Deep Tendon Reflex
... The sensory (afferents) fibers of the spinal nerves carry the sensory impulses from the muscle spindles to the spinal cord. In the spinal cord, the sensory fibers stimulate the motor neurons that send their motor fibers (efferents) to the muscle causing its contraction. ...
... The sensory (afferents) fibers of the spinal nerves carry the sensory impulses from the muscle spindles to the spinal cord. In the spinal cord, the sensory fibers stimulate the motor neurons that send their motor fibers (efferents) to the muscle causing its contraction. ...
Briefed by: Dr. Hayder The human nervous system, by far the most
... hillock & the axon is devoid of the major organelles especially Nissl bodies. The plasma membrane of axon is called axolemma & its cytoplasm called axoplasm. Nerve cells are specialized to receive stimuli from other cells of the system via their processes. Neurons can be grouped into three general t ...
... hillock & the axon is devoid of the major organelles especially Nissl bodies. The plasma membrane of axon is called axolemma & its cytoplasm called axoplasm. Nerve cells are specialized to receive stimuli from other cells of the system via their processes. Neurons can be grouped into three general t ...
6. Peripheral Nervous System
... Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Two motor neurons to many effector tissues: Effector Tissue 1. Cardiac muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Glands ...
... Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Two motor neurons to many effector tissues: Effector Tissue 1. Cardiac muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Glands ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 11-09
... Central Pain Modulation 1. Opiates inhibit the activity of inhibitory interneurons in the PAG. This increases the activity of neurons whose axons descend to the raphe nucleus 2. The activity of axons that descend from the PAG excites raphe nucleus neurons whose axons descend in the dorsal columns of ...
... Central Pain Modulation 1. Opiates inhibit the activity of inhibitory interneurons in the PAG. This increases the activity of neurons whose axons descend to the raphe nucleus 2. The activity of axons that descend from the PAG excites raphe nucleus neurons whose axons descend in the dorsal columns of ...
Nervous System III – Reflexes and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... Transmit information from the ...
... Transmit information from the ...
Effects of activity-dependent strategies on regeneration and
... promote axonal elongation after autograft repair (Sabatier et al., 2008). Besides, low but not high intensity treadmill training potentiates Schwann cell proliferation in the regenerating sciatic nerve in rats (Seo et al., 2009). It can be hypothesized that, when initiated in the denervation phase, ...
... promote axonal elongation after autograft repair (Sabatier et al., 2008). Besides, low but not high intensity treadmill training potentiates Schwann cell proliferation in the regenerating sciatic nerve in rats (Seo et al., 2009). It can be hypothesized that, when initiated in the denervation phase, ...
Memmler`s The Human Body in Health and
... Major nerves originating at the right brachial plexus, anterior view ...
... Major nerves originating at the right brachial plexus, anterior view ...
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
... 2. The trial period will be paid as a rental which may count toward the eventual purchase cost. C. Suppliers are responsible for monitoring utilization of TENS units and supplies. Suppliers must discontinue billing when rental items or ongoing supply items are no longer used by the patient. D. TENS ...
... 2. The trial period will be paid as a rental which may count toward the eventual purchase cost. C. Suppliers are responsible for monitoring utilization of TENS units and supplies. Suppliers must discontinue billing when rental items or ongoing supply items are no longer used by the patient. D. TENS ...
Slide 1
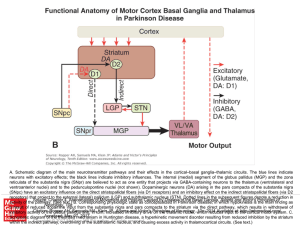
... A. Schematic diagram of the main neurotransmitter pathways and their effects in the cortical–basal ganglia–thalamic circuits. The blue lines indicate neurons with excitatory effects; the black lines indicate inhibitory influences. The internal (medial) segment of the globus pallidus (MGP) and the zo ...
... A. Schematic diagram of the main neurotransmitter pathways and their effects in the cortical–basal ganglia–thalamic circuits. The blue lines indicate neurons with excitatory effects; the black lines indicate inhibitory influences. The internal (medial) segment of the globus pallidus (MGP) and the zo ...
The Nerve Impulse
... • Neurons vary in size, shape, and function. • The shape of a neuron determines it connection with other neurons and its connections with other neurons. • The function is closely related to the shape of a neuron. – Example: Pukinje cells of the cerebellum branch extremely widely within a single ...
... • Neurons vary in size, shape, and function. • The shape of a neuron determines it connection with other neurons and its connections with other neurons. • The function is closely related to the shape of a neuron. – Example: Pukinje cells of the cerebellum branch extremely widely within a single ...
The Nerve Impulse
... • Neurons vary in size, shape, and function. • The shape of a neuron determines it connection with other neurons and its connections with other neurons. • The function is closely related to the shape of a neuron. – Example: Pukinje cells of the cerebellum branch extremely widely within a single ...
... • Neurons vary in size, shape, and function. • The shape of a neuron determines it connection with other neurons and its connections with other neurons. • The function is closely related to the shape of a neuron. – Example: Pukinje cells of the cerebellum branch extremely widely within a single ...
Hsiang-Tung Chang
... of the receptive fields of evoked potentials in the cerebral cortex. After the vote of all the members of the jury, my thesis passed, Burr shook my hand and then, turning to Fulton, he said, 1 would like so much to have a researcher like this one in my laboratory' I consider that the greatest compli ...
... of the receptive fields of evoked potentials in the cerebral cortex. After the vote of all the members of the jury, my thesis passed, Burr shook my hand and then, turning to Fulton, he said, 1 would like so much to have a researcher like this one in my laboratory' I consider that the greatest compli ...
