Central adrenergic receptor changes in the
... obscure detection of receptor alterations in the mutant brain. Results from the current study therefore suggest that in spite of the abnormal presynaptic innervation pattern in the tg/tg mouse, there is little or no corresponding modulation of the postsynaptic receptors on the target cells. One poss ...
... obscure detection of receptor alterations in the mutant brain. Results from the current study therefore suggest that in spite of the abnormal presynaptic innervation pattern in the tg/tg mouse, there is little or no corresponding modulation of the postsynaptic receptors on the target cells. One poss ...
Epistatic interaction of CREB1 and KCNJ6 on rumination and
... blockade abolished depotentiation of long-term potentiation in cultured hippocampal neurons demonstrating that GIRK channels are critical for excitatory synaptic plasticity which is considered a cellular correlate of learning and memory (Chung et al., 2009a,b). CREB1 is a member of the leucine zippe ...
... blockade abolished depotentiation of long-term potentiation in cultured hippocampal neurons demonstrating that GIRK channels are critical for excitatory synaptic plasticity which is considered a cellular correlate of learning and memory (Chung et al., 2009a,b). CREB1 is a member of the leucine zippe ...
Nervous System - Discovery Education
... system every second travel along special cells called neurons or nerve cells. You are born with all the neurons you will ever have, for these special cells can not duplicate themselves like other body cells. Don’t worry, there are more than enough neurons to last a lifetime. In fact, these cells die ...
... system every second travel along special cells called neurons or nerve cells. You are born with all the neurons you will ever have, for these special cells can not duplicate themselves like other body cells. Don’t worry, there are more than enough neurons to last a lifetime. In fact, these cells die ...
Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems
... Learning and Memory • Learning - ability to acquire knowledge or skills • Memory - storage of knowledge gained or skills developed over time • Plasticity - changes in the nervous system that are reflected in behavioral changes to stimuli (i.e. learning and memory) – Changes may include altered cell ...
... Learning and Memory • Learning - ability to acquire knowledge or skills • Memory - storage of knowledge gained or skills developed over time • Plasticity - changes in the nervous system that are reflected in behavioral changes to stimuli (i.e. learning and memory) – Changes may include altered cell ...
Chapter 1
... • The heritability for schizophrenia has been estimated at between .60 and .90. • This means that 10-40% of the variability is due to environmental factors. ...
... • The heritability for schizophrenia has been estimated at between .60 and .90. • This means that 10-40% of the variability is due to environmental factors. ...
Impaired associative learning in schizophrenia: behavioral and
... memory is inadequately established and is unavailable at the fidelity needed when recall is required. In the human brain, the interplay between evolutionarily mature prefrontal and hippocampal regions underlies associative learning. Whereas the precise contributions of each of these regions is the s ...
... memory is inadequately established and is unavailable at the fidelity needed when recall is required. In the human brain, the interplay between evolutionarily mature prefrontal and hippocampal regions underlies associative learning. Whereas the precise contributions of each of these regions is the s ...
Food for Thought: Essential Fatty Acid Protects
... On first sight, the diverse outcome measures studied by Calon and colleagues (Table 1) may appear to be somewhat loosely connected. However, in Figure 5G of their article, they propose a plausible scheme of how these variables may be mechanistically related to each other and to the pathogenesis of A ...
... On first sight, the diverse outcome measures studied by Calon and colleagues (Table 1) may appear to be somewhat loosely connected. However, in Figure 5G of their article, they propose a plausible scheme of how these variables may be mechanistically related to each other and to the pathogenesis of A ...
Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the
... these oscillations. Recurrent excitatory feedback in the CA3 region could be involved in the generation of the oscillations, and propagation to CA1 may depend on the excitatory Schaffer collateral input onto CA1 neurons. During 40-Hz oscillations in the hippocampus in vivo, individual pyramidal neur ...
... these oscillations. Recurrent excitatory feedback in the CA3 region could be involved in the generation of the oscillations, and propagation to CA1 may depend on the excitatory Schaffer collateral input onto CA1 neurons. During 40-Hz oscillations in the hippocampus in vivo, individual pyramidal neur ...
Slide ()
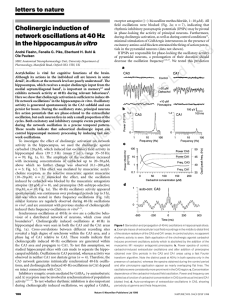
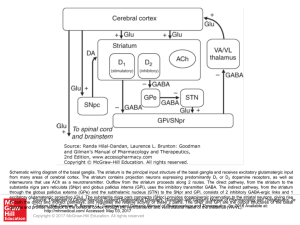
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
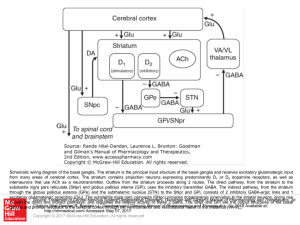
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and
... It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and peripheral nervous systems play essential roles in the transmission and assimilation of the information of our environment. This information is processed through neuronal synaptic communications, mediated by excitatory and inhibitory ...
... It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and peripheral nervous systems play essential roles in the transmission and assimilation of the information of our environment. This information is processed through neuronal synaptic communications, mediated by excitatory and inhibitory ...
Glial Signaling Take Home Messages
... c. D-serine binds the Gly site on neuronal NMDA receptors → ↑ LTP 2. Astrocyte signaling → ↑ LTP is limited to local astrocyte networks 3. Astrocytes are required for some types of synaptic plasticity (like LTP) 4. Human Astrocytes (hAstrocytes) are larger and have more branching than non-primates a ...
