Unimodal or Bimodal Distribution of Synaptic Weights?
... Most Hebbian learning rules or BCM rules used to describe receptive field development exhibit a spontaneous separation of synaptic weights into two groups, i.e., strong and weak synapses, so that the distribution of synaptic weights is bimodal. This implies that even rather ‘weak’, non-significant c ...
... Most Hebbian learning rules or BCM rules used to describe receptive field development exhibit a spontaneous separation of synaptic weights into two groups, i.e., strong and weak synapses, so that the distribution of synaptic weights is bimodal. This implies that even rather ‘weak’, non-significant c ...
The Brain for Not-So
... Ok , so we built a brain…what’s it do now?! The brain is “tuned” to its experience For certain functions/areas there is a “critical period” for “tuning” ...
... Ok , so we built a brain…what’s it do now?! The brain is “tuned” to its experience For certain functions/areas there is a “critical period” for “tuning” ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... receptor on the postsynaptic side of the synapse, it results in a change of the postsynaptic cell's excitability: it makes the postsynaptic cell either more or less likely to fire an action potential. If the number of excitatory postsynaptic events are large enough, they will add to cause an action ...
... receptor on the postsynaptic side of the synapse, it results in a change of the postsynaptic cell's excitability: it makes the postsynaptic cell either more or less likely to fire an action potential. If the number of excitatory postsynaptic events are large enough, they will add to cause an action ...
Neurobiology of Addiction
... WITHDRAWAL AND CRAVINGS If drug is not available to the neuron, unpleasant emotional and physical effects occur, because the normal activating and inhibitory neurotransmitter levels have been altered See example, next slide ...
... WITHDRAWAL AND CRAVINGS If drug is not available to the neuron, unpleasant emotional and physical effects occur, because the normal activating and inhibitory neurotransmitter levels have been altered See example, next slide ...
The Anatomy of a Memory: Insights Into How Information is Stored in
... changes occurred within the cerebellum, whereas when they were trained to challenge a complex obstacle course (acrobat rats) a 30% increase in synapse number was observed (Black et al., 1990). A major contribution to our current understanding of the mechanisms that underlie memory storage has come f ...
... changes occurred within the cerebellum, whereas when they were trained to challenge a complex obstacle course (acrobat rats) a 30% increase in synapse number was observed (Black et al., 1990). A major contribution to our current understanding of the mechanisms that underlie memory storage has come f ...
Overview Synaptic plasticity Synaptic strength
... • Probability of neurotransmitter release p Postsynaptically: • Maximal conductance g associated with one synaptic vesicle ...
... • Probability of neurotransmitter release p Postsynaptically: • Maximal conductance g associated with one synaptic vesicle ...
Long-term depression
... Nervous System is malleable learning occurs Structural changes increased dendritic branching new synapses Changes in synaptic efficiency Long-term potentiation Long-term depression ~ ...
... Nervous System is malleable learning occurs Structural changes increased dendritic branching new synapses Changes in synaptic efficiency Long-term potentiation Long-term depression ~ ...
neuroplasticity 2016
... are felt to occur in a different part of the body – A touch to the chin may be felt as if it were applied to a missing fifth finger ...
... are felt to occur in a different part of the body – A touch to the chin may be felt as if it were applied to a missing fifth finger ...
Giuseppe Minniti, MSc, City University of New York – College of
... state of alcohol dependence is reached. Studies performed in animal models demonstrated that brief exposure to alcohol modifies the expression of various genes. This modulation of gene expression seems to be the underlying molecular mechanism responsible for the alteration of the brain circuits that ...
... state of alcohol dependence is reached. Studies performed in animal models demonstrated that brief exposure to alcohol modifies the expression of various genes. This modulation of gene expression seems to be the underlying molecular mechanism responsible for the alteration of the brain circuits that ...
THE DOGMA OF AN AGING BRAIN
... IMPORTANT WARNING Please note that this PowerPoint Presentation contains animations. In order to view the content properly, an add-in function must be installed into the PowerPoint software. The add-in function is downloadable from the following hyperlink. Swiff Point Player ...