General knowledge about nervous system
... Evolution of Gene Related to Brain's Growth • A gene that helps determine the size of the human brain has been under intense Darwinian pressure in the last few million years. • It has changed its structure 15 times since humans and chimps separated from their common ancestor. • Evolution has been p ...
... Evolution of Gene Related to Brain's Growth • A gene that helps determine the size of the human brain has been under intense Darwinian pressure in the last few million years. • It has changed its structure 15 times since humans and chimps separated from their common ancestor. • Evolution has been p ...
Part 1: Multiple choice
... B. synapse on muscles in the eye, neck, and head C. synapse on local circuit neurons and/or lower motor neurons <––– D. affect motor patterns only indirectly via their inputs to the basal ganglia. E. None of the above 2. A motor pool (as opposed to a motor unit) consists of A. all of the motor neuro ...
... B. synapse on muscles in the eye, neck, and head C. synapse on local circuit neurons and/or lower motor neurons <––– D. affect motor patterns only indirectly via their inputs to the basal ganglia. E. None of the above 2. A motor pool (as opposed to a motor unit) consists of A. all of the motor neuro ...
Chapter 13 - FacultyWeb Support Center
... • Nociceptors—sensitive to pain-causing stimuli (e.g. extreme heat or cold, excessive pressure, inflammatory chemicals) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Nociceptors—sensitive to pain-causing stimuli (e.g. extreme heat or cold, excessive pressure, inflammatory chemicals) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Nervous System
... certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus controls body te ...
... certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus controls body te ...
Immunohistochemical Study of Spinal Motor Neurons Following
... Axotomy causes disturbance in intra-axonal and retrograde transportation of nerve growth factors from target organ to somata of motor neurons. Absence of neurotrophic factor induces some degenerative changes and perhaps neuronal death of motor neurons (33). Ma and et al. in 2003 reported that 16 wee ...
... Axotomy causes disturbance in intra-axonal and retrograde transportation of nerve growth factors from target organ to somata of motor neurons. Absence of neurotrophic factor induces some degenerative changes and perhaps neuronal death of motor neurons (33). Ma and et al. in 2003 reported that 16 wee ...
introduction to peripheral nervous system 26. 02. 2014
... The PNS encompasses the nervous system external to the brain and spinal cord. In the PNS, axons (fibers) are collected into bundles supported by connective tissue to form a nerve. The nervous system contains both the somatic system and the autonomic system, each with portions within the CNS and PNS. ...
... The PNS encompasses the nervous system external to the brain and spinal cord. In the PNS, axons (fibers) are collected into bundles supported by connective tissue to form a nerve. The nervous system contains both the somatic system and the autonomic system, each with portions within the CNS and PNS. ...
Cortical Stimulation Mapping www.AssignmentPoint.com Cortical
... effectively and not die off too quickly, yet low enough to protect brain tissue from damaging currents. Currents are kept at levels that have been determined safe and are only given as short bursts, typically bursts that slowly increase in intensity and duration until a response (such as a muscle mo ...
... effectively and not die off too quickly, yet low enough to protect brain tissue from damaging currents. Currents are kept at levels that have been determined safe and are only given as short bursts, typically bursts that slowly increase in intensity and duration until a response (such as a muscle mo ...
2.1 Resonding for change
... Key Words: stimuli, receptors, impulses, sense organs, CNS, neurons, nerves, secretory organs ...
... Key Words: stimuli, receptors, impulses, sense organs, CNS, neurons, nerves, secretory organs ...
The Muscular System - Catherine Huff`s Site
... the myosin filaments) ratchet back and forth and pull the actin filaments on both sides toward center of the myosin filaments. • Sliding of filaments shortens sarcomere, thereby causing contraction. ...
... the myosin filaments) ratchet back and forth and pull the actin filaments on both sides toward center of the myosin filaments. • Sliding of filaments shortens sarcomere, thereby causing contraction. ...
The Muscular System
... the myosin filaments) ratchet back and forth and pull the actin filaments on both sides toward center of the myosin filaments. • Sliding of filaments shortens sarcomere, thereby causing contraction. ...
... the myosin filaments) ratchet back and forth and pull the actin filaments on both sides toward center of the myosin filaments. • Sliding of filaments shortens sarcomere, thereby causing contraction. ...
• In vertebrates
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Anatomy Written Exam #2 Cranial Nerves Introduction Embryological
... i. Afferents from thalamus and cerebral cortex ii. GABA efferents back to thalamus c. Functional Organization of Thalamic Nuclei All thalamic nuclei, except or the reticular nucleus, project to IPSILATERAL cerebral cortex 1. Specific Nuclei- have point to point projections between individual thala ...
... i. Afferents from thalamus and cerebral cortex ii. GABA efferents back to thalamus c. Functional Organization of Thalamic Nuclei All thalamic nuclei, except or the reticular nucleus, project to IPSILATERAL cerebral cortex 1. Specific Nuclei- have point to point projections between individual thala ...
Chp 9: Nervous tissue chp 11: autonomic nervous system chp 12
... Sensory functions _ (AFFECTORS) Sensory receptors_ detect stimuli inside and outside the body. - Sensory or afferent neurons carry information from cranial to spinal nerves into brain and spinal cord or visa versa ...
... Sensory functions _ (AFFECTORS) Sensory receptors_ detect stimuli inside and outside the body. - Sensory or afferent neurons carry information from cranial to spinal nerves into brain and spinal cord or visa versa ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.