peripheral nervous system
... smooth muscle of blood vessels, together with the cardiac muscle, and further divided into sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerve. ...
... smooth muscle of blood vessels, together with the cardiac muscle, and further divided into sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerve. ...
peripheral nervous system
... Can you get scared to death? It can increase the likelihood of a heart attack, but only if the person was going to have one in the next few weeks anyway. Is it true that left-handed people are smarter than right handed people? Not really. Right handed people use their left brain and lefties use thei ...
... Can you get scared to death? It can increase the likelihood of a heart attack, but only if the person was going to have one in the next few weeks anyway. Is it true that left-handed people are smarter than right handed people? Not really. Right handed people use their left brain and lefties use thei ...
5 PNS and ANS
... Can you get scared to death? It can increase the likelihood of a heart attack, but only if the person was going to have one in the next few weeks anyway. Is it true that left-handed people are smarter than right handed people? Not really. Right handed people use their left brain and lefties use thei ...
... Can you get scared to death? It can increase the likelihood of a heart attack, but only if the person was going to have one in the next few weeks anyway. Is it true that left-handed people are smarter than right handed people? Not really. Right handed people use their left brain and lefties use thei ...
4 PNS and ANS
... Can you get scared to death? It can increase the likelihood of a heart attack, but only if the person was going to have one in the next few weeks anyway. Is it true that left-handed people are smarter than right handed people? Not really. Right handed people use their left brain and lefties use thei ...
... Can you get scared to death? It can increase the likelihood of a heart attack, but only if the person was going to have one in the next few weeks anyway. Is it true that left-handed people are smarter than right handed people? Not really. Right handed people use their left brain and lefties use thei ...
Chapter 13 Student Guide
... The perception of pain protects the body from damage and is stimulated by extremes of pressure and temperature, as well as chemicals released from damaged tissues. The pain threshold is the stimulus intensity at which we begin to perceive pain and is the same for most people, although pain tolerance ...
... The perception of pain protects the body from damage and is stimulated by extremes of pressure and temperature, as well as chemicals released from damaged tissues. The pain threshold is the stimulus intensity at which we begin to perceive pain and is the same for most people, although pain tolerance ...
Peripheral Nervous System Structure of a Nerve Cranial Nerves
... may be speeded up or slowed down, blood pressure may be adjusted, and stomach secretions may be increased or decreased. Most of this fine-tuning occurs without our awareness or attention—few of us realize when our pupils dilate or our arteries constrict—hence the ANS is also called the involuntary n ...
... may be speeded up or slowed down, blood pressure may be adjusted, and stomach secretions may be increased or decreased. Most of this fine-tuning occurs without our awareness or attention—few of us realize when our pupils dilate or our arteries constrict—hence the ANS is also called the involuntary n ...
Note 11
... medulla oblongata – controls reflex action and involuntary actions e.g. breathing rate, heart beat rate In cerebrum and cerebellum, the grey matter surrounds the white matter; while in medulla oblongata, white matter surrounds the grey matter ...
... medulla oblongata – controls reflex action and involuntary actions e.g. breathing rate, heart beat rate In cerebrum and cerebellum, the grey matter surrounds the white matter; while in medulla oblongata, white matter surrounds the grey matter ...
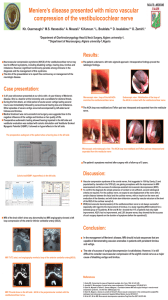
meniere s disease presented with micro vascular compression of the
... To confirm the diagnosis the simple presence of contact is not sufficient, several radiological criteria are required. For the auditory nerve, we expect to see displacement of the nerve with a certain distance between the facial and the cochlear nerves, with an imprint on the nerve and areduction ...
... To confirm the diagnosis the simple presence of contact is not sufficient, several radiological criteria are required. For the auditory nerve, we expect to see displacement of the nerve with a certain distance between the facial and the cochlear nerves, with an imprint on the nerve and areduction ...
I) Mark right or false beside each sentence and correct the wrong
... 9- The postganglionic fibre of parasympathetic nervous system releases acetylcholine that binds muscarinic receptors on the effector organs. ( ) ﺻﺢ 10- The postganglionic fibre of sympathetic nervous system releases norepinephrine that binds adrenergic receptors on the effector organs. ( )ﺻﺢ 11- ...
... 9- The postganglionic fibre of parasympathetic nervous system releases acetylcholine that binds muscarinic receptors on the effector organs. ( ) ﺻﺢ 10- The postganglionic fibre of sympathetic nervous system releases norepinephrine that binds adrenergic receptors on the effector organs. ( )ﺻﺢ 11- ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... 1) ↓ brain size & weight (especially cerebral cortex) 2) ↓ # neurons (do not regenerate) 3) ↓ blood flow to brain as fatty deposits accumulate in blood vessels 4) Changes in synaptic organization (# dendrite branches, synapses lost, neurotransmitter production ↓) 5) Cellular changes (accumulation of ...
... 1) ↓ brain size & weight (especially cerebral cortex) 2) ↓ # neurons (do not regenerate) 3) ↓ blood flow to brain as fatty deposits accumulate in blood vessels 4) Changes in synaptic organization (# dendrite branches, synapses lost, neurotransmitter production ↓) 5) Cellular changes (accumulation of ...
Neurons
... Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS)- brain and spinal chord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)- all nerves extending from and going to the CNS Composed of over 100 billion neurons ...
... Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS)- brain and spinal chord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)- all nerves extending from and going to the CNS Composed of over 100 billion neurons ...