... IMPORTANT WARNING Please note that this PowerPoint Presentation contains animations. In order to view the content properly, an add-in function must be installed into the PowerPoint software. The add-in function is downloadable from the following hyperlink. Swiff Point Player ...
UsabilityPs3
... typically pause to eat, groom or rub their whiskers. Electrodes in rat’s hippocampus monitored so-called place neurons, which fire in specific sequence as a rat navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurr ...
... typically pause to eat, groom or rub their whiskers. Electrodes in rat’s hippocampus monitored so-called place neurons, which fire in specific sequence as a rat navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurr ...
UsabilityPs3
... typically pause to eat, groom or rub their whiskers. Electrodes in rat’s hippocampus monitored so-called place neurons, which fire in specific sequence as a rat navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurr ...
... typically pause to eat, groom or rub their whiskers. Electrodes in rat’s hippocampus monitored so-called place neurons, which fire in specific sequence as a rat navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurr ...
1 - UCL
... memory retrieval a substantial fraction of neurons produce spikes which are phaselocked with the theta range (3 – 8 Hz) of the Local Field Potential (LFP), can an increase of phase-locked spikes during learning predict an increase in memory retrieval strength? The investigation is important because ...
... memory retrieval a substantial fraction of neurons produce spikes which are phaselocked with the theta range (3 – 8 Hz) of the Local Field Potential (LFP), can an increase of phase-locked spikes during learning predict an increase in memory retrieval strength? The investigation is important because ...
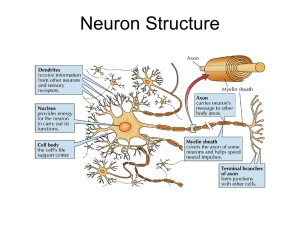
Neuron Function 2
... 1. An arriving action potential depolarizes the synaptic knob 2. Ca+2 ions enter the cytoplasm of the synaptic knob. 3. ACh release occurs through diffusion and exocytosis of neurotransmitter vesicles 4. ACh diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. ...
... 1. An arriving action potential depolarizes the synaptic knob 2. Ca+2 ions enter the cytoplasm of the synaptic knob. 3. ACh release occurs through diffusion and exocytosis of neurotransmitter vesicles 4. ACh diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. ...
Eagleman Ch 4. Neuroplasticity
... sustain the neurons. Generally, they are secreted by the target to promote survival in the neurons that reach the target. They allow the cell to differentiate. In young cells, they prevent apoptosis in cells that make appropriate connections. ...
... sustain the neurons. Generally, they are secreted by the target to promote survival in the neurons that reach the target. They allow the cell to differentiate. In young cells, they prevent apoptosis in cells that make appropriate connections. ...
Abstract
... voltage-sensitive dyes are available to monitor millisecond time scale neural activities without use of invasive electrodes. Many useful fluorescent indicator proteins that reflect changes of membrane potential, ionic concentrations, protein conformational changes, protein-protein interactions, pro ...
... voltage-sensitive dyes are available to monitor millisecond time scale neural activities without use of invasive electrodes. Many useful fluorescent indicator proteins that reflect changes of membrane potential, ionic concentrations, protein conformational changes, protein-protein interactions, pro ...
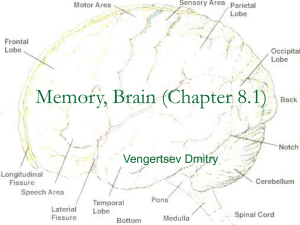
• Ch 49 • Nervous Systems • Neuronal Circuits • Each single
... The cerebrospinal fluid is filtered from blood and functions to cushion the brain and spinal cord as well as to provide nutrients and remove wastes ...
... The cerebrospinal fluid is filtered from blood and functions to cushion the brain and spinal cord as well as to provide nutrients and remove wastes ...
Final Exam - UF Psychology
... e . occurs only with tobacco and narcotics, whereas psychological dependence can develop to any drug. ...
... e . occurs only with tobacco and narcotics, whereas psychological dependence can develop to any drug. ...
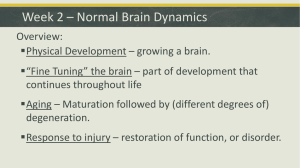
PPT Guide Brain Development
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...