... c. D-serine binds the Gly site on neuronal NMDA receptors → ↑ LTP 2. Astrocyte signaling → ↑ LTP is limited to local astrocyte networks 3. Astrocytes are required for some types of synaptic plasticity (like LTP) 4. Human Astrocytes (hAstrocytes) are larger and have more branching than non-primates a ...
Module 3 - Victor Valley College
... • Parkinson’s Disease – It is caused by destruction of neurons that produce dopamine – L-dopa is a medication that boosts the levels of dopamine in the brain – eventually the drug causes involuntary jerky movements – after prolonged use, L-dopa’s beneficial effect may be replaced by unwanted jerky m ...
... • Parkinson’s Disease – It is caused by destruction of neurons that produce dopamine – L-dopa is a medication that boosts the levels of dopamine in the brain – eventually the drug causes involuntary jerky movements – after prolonged use, L-dopa’s beneficial effect may be replaced by unwanted jerky m ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... neuron and the dendrite of another Axosomatic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Other types of synapses include: Axoaxonic (axon to axon) Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) Dendrosomatic (dendrites to soma) ...
... neuron and the dendrite of another Axosomatic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Other types of synapses include: Axoaxonic (axon to axon) Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) Dendrosomatic (dendrites to soma) ...
Lecture 26
... language deficits in persons with damage to that area (and later based on increased neural activity in that area during speech). But this does not necessarily mean that Broca’s area evolved for a primary function in language per se. Might it have evolved in relation to some more generalized function ...
... language deficits in persons with damage to that area (and later based on increased neural activity in that area during speech). But this does not necessarily mean that Broca’s area evolved for a primary function in language per se. Might it have evolved in relation to some more generalized function ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... neuron and the dendrite of another Axosomatic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Other types of synapses include: Axoaxonic (axon to axon) Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) Dendrosomatic (dendrites to soma) ...
... neuron and the dendrite of another Axosomatic – synapses between the axon of one neuron and the soma of another Other types of synapses include: Axoaxonic (axon to axon) Dendrodendritic (dendrite to dendrite) Dendrosomatic (dendrites to soma) ...
You submitted this quiz on Tue 6 May 2014 6:55 PM CDT. You got a
... Correct 0.20 Arachnoid cells are a type of meningeal cell, which produce a relatively common type of benign brain tumor known as a meningioma. Pituitary cells ...
... Correct 0.20 Arachnoid cells are a type of meningeal cell, which produce a relatively common type of benign brain tumor known as a meningioma. Pituitary cells ...
Modeling working memory and decision making using generic
... contain behavior-relevant information ...
... contain behavior-relevant information ...
Neurotransmitters
... • A single EPSP cannot induce an AP • EPSPs can summate to influence postsynaptic neuron • IPSPs can also summate • Most neurons receive both excitatory and inhibitory inputs from thousands of other neurons – Only if EPSP's predominate and bring to threshold AP © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • A single EPSP cannot induce an AP • EPSPs can summate to influence postsynaptic neuron • IPSPs can also summate • Most neurons receive both excitatory and inhibitory inputs from thousands of other neurons – Only if EPSP's predominate and bring to threshold AP © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Science 6th primary. 1st term unit 4 lesson 1 Why does this
... Examine slide of cross-section of spinal cord by microscope. ...
... Examine slide of cross-section of spinal cord by microscope. ...
Chapter 3 Biological Aspects of Psychology
... How do neurons actually communicate? • NT binds to receptor sites on the receiving neuron • The receptors open allowing positive sodium ions to enter and excite or inhibit the action potential • Receptor sites are tuned to recognize and respond to some neurotransmitters and not others ...
... How do neurons actually communicate? • NT binds to receptor sites on the receiving neuron • The receptors open allowing positive sodium ions to enter and excite or inhibit the action potential • Receptor sites are tuned to recognize and respond to some neurotransmitters and not others ...
Schizophrenia is a multi-faceted disorder with highly complex p
... This collaborative approach is essential to integrate findings across several domains of basic research, and translate them into informing clinical and pharmacologic practice . Figure 1 provides a schematic overview of this collaborative proposal emphasizing the central role of computational models ...
... This collaborative approach is essential to integrate findings across several domains of basic research, and translate them into informing clinical and pharmacologic practice . Figure 1 provides a schematic overview of this collaborative proposal emphasizing the central role of computational models ...
Course Introduction: The Brain, chemistry, neural signaling
... IPSPs will counteract the effect of EPSPs at the same neuron. Summation means the effect of many coincident IPSPs and EPSPs at one neuron. If there is sufficient depolarization at the axon hillock, an action potential will be triggered. ...
... IPSPs will counteract the effect of EPSPs at the same neuron. Summation means the effect of many coincident IPSPs and EPSPs at one neuron. If there is sufficient depolarization at the axon hillock, an action potential will be triggered. ...
Multiple sites of spike initiation in a single dendritic
... We were encouraged to look for multiple spike-initiating zones because of the observation of Kennedy and Mellon 4 that, in MTIs with bilateral receptive fields, the apparent voltage thzeshold for firing differed for synaptic input from the two sides. Synaptic input from roots ipsilateral to the dend ...
... We were encouraged to look for multiple spike-initiating zones because of the observation of Kennedy and Mellon 4 that, in MTIs with bilateral receptive fields, the apparent voltage thzeshold for firing differed for synaptic input from the two sides. Synaptic input from roots ipsilateral to the dend ...