NEUROMUSCULAR MONITORING
... • Threshold current : It is the lowest current required to depolarize the most sensitive fibres in a given nerve bundle to elicit a detectable muscle response. • Supramaximal current : It is approximately10-20% higher intensity than the current required to depolarize all fibres in a particular nerv ...
... • Threshold current : It is the lowest current required to depolarize the most sensitive fibres in a given nerve bundle to elicit a detectable muscle response. • Supramaximal current : It is approximately10-20% higher intensity than the current required to depolarize all fibres in a particular nerv ...
Document
... • There are four nerve cell groups of the posterior gray column: two that extend throughout the length of the cord and two that are restricted to the thoracic and lumbar segments. • The substantia gelatinosa group is situated at the apex of the posterior gray column throughout the length of the spin ...
... • There are four nerve cell groups of the posterior gray column: two that extend throughout the length of the cord and two that are restricted to the thoracic and lumbar segments. • The substantia gelatinosa group is situated at the apex of the posterior gray column throughout the length of the spin ...
AP – All or nothing
... an unmyelinated axon? • How does an action potential pass along a myelinated axon? • What factors affect the speed of conductance of an action potential? • What is the refractory period? • What is meant by the “all or nothing” ...
... an unmyelinated axon? • How does an action potential pass along a myelinated axon? • What factors affect the speed of conductance of an action potential? • What is the refractory period? • What is meant by the “all or nothing” ...
Lorem Ipsum - University of Western Australia
... Nerves grow out in to the mesoderm Nerve fibres follow surface clues (glyco proteins), entering the front of each myotome As limb buds grow the fibres extend and innervate overlapping but regular areas of the limb. ...
... Nerves grow out in to the mesoderm Nerve fibres follow surface clues (glyco proteins), entering the front of each myotome As limb buds grow the fibres extend and innervate overlapping but regular areas of the limb. ...
The Nervous System (ppt).
... are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges is to prot ...
... are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges is to prot ...
BIOL 241 Autonomic Nervous System 1 I. Visceral Reflexes A. All
... B. Autonomic neurons 1. not somatic 2. requires two neurons a. preganglionic b. postganglionic C. Somatic vs. visceral effectors 1. skeletal muscle (somatic) 2. visceral effectors a. heartb. smooth musclec. ANS activity d. denervation hypersensitivity D. Receptors II. ANS Divisions A. Sympathetic di ...
... B. Autonomic neurons 1. not somatic 2. requires two neurons a. preganglionic b. postganglionic C. Somatic vs. visceral effectors 1. skeletal muscle (somatic) 2. visceral effectors a. heartb. smooth musclec. ANS activity d. denervation hypersensitivity D. Receptors II. ANS Divisions A. Sympathetic di ...
A. Sensation
... a. located in blood vessels, visceral organs, and nervous system b. provide information about internal envrionment c. impulses produced usually are not consciously perceived but may be felt as pain or pressure ...
... a. located in blood vessels, visceral organs, and nervous system b. provide information about internal envrionment c. impulses produced usually are not consciously perceived but may be felt as pain or pressure ...
REGULATION
... the outside and the polarity is returned back to that of the resting neuron. IV. Transmission at the synapse A. During impulse (electrical energy), a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine and norepinephrine, is released into the synaptic cleft (space between 2 neurons). B. The electrical impulse is now co ...
... the outside and the polarity is returned back to that of the resting neuron. IV. Transmission at the synapse A. During impulse (electrical energy), a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine and norepinephrine, is released into the synaptic cleft (space between 2 neurons). B. The electrical impulse is now co ...
Guided Notes
... chemicals which transmit the impulse electrically from one nerve to the next or to the end target ii. Separated from next neuron (or organ or muscle) by the __________________________________. The entire junction between 2 nerves or a nerve and another structure is known as the _________________ 3. ...
... chemicals which transmit the impulse electrically from one nerve to the next or to the end target ii. Separated from next neuron (or organ or muscle) by the __________________________________. The entire junction between 2 nerves or a nerve and another structure is known as the _________________ 3. ...
Anatomic and Biomechanical principles related to splinting
... work together. Optimal client outcomes rely on biomechanics Weak muscles are supported, and the pull of stronger muscles is counteracted. Reduces risk of skin irritation due to pressure Ultimately may lead to patient comfort, compliance, and function ...
... work together. Optimal client outcomes rely on biomechanics Weak muscles are supported, and the pull of stronger muscles is counteracted. Reduces risk of skin irritation due to pressure Ultimately may lead to patient comfort, compliance, and function ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
Chapter 11
... • includes structures in the frontal and temporal cortex, basal nuclei, thalamus, hypothalamus, and deep nuclei • controls emotional experience and expression • produces feelings • recognizes life threatening upsets in a person's physical or psychological condition and counters them ...
... • includes structures in the frontal and temporal cortex, basal nuclei, thalamus, hypothalamus, and deep nuclei • controls emotional experience and expression • produces feelings • recognizes life threatening upsets in a person's physical or psychological condition and counters them ...
how seacure helps clearing - SeaCure Custom Mouthpiece
... Eustachian tube (see arrow) one end of which is connected to the middle ear and the other end to the back of the throat. This end is usually closed but can be opened by jaw movement and the action of “clearing”. As the diver moves deeper the increasing pressure must be equalized to avoid pain or eve ...
... Eustachian tube (see arrow) one end of which is connected to the middle ear and the other end to the back of the throat. This end is usually closed but can be opened by jaw movement and the action of “clearing”. As the diver moves deeper the increasing pressure must be equalized to avoid pain or eve ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.