or death may result ...
... • Commonly called a stroke • The result of a ruptured blood vessel supplying a region of the brain • Brain tissue supplied with oxygen from that blood source dies • Loss of some functions or death may result ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.