Nervous System
... The Vertebrate Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) = includes brain and spinal cord ...
... The Vertebrate Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) = includes brain and spinal cord ...
GROUP “A” L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 1 1 -
... and interior structures of cortical and sub-cortical regions; anatomical connectivity among the various regions; blood supply to brain and the CSF system; cytoarchitecture and modular organization in the brain. ...
... and interior structures of cortical and sub-cortical regions; anatomical connectivity among the various regions; blood supply to brain and the CSF system; cytoarchitecture and modular organization in the brain. ...
Nervous Systems - manorlakesscience
... Plays a key role in memory, maintaining sensation, motor (movement) activities. ...
... Plays a key role in memory, maintaining sensation, motor (movement) activities. ...
Cognitive neuroscience
... performing a function in virtue of its components parts, component operations, and their organization. • The orchestrated functioning of the mechanism is responsible for one or more phenomena.” (Bechtel & Abrahamsen, 2005; Bechtel, 2006, 2009, 2008) ...
... performing a function in virtue of its components parts, component operations, and their organization. • The orchestrated functioning of the mechanism is responsible for one or more phenomena.” (Bechtel & Abrahamsen, 2005; Bechtel, 2006, 2009, 2008) ...
Neuroscience and Behavior - Bremerton School District
... A functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
... A functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
A1984TV50600001
... separate determination of norepinephrlne and dopamine without reliance on cumbersome procedures, such as thin-layer chromatography. “The study demonstrated that both norepinephrine and dopamine were detectable in the fetal rat brain as early as 15 days of gestation, when the brain weighed less than ...
... separate determination of norepinephrlne and dopamine without reliance on cumbersome procedures, such as thin-layer chromatography. “The study demonstrated that both norepinephrine and dopamine were detectable in the fetal rat brain as early as 15 days of gestation, when the brain weighed less than ...
How To Make a Neuron Model
... 5. Wrap another pipe cleaner on the end of the axon. This will be the synaptic terminal. ...
... 5. Wrap another pipe cleaner on the end of the axon. This will be the synaptic terminal. ...
NEUROTRANSMITTERS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... shown that these neurons ramify extensively, so that majority of cortical neurons are, in fact, exposed to nNOS nerve terminals [13]. Physiological concentrations of H2S, on the other hand, are supposed to enhance glutamatergic transmission mediated through NMDA receptors [14]. Endocannabinoids (ana ...
... shown that these neurons ramify extensively, so that majority of cortical neurons are, in fact, exposed to nNOS nerve terminals [13]. Physiological concentrations of H2S, on the other hand, are supposed to enhance glutamatergic transmission mediated through NMDA receptors [14]. Endocannabinoids (ana ...
Chapter 14
... correct voluntary muscle contraction and posture based on sensory data from body about actual movements sense of equilibrium ...
... correct voluntary muscle contraction and posture based on sensory data from body about actual movements sense of equilibrium ...
9.5 & 9.11 PP - Mrs. heninger
... Real-world connection How drugs interact with the nervous system. Vocabulary nerve pathways, synapse, synaptic cleft, synaptic transmission, neurotransmitters, resting potential, action potential, reflex arc, receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, effector. ...
... Real-world connection How drugs interact with the nervous system. Vocabulary nerve pathways, synapse, synaptic cleft, synaptic transmission, neurotransmitters, resting potential, action potential, reflex arc, receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, effector. ...
Cognitive Development - Oakland Schools Moodle
... At birth, the brain has billions of nerve cells called neurons (born with all that you will have –are developed throughout life) Dramatic changes to neurons can happen Babies’ brains begin to develop links between the neurons called neural pathways These pathways are how the brain is “wired” to cont ...
... At birth, the brain has billions of nerve cells called neurons (born with all that you will have –are developed throughout life) Dramatic changes to neurons can happen Babies’ brains begin to develop links between the neurons called neural pathways These pathways are how the brain is “wired” to cont ...
ch4_1 - Homework Market
... many synapses. • Final cellular activity is a summation of these many excitatory and inhibitory synaptic signals. ...
