The tetrapartite synapse_ Extracellular matrix remodeling
... For MMPs to appropriately participate in the neuronal processes including cellular reorganization and remodeling in synaptic plasticity and memory, they must be appropriately expressed, localized and temporally activated (Sternlicht and Werb, 2001b). As such, the regulation of MMP expression and act ...
... For MMPs to appropriately participate in the neuronal processes including cellular reorganization and remodeling in synaptic plasticity and memory, they must be appropriately expressed, localized and temporally activated (Sternlicht and Werb, 2001b). As such, the regulation of MMP expression and act ...
Physical Development I
... • Linked to lower arousal, reflexes, and self-regulation at 1 month of age • Impaired motor development at 2 years of age • Decreased rate of growth through 10 years of age • Impaired language development and information processing • Susceptibility to developing ADHD • Increased Behavioral problems, ...
... • Linked to lower arousal, reflexes, and self-regulation at 1 month of age • Impaired motor development at 2 years of age • Decreased rate of growth through 10 years of age • Impaired language development and information processing • Susceptibility to developing ADHD • Increased Behavioral problems, ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... • NO causes presynaptic neuron to increase neurotransmitter release ...
... • NO causes presynaptic neuron to increase neurotransmitter release ...
Document
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of sound? • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive sound information subsequently project the information to the primary auditory cortex. Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary auditory cortex (SII) ...
... What are the major areas of the brain that are associated with the perception of sound? • The majority of thalamic neurons that receive sound information subsequently project the information to the primary auditory cortex. Thereafter, information is projected to the secondary auditory cortex (SII) ...
PSYC 100 Chapter 2
... The areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions, but rather in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking and speaking, are known as association areas. More “intelligent” animals have more association areas of their cortex. These area ...
... The areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions, but rather in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking and speaking, are known as association areas. More “intelligent” animals have more association areas of their cortex. These area ...
The Human Brain
... a 42 inch long, 1.2 inch wide, metal rod to be blown right up through his skull and out the top. The rod entered his skull below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
... a 42 inch long, 1.2 inch wide, metal rod to be blown right up through his skull and out the top. The rod entered his skull below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. ...
9 Functions of the Middle Prefrontal Cortex
... Body Regulation is achieved by the Autonomic (automatic) Nervous System. The system generally works without conscious control and regulates functions like heart rate, breathing, digestion, vascular tone, inflammation and immune response, etc. It gives us the ability to come back to base line, homeos ...
... Body Regulation is achieved by the Autonomic (automatic) Nervous System. The system generally works without conscious control and regulates functions like heart rate, breathing, digestion, vascular tone, inflammation and immune response, etc. It gives us the ability to come back to base line, homeos ...
AL4AI--Google2007
... Some behaviors are innate, so the wiring diagram (the connections) must matter But some behaviors are learned, so learning— phenotypic plasticity—must also matter ...
... Some behaviors are innate, so the wiring diagram (the connections) must matter But some behaviors are learned, so learning— phenotypic plasticity—must also matter ...
studying neurogenesis in cephalopods - UMR BOREA
... is known about the molecular pathways underlying their development. Similarly, the diversity of cephalopod nervous systems indicates a high flexibility and adaptability, which makes them a relevant biological material for evolutionary studies. Nevertheless, neither their development nor the mechanis ...
... is known about the molecular pathways underlying their development. Similarly, the diversity of cephalopod nervous systems indicates a high flexibility and adaptability, which makes them a relevant biological material for evolutionary studies. Nevertheless, neither their development nor the mechanis ...
Sens1-General
... General principles of sensory function 1. Each sensory organ and receptor is specialized to convert one form of stimulus into sensory neuron action potentials. 2. Each modality has a discrete pathway to the brain. 3. The specific sensation and location of stimulus perceived is determined by area ...
... General principles of sensory function 1. Each sensory organ and receptor is specialized to convert one form of stimulus into sensory neuron action potentials. 2. Each modality has a discrete pathway to the brain. 3. The specific sensation and location of stimulus perceived is determined by area ...
BRAIN RESEARCH METHODS
... Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI scan) -works the same as an MRI -BUT makes brain activity visible - allows scientists to pinpoint areas in the brain that controls feeling, thoughts & actions -eg when a person taps their fingers – the motor cortex will be highlighted -detects changes in ...
... Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI scan) -works the same as an MRI -BUT makes brain activity visible - allows scientists to pinpoint areas in the brain that controls feeling, thoughts & actions -eg when a person taps their fingers – the motor cortex will be highlighted -detects changes in ...
Slide ()
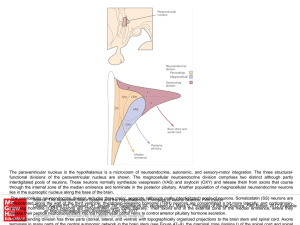
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Slide ()
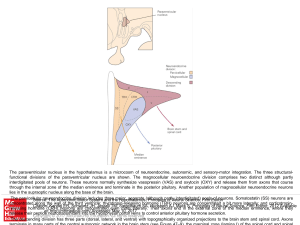
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Nervous System
... In a simple reflex, only a sensory nerve and motor nerve involved – example, “kneejerk” reflex Disorders of Nervous System ...
... In a simple reflex, only a sensory nerve and motor nerve involved – example, “kneejerk” reflex Disorders of Nervous System ...
Chapter 13 - Los Angeles City College
... (brain and spinal cord). 2. Integration: Interpretation of sensory signals and development of a response. Occurs in brain and spinal cord. 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows ...
... (brain and spinal cord). 2. Integration: Interpretation of sensory signals and development of a response. Occurs in brain and spinal cord. 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows ...
– Cell loss Brain, Neuron
... neuronal necrosis. Compare this image with those of Figure 2 and Figure 3 depicting the same region of hippocampus in a control animal. The atrophy of this portion of the hippocampus interferes with normal function, notably learning, memory, and spatial recognition processes. Neuronal cell loss due ...
... neuronal necrosis. Compare this image with those of Figure 2 and Figure 3 depicting the same region of hippocampus in a control animal. The atrophy of this portion of the hippocampus interferes with normal function, notably learning, memory, and spatial recognition processes. Neuronal cell loss due ...
Lecture Outline
... o A thick band of axons known as the corpus callosum enables communication between the right and left cerebral cortices. ...
... o A thick band of axons known as the corpus callosum enables communication between the right and left cerebral cortices. ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_8_lecture_part_1
... Synaptic Changes in Memory – LTP 5) This depolarizes the cell and activates NMDA receptor channels (which were inactive due to a Mg2+ blocking the pore). 6) NMDA allows Ca2+ and Na+ in. 7) The Ca2+ binds to a protein called calmodulin, which in turn activates an enzyme called CaMKII. 8) CaMKII caus ...
... Synaptic Changes in Memory – LTP 5) This depolarizes the cell and activates NMDA receptor channels (which were inactive due to a Mg2+ blocking the pore). 6) NMDA allows Ca2+ and Na+ in. 7) The Ca2+ binds to a protein called calmodulin, which in turn activates an enzyme called CaMKII. 8) CaMKII caus ...
It`s All About Relationships
... When a baby is born, only about ______ of his neurons are connected out of the possibility of a quadrillion. The wiring of the brain; _________ and _______________. Genetics – the hard wiring Life experience – the soft wiring ...
... When a baby is born, only about ______ of his neurons are connected out of the possibility of a quadrillion. The wiring of the brain; _________ and _______________. Genetics – the hard wiring Life experience – the soft wiring ...
A Short Review Quiz Together
... Neurons that are not needed have a programmed death. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers and toes apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. ...
... Neurons that are not needed have a programmed death. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers and toes apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. ...
Chapter 17: Nervous System - Johnston Community College
... Transmission Across a Synapse The tip of an axon forms an axon bulb that is close to a dendrite or cell body of another neuron; this region of close proximity is called the synapse. Transmission of a nerve impulse takes place when a neurotransmitter molecule stored in synaptic vesicles in the axon ...
... Transmission Across a Synapse The tip of an axon forms an axon bulb that is close to a dendrite or cell body of another neuron; this region of close proximity is called the synapse. Transmission of a nerve impulse takes place when a neurotransmitter molecule stored in synaptic vesicles in the axon ...
the potential for abuse: addiction
... found in the body, the mesolimbic dopamine system in particular plays a crucial role as the “pleasure center” of the brain by reinforcing rewarding behavior (Hyman, 2005). This pathway contains dopaminergic neurons along which signals are carried from one region of the brain to another. ...
... found in the body, the mesolimbic dopamine system in particular plays a crucial role as the “pleasure center” of the brain by reinforcing rewarding behavior (Hyman, 2005). This pathway contains dopaminergic neurons along which signals are carried from one region of the brain to another. ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... • Oligodendrocytes: They coat axons in the CNS with their cell membrane forming a specialized membrane called myelin sheath. The myelin sheath provides insulation to the axon that allows electrical signals to propagate more ...
... • Oligodendrocytes: They coat axons in the CNS with their cell membrane forming a specialized membrane called myelin sheath. The myelin sheath provides insulation to the axon that allows electrical signals to propagate more ...
as a PDF - University of Sussex
... a minimum to save energy began with the idea of sparse coding in sensory systems [17], [23]. More recently, cells ...
... a minimum to save energy began with the idea of sparse coding in sensory systems [17], [23]. More recently, cells ...