... many synapses. • Final cellular activity is a summation of these many excitatory and inhibitory synaptic signals. ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... the olfactory mucosa. 3. Multipolar – have many (at least 2) dendrites and one axon. Most common neuron in the body. ...
... the olfactory mucosa. 3. Multipolar – have many (at least 2) dendrites and one axon. Most common neuron in the body. ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... neurotransmitters are either Agonists or Antagonists. There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit ...
... neurotransmitters are either Agonists or Antagonists. There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit ...
- Backpack
... Each recognizer computes the probability that its pattern has been recognized. Takes into consideration the observed magnitude of each input. ...
... Each recognizer computes the probability that its pattern has been recognized. Takes into consideration the observed magnitude of each input. ...
SNS—brain and spinal cord
... Brain—control center of the nervous system surrounded by the skull which provides protection and support. Two hemispheres and four major regions. Left and right hemisphere. ...
... Brain—control center of the nervous system surrounded by the skull which provides protection and support. Two hemispheres and four major regions. Left and right hemisphere. ...
case studies In-depth examinations of an individual or a single event
... basal ganglia A collection of subcortical structures that are involved in memory. These structures include the caudate nucleus, the putamen, the globus pallidus, and the subthalamic nucleus and are located above and around the thalamus. Important for memories involving habits and motor skills ...
... basal ganglia A collection of subcortical structures that are involved in memory. These structures include the caudate nucleus, the putamen, the globus pallidus, and the subthalamic nucleus and are located above and around the thalamus. Important for memories involving habits and motor skills ...
Chapter 1 - Faculty Server Contact
... between the nervous system and behavior by experimentally altering specific nervous system structures and then observing the effects on behavior. Psychophysiology - study of the relationship between physiology and behavior by analysis of the physiological responses of human subjects engaged in vario ...
... between the nervous system and behavior by experimentally altering specific nervous system structures and then observing the effects on behavior. Psychophysiology - study of the relationship between physiology and behavior by analysis of the physiological responses of human subjects engaged in vario ...
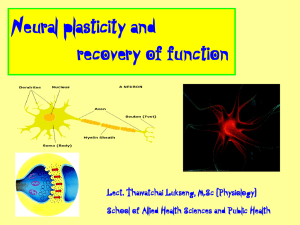
Neural plasticity and recovery of function
... Brain recovery mechanisms (cont.) – Redundancy theory • Various area same function • Believe that violent status depending on normal neurons (not injured) > lesion area ...
... Brain recovery mechanisms (cont.) – Redundancy theory • Various area same function • Believe that violent status depending on normal neurons (not injured) > lesion area ...
Document
... not necessary for the comprehension and production of that language In contrast, "experience-dependent" plasticity occurs in adulthood in response to new or novel situations – Plasticity in this case is manifested by smaller bursts of new synaptic growth within a localized region of the brain that i ...
... not necessary for the comprehension and production of that language In contrast, "experience-dependent" plasticity occurs in adulthood in response to new or novel situations – Plasticity in this case is manifested by smaller bursts of new synaptic growth within a localized region of the brain that i ...
KS4_nervous_models_Pupil_Sheets
... complex network of neurons. In order for impulses to get from one place to another they have to be able to pass from neuron to neuron. The gaps between neurons are called synapses ...
... complex network of neurons. In order for impulses to get from one place to another they have to be able to pass from neuron to neuron. The gaps between neurons are called synapses ...
Brain Basics
... fMRI was used to generate the ‘typical subject’s’ parcellation from a highly detailed 210-subject group average data set. New “language area,” are 55b, more activated for story vs. ...
... fMRI was used to generate the ‘typical subject’s’ parcellation from a highly detailed 210-subject group average data set. New “language area,” are 55b, more activated for story vs. ...